تعتبر Motor Smaft Machining عملية أساسية ولكنها معقدة في الهندسة الدقيقة. These shafts serve as mechanical components that transmit rotational power from a motor to a driven component. Whether used in electric vehicles, industrial motors, توربينات, or medical equipment, a motor shaft’s geometry, مادة, and surface finish directly influence system efficiency and reliability. This guide provides an in-depth overview of motor shaft machining, covering shaft types, العمليات, machining techniques, اختيار المواد, التشطيب, ومراقبة الجودة.
What Is Motor Shaft Machining?
Motor shaft machining is the process of transforming raw metal stock into precision cylindrical components capable of transmitting torque and rotary motion. These shafts are machined to tight dimensional tolerances and smooth surface finishes, ensuring reliable operation under varying loads, سرعات, والظروف البيئية.
استخدام CNC (التحكم العددي بالكمبيوتر) آلات, cutting tools remove material to form key features such as diameters, shoulders, الأخاديد, الخطوط, and tapers. Precision is paramount—errors in shaft geometry can cause vibration, يرتدي, or failure in critical assemblies.
Types of Motor Shafts
Motor shafts come in a variety of geometries, each tailored for specific mechanical applications:
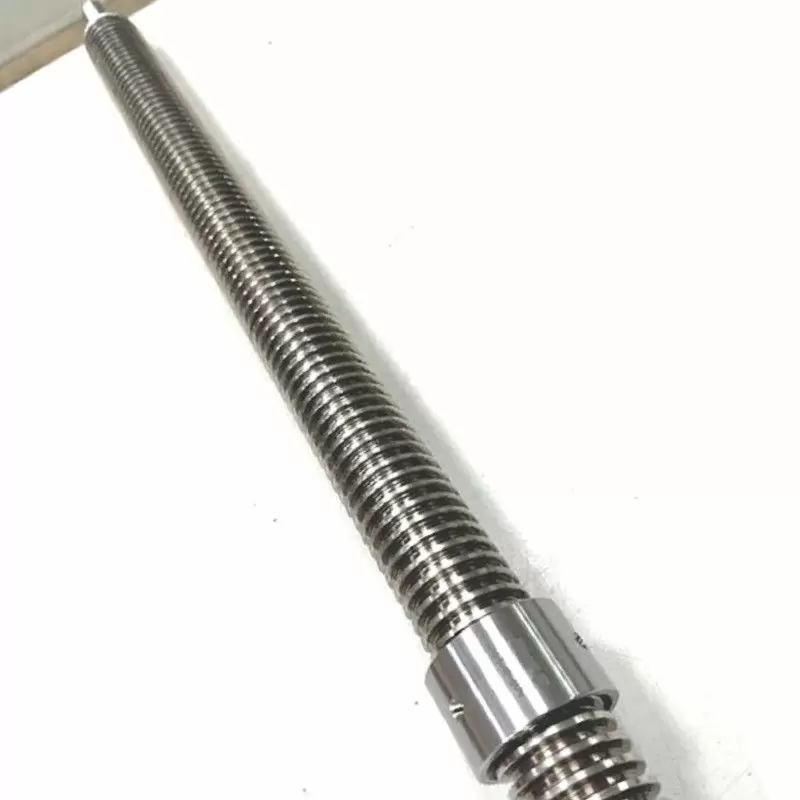
Threaded Shafts
These shafts have external threads at one or both ends, or along the entire length, enabling them to serve as fasteners or connectors in assemblies. Threaded shafts are commonly used in electric actuators, linear drives, and clamping mechanisms.
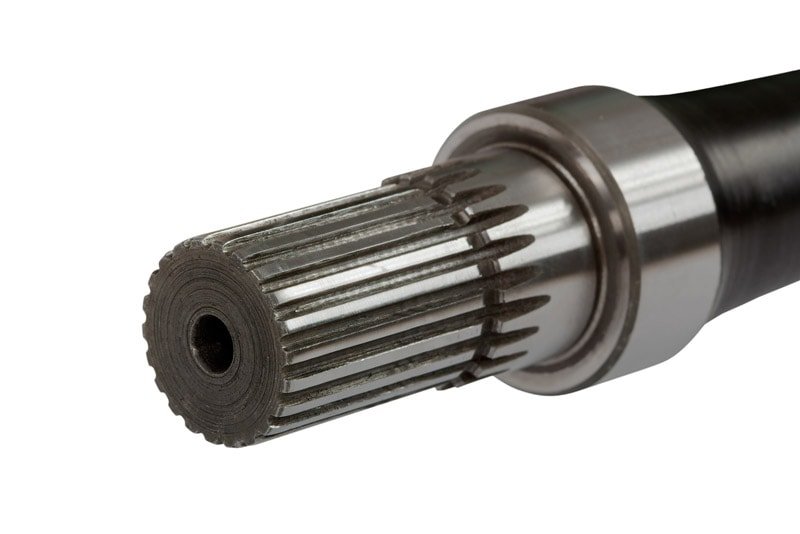
Splined Shafts
Featuring longitudinal grooves or ridges, splined shafts interlock with mating components to ensure torque transfer without slippage. Widely used in gearboxes, aircraft engines, and vehicle drivetrains, they allow axial movement while maintaining rotation synchronization.
Hollow Shafts
Designed with a central bore, hollow shafts reduce weight while retaining strength. The cavity can house wiring, fluid channels, or instrumentation. Common in aerospace, الروبوتات, and automation systems, they reduce inertia and improve response.
Keyed Shafts
These shafts feature a longitudinal keyway cut along the outer diameter, designed to fit a matching key and keyway in the mating hub. This creates a strong mechanical lock for torque transmission and alignment in pumps, المحركات, and pulleys.
Tapered Shafts
Tapered shafts have diameters that decrease gradually along the length, offering a self-locking fit with mating components. Common in wheel hubs and flywheels, they provide secure connections without the need for additional fasteners.
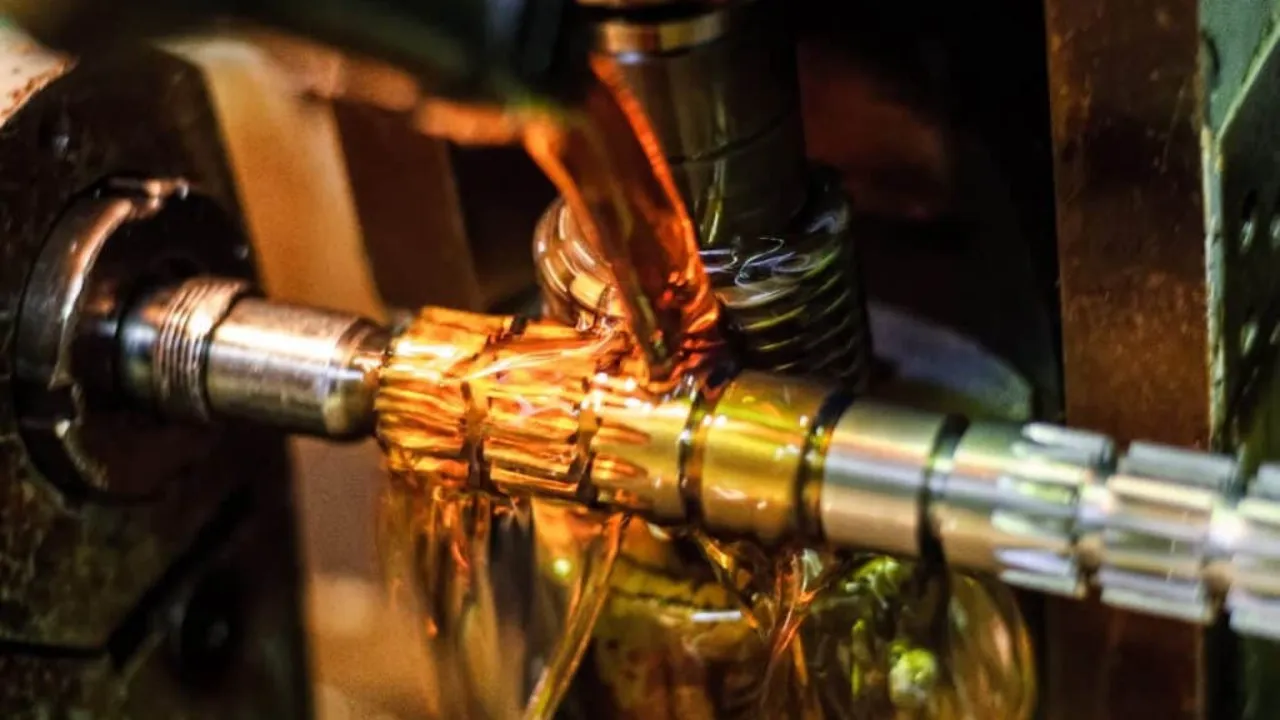
Processes Involved in Motor Shaft Machining
Load and Torque Calculation
قبل بدء التشغيل, engineers must calculate the maximum expected torque, axial, and radial loads. These values influence the shaft’s diameter, القوة المادية, and stress concentrations, ensuring the design meets fatigue life and safety requirements.
Design on CAD
Using CAD software like SolidWorks or Autodesk Inventor, engineers create detailed 2D drawings and 3D models. CAD design ensures all dimensional and tolerance requirements are specified and allows for design optimization before production.
CAM Programming and CNC Machining
The CAD model is imported into CAM (التصنيع بمساعدة الحاسوب) software to generate toolpaths and G-code. This code guides CNC machines through precise movements—turning, طحن, حفر, or grinding—to create the finished shaft geometry.
التشطيب السطح
Post-machining, surface treatments enhance dimensional accuracy, مظهر, ارتداء المقاومة, وحماية التآكل. These treatments vary based on application and material.
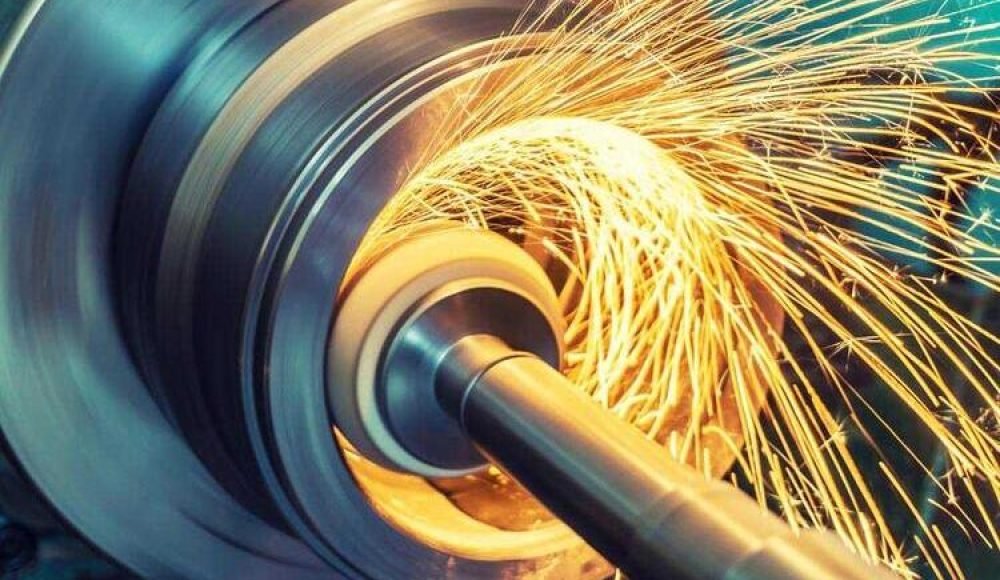
Various CNC Machining Techniques in Motor Shaft Production
تحول باستخدام الحاسب الآلي
CNC turning is ideal for producing concentric features. The metal blank is rotated while stationary cutting tools shape the exterior. Common operations include facing, OD/ID turning, الأخدود, خيوط, and taper turning.
الطحن باستخدام الحاسب الآلي
Milling uses rotary cutting tools to form non-cylindrical features like flats, فتحات, و Keyways. Multi-axis CNC milling enables complex geometries and precision cut-outs.
الحفر باستخدام الحاسب الآلي
Precision holes for fasteners, تشحيم, or wire routing are produced using automated drilling. This ensures accurate hole positioning, consistent diameters, والتكرار.
طحن باستخدام الحاسب الآلي
Grinding ensures the final surface finish and dimensional tolerance (often within ±0.002 mm). Abrasive wheels remove minimal material, ideal for achieving high concentricity and low surface roughness (رع < 0.4 ميكرومتر).
معالجة التفريغ الكهربائي (موسيقى الرقص الإلكترونية)
EDM removes material via electrical discharges, useful for cutting hardened alloys or creating complex internal features that are not feasible with traditional machining. It is slow but highly precise.
Types of Materials Used in Motor Shaft Machining
الألومنيوم
Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, الألومنيوم (على سبيل المثال, 6061, 7075) is ideal for low-load applications in robotics, الأتمتة, and small motors. Its high machinability also allows cost-effective production.
الكربون الصلب
الدرجات مثل 1045 و 1144 are economical and strong. Carbon steel shafts are widely used in industrial machinery where corrosion is not a critical concern.
الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ
الدرجات 304 و 316 offer superior corrosion resistance and strength. These are often used in food processing, البحرية, والأجهزة الطبية. 316 is more corrosion-resistant, بينما 304 is more cost-effective.
سبائك الصلب
Chromoly and other alloy steels are heat-treatable and extremely tough. These materials are chosen for high-stress applications like automotive crankshafts and heavy-duty transmissions.
نحاس
With excellent machinability and corrosion resistance, brass is suitable for decorative or low-friction shaft applications such as electrical contacts or instrument components.
التيتانيوم
Titanium’s exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance make it suitable for aerospace and marine shafts. Though expensive, it performs well in extreme environments.
سبائك النيكل
Alloys like Inconel withstand high temperatures, أكسدة, والتآكل. Used in gas turbines and jet engines, they are difficult to machine but unmatched in performance.
Factors to Consider During Motor Shaft CNC Machining
تكاليف المواد
Choose a material that balances cost, mechanical performance, ومقاومة التآكل. Carbon steel is economical, while titanium and Inconel significantly increase part cost.
Machining Time and Complexity
Shafts with complex features (الخطوط, internal threads, hollow bores) require longer machining cycles, increasing cost and setup time.
تكاليف الأدوات
Premium tools are required for hardened materials like Inconel. Tool life and replacement frequency affect long-term costs.
Labor and Automation
CNC automation reduces labor needs, but manual setup and inspection are still necessary. Complex shafts may require multi-setup machining.
المعالجة الحرارية
Processes like hardening, هدأ, and nitriding improve fatigue strength and surface wear resistance. لكن, they add cost and may require additional machining after treatment.
تاكيد الجودة
Precision components require dimensional verification, surface roughness measurement, and hardness testing—these steps are essential but time-consuming.
Surface Finishing Processes in Motor Shaft Machining
أنودة
Primarily for aluminum, anodizing increases corrosion resistance and can be dyed for visual identification. It forms a durable oxide layer on the shaft surface.
الكهربائي
Adds a thin layer of chromium, النيكل, or zinc for corrosion resistance, wear protection, والجمال.
Phosphating
Creates a crystalline phosphate layer on steel surfaces to resist corrosion and promote paint adhesion.
Passivating
Used for stainless steel shafts to remove iron contamination, enhancing corrosion resistance by forming a passive chromium-rich surface layer.
نيترة
Diffuses nitrogen into alloy steel surfaces, producing a hard case with minimal distortion. Ideal for high-wear applications like drive shafts.
Thermal Spraying
A high-performance coating method where molten materials are sprayed onto the shaft, improving wear, حرارة, and corrosion resistance without altering base dimensions.
Quality Control in Motor Shaft Machining
التفتيش الأبعاد
Critical dimensions are verified using CMMs, ميكرومتر, and gauges to ensure compliance with tolerances (typically ±0.01 mm or tighter).
Surface Roughness Testing
Profilometers or tactile testers are used to verify Ra values, especially for bearing surfaces or sealing interfaces.
Material Verification
Spectrometry, hardness testing, and tensile testing ensure the correct grade and properties of the base metal.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintaining machining records, شهادات المواد, and inspection reports helps track production quality and satisfy regulatory standards.
Visual and Defect Inspection
Shafts are inspected for scratches, بيرز, علامات الأداة, or surface abnormalities that could impact performance.
خاتمة
Motor shaft machining is a cornerstone of mechanical design and production, playing a vital role in rotating systems across nearly every industry. From design and material selection to finishing and quality control, each stage must be executed with precision and attention to detail.
في قمم الدقة, we specialize in producing motor shafts that meet the highest standards of accuracy, أداء, والمتانة. Contact us today for expert advice or to request a custom machining quote tailored to your application needs.
الأسئلة الشائعة
1. Why is concentricity the most critical geometric tolerance for motor shafts?
Concentricity is paramount because a motor shaft’s function is purely rotational, transmitting torque at high speeds. Poor concentricity means the shaft’s centerline is misaligned with its axis of rotation, leading to:
-
Severe Vibration: Causes noise and dynamic imbalance.
-
Bearing Wear: Premature failure of bearings due to uneven loading.
- Reduced Efficiency: Loss of power and heat generation.
Manufacturers often use CNC grinding as the final process to ensure concentricity and diameter tolerance are within the required micron-level specifications.
2. How do keyed shafts and splined shafts differ in torque transmission?
Both types transfer torque without slippage, but they differ in engagement and load distribution:
-
Keyed Shafts: Rely on a single keyway and key to lock the hub, concentrating the load and stress at a single point, which is suitable for moderate torque applications.
-
Splined Shafts: Feature multiple longitudinal grooves (الخطوط), distributing the torque load evenly across a much larger surface area. This allows splined shafts to handle significantly higher torque loads and provides greater alignment precision, making them common in heavy-duty transmissions.
3. Why are hollow shafts preferred over solid shafts in high-performance applications like robotics?
Hollow shafts are preferred because they significantly reduce rotational inertia while often retaining sufficient strength. Reducing inertia allows the motor system (especially in robotics or automation) ل accelerate, decelerate, and reverse direction faster and with less energy. بالإضافة إلى ذلك, the central bore provides a convenient channel for routing internal wiring, أجهزة الاستشعار, or fluid lines without external interference.
4. What finishing process is used to enhance the surface hardness and fatigue strength of alloy steel shafts?
نيترة is the key finishing process. Nitriding involves diffusing nitrogen into the surface of alloy steel at elevated temperatures. This creates a hard, ارتداء مقاومة case depth without the need for quenching, thus causing minimal dimensional distortion. This makes it ideal for high-wear areas like bearing journals or gear engagement surfaces, significantly improving the shaft’s fatigue life under cyclic loading.
5. Why is Electrical Discharge Machining (موسيقى الرقص الإلكترونية) sometimes used in motor shaft production despite being slow?
EDM is used exclusively when the required feature cannot be machined using conventional methods due to صلابة المواد أو geometry complexity. It is often used to:
-
Cut keyways or slots in already fully hardened alloy steel shafts.
- Create complex internal features or precise micro-holes without introducing mechanical stress.
EDM removes material through spark erosion, making the process slow but capable of extreme precision regardless of the material’s hardness.
6. How does the choice of stainless steel grade (304 مقابل. 316) impact shaft application?
-
304 الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ: Offers good corrosion resistance, قابلية ممتازة, and is generally more فعالة من حيث التكلفة. It is suitable for general industrial, طعام, and non-marine applications.
-
316 الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ: يتضمن الموليبدينوم, which provides significantly مقاومة تآكل متفوقة, particularly against chlorides, الماء المالح, and strong acids. It is the preferred, albeit more expensive, choice for marine, pharmaceutical, and chemical processing shafts.
7. What role does Surface Roughness Testing (قيم را) play in motor shaft quality control?
Surface Roughness Testing, usually measuring the average roughness ($Ra$), is critical because the shaft’s surface interacts directly with bearings and seals.
-
Low Ra (الانتهاء السلس): Essential for bearing journals to minimize friction, توليد الحرارة, and wear on the bearing.
-
Controlled Ra: Critical for أسطح الختم (where the shaft passes through a seal) to ensure the seal maintains integrity without rapidly wearing out the lip. Roughness that is too high or too low can cause failure. Typical Ra requirements for bearing surfaces are often less than 0.4 ميكرومتر.