التصنيع باستخدام الحاسب الآلي تحظى بشعبية لميزة الأتمتة. لا يؤدي فقط إلى تسريع السرعة. ولكن أيضًا تعزيز الدقة والدقة العالية. إلى جانب ذلك, يتم استخدامه في العديد من التطبيقات في العديد من الصناعات. لذا, عندما نتحدث عن التصنيع باستخدام الحاسب الآلي ومنتجاتها المخرجة. نحن أيضًا نأخذ في الاعتبار المواد التي نستخدمها في عملية التصنيع باستخدام الحاسب الآلي. في هذه المقالة, سوف نستكشف المواد المختلفة المثالية لآلات CNC, العوامل التي يجب مراعاتها عند اختيار المواد, ونصائح لتحسين خيارات المواد لمشاريعك.
فئات مختلفة من المواد في تصنيع CNC
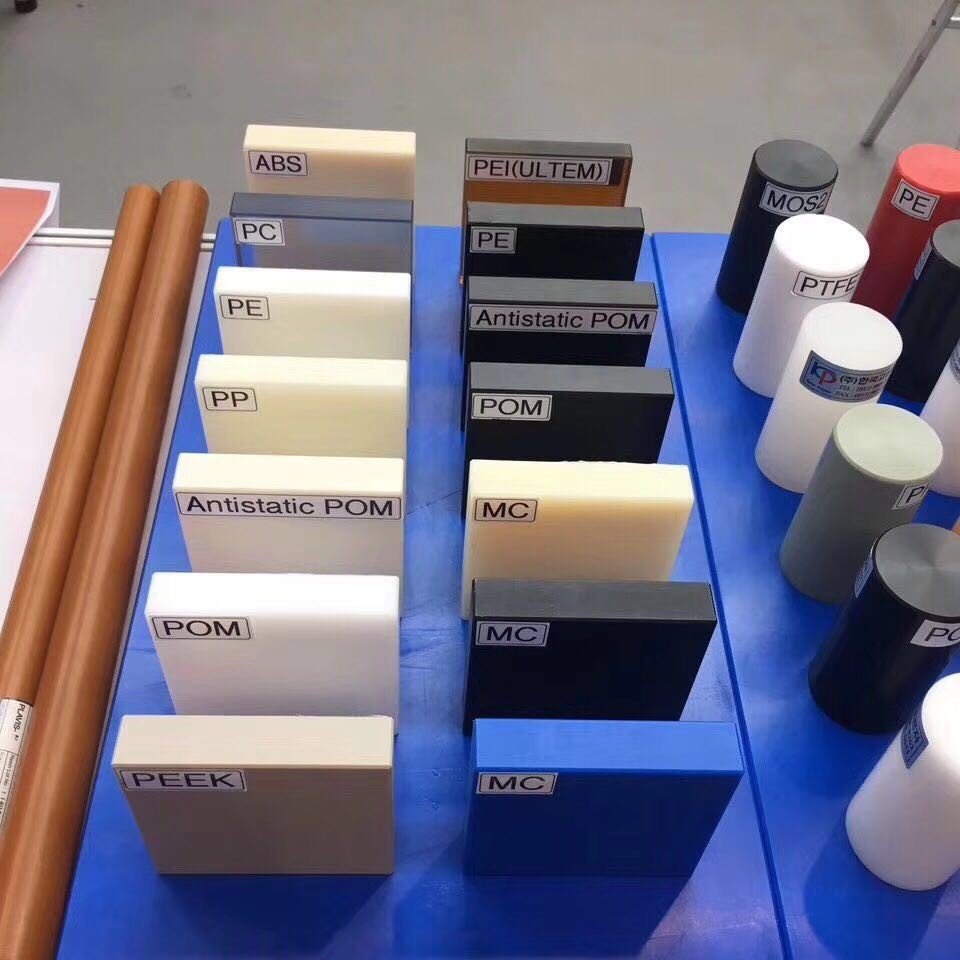
تعتبر Machining CNC عملية متعددة الاستخدامات قادرة على العمل مع مجموعة واسعة من المواد. في حين أن المعادن والبلاستيك هي المواد الأكثر استخدامًا, يمكن للآلات CNC أيضًا استيعاب مواد مثل السيراميك, خشب, والمواد المركبة. كل فئة مادية لها مزايا وتحديات متميزة, مما يجعل من المهم اختيار الصحيح اعتمادًا على التطبيق.
فئات مواد التصنيع باستخدام الحاسب الآلي:
- المعادن- شائع الاستخدام في الصناعات مثل الفضاء, السيارات, والأجهزة الطبية بسبب متانتها وقوتها.
- البلاستيك- شعبية في السلع الاستهلاكية والصناعات الطبية, حيث خفيفة الوزن, هناك حاجة إلى أجزاء مقاومة للتآكل.
- المركبات- تستخدم في الصناعات المتخصصة مثل تصنيع المعدات الرياضية والفضاء, تقديم نسب عالية القوة إلى الوزن.
- الخشب والسيراميك-يستخدم للإنتاج المتخصص ومنخفض الحجم, عادة للمنتجات الفنية أو الفريدة.
أنواع المواد المعدنية لآلات CNC والأمثلة
المعادن هي المادة المتواصلة لمعظم عمليات تصنيع CNC بسبب قوتها, مقاوم للحرارة, والقدرة على تحمل الأحمال الثقيلة. أقل, نستكشف المعادن الأكثر استخدامًا في تصنيع CNC.
الألومنيوم
الألومنيوم هو واحد من المعادن الأكثر استخدامًا في تصنيع CNC. تشمل مزاياها كثافة منخفضة, نسبة عالية من القوة إلى الوزن, وقدرة ممتازة على الآلات. سبائك الألومنيوم, مثل 6061 و 7075, تستخدم على نطاق واسع في الصناعات التي تتطلب مواد خفيفة ولكنها قوية, مثل الفضاء, السيارات, والالكترونيات الاستهلاكية. إنه مقاوم للتآكل ويوفر تشطيبات سطح ممتازة, مما يجعلها مناسبة لكل من الأجزاء الوظيفية والجمالية.
الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ
الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ معروف بمقاومة التآكل, صلابة, وقوة عالية. غالبًا ما يتم استخدامه في الأجهزة الطبية, الفضاء الجوي, والتطبيقات البحرية. في حين أن الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ لديه مقاومة متفوقة للتآكل, صلابة يمكن أن تجعل من الصعب على الآلة. تشمل الدرجات الشائعة من الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ المستخدمة في تصنيع CNC 303, 304, و 316.
الصلب الكربوني وسبائكه
يستخدم الفولاذ الكربوني على نطاق واسع بسبب قابليته للآلات الممتازة, قوة, والقدرة على تحمل التكاليف. إنه مفضل بشكل خاص للتطبيقات التي تتطلب خصائص ميكانيكية قوية مثل المكونات الهيكلية, التروس, والسحابات. لكن, إن نقص مقاومة التآكل في الصلب الكربوني يحد من تطبيقاته في البيئات القاسية ما لم يتم طلاءه.
النحاس وسبائكها
يتم اختيار النحاس من أجل الموصلية الحرارية والكهربائية العالية. غالبًا ما يتم استخدامه في المكونات الكهربائية مثل الأسلاك والموصلات, وكذلك في أنظمة التبريد. نحاس و برونزية, سبائك نحاس, تقديم محسّن للآلات ومقاومة التآكل, جعلها مثالية لتصنيع المكونات الدقيقة مثل التروس, رمان, والموصلات.
التيتانيوم
يقدم التيتانيوم مزيجًا استثنائيًا من القوة والخصائص الخفيفة الوزن. يستخدم على نطاق واسع في الصناعات عالية الأداء, بما في ذلك الفضاء والزراعة الطبية. لكن, التيتانيوم يصعب الجهاز بسبب صلقتها, هناك حاجة إلى عمليات الأدوات والآلات المتخصصة.
المغنيسيوم
المغنيسيوم هو واحد من أخف المعادن, مما يجعلها خيارًا مناسبًا للتطبيقات التي تتطلب انخفاض الوزن, مثل السيارات والفضاء. خصائص المغنيسيوم تجعلها ممتازة للتطبيقات ذات درجة الحرارة العالية. لكن, إن قابليته للاشتعال أثناء الآلات يمثل تحديًا.
أنواع المواد البلاستيكية لآلات CNC والأمثلة
بينما تهيمن المعادن على تصنيع CNC, يكتسب المواد البلاستيكية الجر, خاصة بالنسبة للتطبيقات التي يخفيفة الوزن, متانة, والمرونة ضرورية. يتم استخدام المواد البلاستيكية التالية بشكل متكرر في تصنيع CNC:
أكريليك (PMMA)
أكريليك, أو PMMA, يستخدم على نطاق واسع لوضوحه وصراقته البصرية. غالبًا ما يتم استخدامه كبديل للزجاج في تطبيقات مثل Windows, عروض, واللافتات. الأكريليك متعدد الاستخدامات ولكنه عرضة للتصدع, خاصة تحت الضغط العالي, التي يجب مراعاتها أثناء الآلات.
البولي بروبلين (ص)
تشتهر البولي بروبيلين بمقاومة كيميائية وقوة التعب. يتم استخدامه بشكل شائع في التطبيقات الطبية والسلع الاستهلاكية. لكن, إن ميله إلى التليين في درجات حرارة عالية يجعل من الصعب على الجهاز في بعض الحالات.
اسيتال (بوم/ديلرين)
تشتهر الأسيتال بقوته الفائقة, مقاومة الرطوبة, وقدرة ممتازة على الآلات. يتم استخدامه بشكل متكرر في مكونات دقيقة مثل التروس والمحامل بسبب قدرتها على الحفاظ على شكلها حتى تحت الأحمال الثقيلة.
نايلون
النايلون قوي, متين, والمواد المقاومة للتأثير المستخدمة في العديد من التطبيقات, بما في ذلك المحامل, التروس, والمكونات الكهربائية. كما أن لديها احتكاك منخفض, مما يجعلها خيارًا شائعًا للأجزاء المعرضة للارتداء.
عضلات المعدة
ABS هو بلاستيك بأسعار معقولة مع قابلية جيدة للآلات, قوة الشد, والمقاومة تأثير. يتم استخدامه في إنتاج قطع غيار السيارات, حاويات واقية, والنماذج الأولية. ABS أيضا قابلة للتلوين للغاية, جعلها خيارًا جيدًا للتطبيقات الجمالية.
أوهمو-PE
البولي إيثيلين عالية الجزيئية عالية الجزيئية (أوهمو-PE) مقاوم للغاية للارتداء والتآكل, مما يجعلها مناسبة للتطبيقات مثل المحامل, التروس, والأسطح المنزلق. على الرغم من أنه قد يكون من الصعب الجهاز, خصائصها الاستثنائية تجعلها مادة قيمة للبيئات ذات الضغط العالي.
البولي (الكمبيوتر)
تشتهر البولي بكربونات بمقاومة التأثير الممتازة والوضوح البصري. غالبًا ما يتم استخدامه في تطبيقات درجات الحرارة العالية, وكذلك في إنتاج المكونات الإلكترونية, أجهزة طبية, وقطع غيار السيارات.
polyethetherketone (نظرة خاطفة)
Peek هو بلاستيك عالي الأداء مع مقاومة كيميائية رائعة, القوة الميكانيكية, واستقرار الأبعاد, جعلها مثالية للاستخدام في البيئات القاسية مثل الفضاء, تجهيز الأغذية, والنفط والغاز.
بولي فينيل كلوريد (بولي كلوريد الفينيل)
PVC هو بلاستيك منخفض التكلفة مع قابلية ممتازة. يتم استخدامه في التطبيقات التي تتطلب مقاومة للمواد الكيميائية والتأثير العالي, مثل أنظمة السباكة, التركيبات الكهربائية, ومكونات السيارات.
عرض سريع: مخطط مواد الآلات CNC
إليك نظرة عامة سريعة على مواد CNC الشائعة, خصائصهم الرئيسية, وبعض الأمثلة على المكان الذي يستخدمون.
| نوع المادة | مادة | الخصائص الرئيسية | التطبيقات المشتركة | الدرجات & الرموز |
| معدن | الألومنيوم | وزن خفيف, مقاومة للتآكل, قابلية ممتازة | إطارات الفضاء, قطع غيار السيارات, إلكترونيات, بناء | آل 1050, آل 6061, آل 7075 |
| الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ | قوي, مقاومة للتآكل, مقاوم للحرارة | المعدات الطبية, البحرية, حاويات في الهواء الطلق | SS 303, SS 304, SS 316 | |
| الكربون الصلب | قوة عالية, قابلية ممتازة | السحابات الميكانيكية, المكونات الهيكلية | 1018, 4130, 4140 | |
| نحاس | الموصلية الحرارية/الكهربائية العظيمة, طيع, مقاومة للتآكل | الأسلاك الكهربائية, الأجهزة المغناطيسية, مجوهرات | النحاس, النحاس + الزنك, النحاس + يكون | |
| التيتانيوم | نسبة القوة إلى الوزن عالية, مقاومة للتآكل | الفضاء الجوي, جيش, الأجزاء الطبية الحيوية | أنت تبني 1, أنت تبني 2 | |
| المغنيسيوم | ضوء, خصائص حرارية ممتازة | مكونات المحرك, السيارات, الفضاء الجوي | ملغ, سبائك المغنيسيوم | |
| بلاستيك | أكريليك (PMMA) | وضوح بصري عالية, جامد, متين | لافتات, تركيبات الإضاءة, قطع غيار السيارات, بضائع المستهلكين | PMMA-acrylic, PMMA-High Temp |
| نايلون (PA6) | قوي, متين, مقاومة الصدمة, جيد لمقاومة البلى | التروس, رمان, قطع غيار السيارات | PA6, PA66, نايلون 6-6 | |
| البولي (الكمبيوتر) | مقاوم تحطيم, مقاوم للحرارة, الوضوح البصري | الأجهزة الطبية, قطع غيار السيارات, المكونات الإلكترونية | الكمبيوتر, الكمبيوتر + ملء الزجاج | |
| نظرة خاطفة | مقاومة كيميائية عالية, يحافظ على الصلابة في درجات حرارة عالية | الفضاء الجوي, أجهزة طبية, مكونات أشباه الموصلات | نظرة خاطفة | |
| عضلات المعدة | قدرة جيدة على الماكينات, مقاومة الصدمة, قوة الشد | حاويات, النماذج الأولية السريعة, قطع غيار السيارات | عضلات المعدة, ABS عالية درجة الحرارة | |
| مركب | ألياف كربونيه | قوة عالية, خفيفة الوزن, صلابة عالية | الفضاء الجوي, السيارات, ادوات رياضية | ألياف الكربون, CRP, CFRTP |
ما هي المواد الأكثر استخدامًا للآلات?
عندما يتعلق الأمر بآلات CNC, المعادن والبلاستيك هي المواد الأكثر استخدامًا. لكن, إذا كان علينا اختيار واحد, الألومنيوم يحتل المركز الأول.
لماذا يحظى الألمنيوم بشعبية كبيرة?
- سهلة الآلة- يقطع بسلاسة دون التآكل المفرط على الأدوات.
- خفيفة الوزن ولكن قوية- مثالي للصناعات مثل الفضاء والسيارات.
- مقاومة للتآكل-رائع للتطبيقات في الهواء الطلق والعالي.
- بسعر معقول- بالمقارنة مع التيتانيوم أو الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ, الألومنيوم صديق للميزانية.
- قابلة لإعادة التدوير-صديقة للبيئة ومتاحة على نطاق واسع.
مواد شهيرة أخرى لآلات CNC:
- فُولاَذ- قوي, متين, وتستخدم في التطبيقات الشاقة.
- نحاس- ممتاز للأجزاء الدقيقة والمكونات الكهربائية.
- بلاستيك (عضلات المعدة, بوم, نايلون)- خفيفة الوزن, بسعر معقول, ورائع للنماذج الأولية.
ما هي المادة الأسهل في الآلة?
إذا كنت تبحث عن مادة تخفيضات مثل الزبدة, نحاس هي واحدة من أسهل الآلة.
لماذا من السهل جدًا للآلة النحاس?
- ناعم وسلس- يقطع بشكل نظيف دون تقطيع.
- الاحتكاك المنخفض- يقلل من تراكم الحرارة, لذلك لا يضر أدوات.
- الانتهاء من السطح العظيم-يحتاج القليل أو معدوم بعد المعالجة.
- لا يعمل هاردين- على عكس الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ, يبقى النحاس سهلاً للآلة.
مواد أخرى سهلة للآلة:
- الألومنيوم- تقريبا سهلة مثل النحاس ولكن أقوى.
- البلاستيك (عضلات المعدة, بوم, نايلون)- هذه القطع بسرعة ولا أدوات ممل.
- الفولاذ الطري- ليونة من الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ وأسهل لقطع.
ما هي المواد التي يصعب الآلة?
بعض المواد تناول أدوات القطع, تسبب الحرارة المفرطة, أو تتطلب تقنيات خاصة إلى الآلة. ال الأكثر صعوبة مواد العمل مع تشمل التيتانيوم, إنكونيل, وصلب الصلب.
لماذا يصعب هذه المواد?
- التيتانيوم-نسبة عالية من القوة إلى الوزن تجعل الأمر صعبًا, لكنه يولد أيضًا الكثير من الحرارة, تسبب في ارتداء الأداة.
- إنكونيل (سبيكة النيكل)-تستخدم في تطبيقات الفضاء والتسخين العالي, هذا المعدن صعب للغاية ويقاوم القطع.
- تصلب الصلب- إنه أمر رائع بالنسبة للمتانة ولكنه يتطلب سرعات بطيئة, أدوات خاصة, ومبرد للآلة بفعالية.
- ألياف كربونيه & المركبات- هذه يمكن أن تهتم, كسر, أو إنتاج غبار ضار عند الآلات.
نصائح لتصنيع المواد الصلبة:
✔ استخدم الأدوات المغطاة بالكربيد أو الماس لحياة الأدوات أطول.
✔ تطبيق سائل التبريد لمنع ارتفاع درجة الحرارة.
✔ استخدم سرعات بطيئة ومعدلات تغذية مناسبة لتقليل ارتداء الأدوات.
✔ النظر آلات CNC متخصصة مصمم للمعادن الصلبة.
إذا كان مشروعك يتطلب دائمة للغاية أجزاء, هذه المواد تستحق التحدي, لكن كن مستعدًا لأوقات التشغيل الطويلة وتكاليف أعلى.
العوامل الرئيسية لاختيار مواد تصنيع CNC
كيف تتأكد من أنك تختار أفضل المواد? هناك العديد من العوامل المهمة التي يجب مراعاتها, وفهم هذه يمكن أن تساعدك على اتخاذ قرارات أكثر استنارة.
تطبيقات جزء
أول شيء تفكر فيه هو ما سيتم استخدام دورك بالفعل. المواد المختلفة أكثر ملاءمة لتطبيقات مختلفة. على سبيل المثال, إذا كنت تقوم بإنشاء أجزاء لصناعة الفضاء, ستحتاج إلى مواد خفيفة الوزن ولكنها قوية, يحب التيتانيوم أو الألومنيوم. على الجانب الآخر, إذا كنت تصنع أجزاء لنظام معالجة الأغذية, قد تحتاج إلى مادة مقاومة لدرجات الحرارة العالية والمواد الكيميائية القاسية, مثل الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ أو نظرة خاطفة بلاستيك.
كل مادة لها نقاط القوة والضعف, وتريد مطابقة خصائص المواد مع مطالب التطبيق. فهم البيئة سيعمل الجزء الخاص بك - سواء كان سيواجه ضغطًا عاليًا, درجات الحرارة القصوى, أو البلى المستمر - يمكن أن توجهك إلى اختيار المواد الصحيح.
وزن الجزء
يلعب وزن الجزء الخاص بك دورًا مهمًا في اختيار المواد. بالنسبة للأجزاء التي تحتاج إلى أن تكون خفيفة وسهلة التعامل (مثل المكونات في السيارات أو الفضاء الجوي الصناعات), ستحتاج إلى مواد ذات كثافة منخفضة, مثل الألومنيوم أو التيتانيوم. هذه المواد ليست خفيفة الوزن فحسب ولكنها متينة وقوية أيضًا.
في المقابل, إذا كان دورك سيحتاج إلى دعم الأحمال الثقيلة, ستحتاج إلى مادة أكثر كثافة وأقوى, مثل فُولاَذ. يساعد فهم متطلبات الوزن في دورك على ضمان أداءه كما هو متوقع دون تكاليف المواد غير الضرورية أو وقت المعالجة.
دقة جزئية والتسامح
غالبًا ما تكون الدقة واحدة من الجوانب الأكثر أهمية عند اختيار مادة. بعض المواد أسهل في الآلة إلى أبعاد دقيقة من غيرها. على سبيل المثال, الألومنيوم من الأسهل عمومًا الآلة إلى التحمل الضيق مقارنة بالمواد الأكثر صرامة مثل التيتانيوم أو الصلب الكربوني. كلما كانت المادة أكثر صعوبة في الآلة, كلما زادت التكلفة والوقت الذي يستغرقه تحقيق الدقة المطلوبة.
إذا كان الجزء الخاص بك يتطلب دقة عالية وتسامح ضيق, كن مستعدًا للعمل مع مواد يصعب على الجهاز أو قد تتطلب عمليات إضافية (مثل المعالجة الحرارية أو الأدوات المتخصصة). تأكد من العوامل في مستوى الدقة المطلوبة عند اختيار مادة, لأنه سيؤثر بشكل مباشر على تكاليف الآلات والجداول الزمنية.
خصائص جزء
فكر في الخصائص التي يحتاجها الجزء الخاص بك. على سبيل المثال:
- قوة: هل يحتاج الجزء الخاص بك إلى تحمل الأحمال الثقيلة? مواد مثل فُولاَذأو التيتانيوم توفير قوة ممتازة.
- المقاومة للتآكل: هل سيتعرض دورك للرطوبة أو المواد الكيميائية? يعتبر الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأأو الألومنيوم.
- الاستقرار الحراري: هل سيتعرض الجزء الخاص بك لدرجات حرارة عالية? سيراميكو التيتانيوم هي رائعة لمقاومة الحرارة.
كل مادة لها خصائص محددة تجعلها مثالية لبيئات واستخدامات معينة. عند اختيار مادة, ضع في اعتبارك كيف ستساعد هذه الخصائص على العمل بشكل جيد في تطبيقها المقصود.
جماليات المنتج
أحيانا, الطريقة التي يبدو بها الجزء لا تقل أهمية عن أداءه. على سبيل المثال, في بضائع المستهلكين أو إلكترونيات, يمكن أن يلعب ظهور الجزء دورًا رئيسيًا في قبول المستهلك. مواد مثل البلاستيك (على سبيل المثال, عضلات المعدة أو البولي) يمكن تشكيلها وتلوينها بسهولة لتلبية مواصفات التصميم.
على الجانب الآخر, المعادن يحب الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ و الألومنيوم يمكن أيضًا توفير أنيقة, نظرة حديثة. إذا كانت الجماليات مصدر قلق كبير, تأكد من اختيار المواد التي يمكن الانتهاء منها بسهولة أو أن تكون بالفعل نظرة تهدف إليها.
خيارات الانتهاء من السطح
عند تصنيع جزء, الانتهاء من السطح مهم لكل من مظهره ووظائفه. بعض المواد, يحب الألومنيوم أو الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ, أسهل في التلميع والانتهاء, بينما الآخرين, يحب الصلب الكربوني أو بعض المواد البلاستيكية, قد تتطلب خطوات تشطيب إضافية لتحقيق المظهر أو النعومة المطلوبة.
تلعب التشطيبات السطحية أيضًا دورًا في أداء الجزء. على سبيل المثال, الأجزاء التي سيتم استخدامها في بيئات عالية التقنية (مثل التروس أو المحامل) سوف تحتاج إلى النهاية التي تقلل من التآكل, في حين أن الأجزاء المستخدمة في التطبيقات الطبية أو الطيران قد تتطلب سلسة, سطح مصقول للوظيفة والأسباب الجمالية.
القدرة على التصنيع
بعض المواد أسهل في الآلة من غيرها, والتي يمكن أن تؤثر على كل من التكلفة والوقت الذي يستغرقه إنتاج الجزء. مواد ليونة مثل الألومنيوم و البلاستيك أسهل في الآلة ويمكن أن تقلل من تآكل الأدوات ووقت الإنتاج الكلي. على الجانب الآخر, مواد أصعب مثل التيتانيوم أو التنغستن أكثر صعوبة في الآلة, تتطلب أدوات متخصصة, وقت إضافي, وربما ارتفاع التكاليف.
إذا كان لمشروعك مواعيد نهائية صارمة أو قيود على الميزانية, من المهم مراعاة قابلية المادة, نظرًا لأن اختيار مادة يصعب للغاية على الماكينة يمكن أن يزيد بشكل كبير من الوقت وتكلفة الإنتاج.
يكلف
التكلفة هي دائمًا عاملة في اختيار المواد. في حين أنه من المغري الذهاب للحصول على مادة أعلى الأداء, قد لا يكون الخيار الأكثر فعالية من حيث التكلفة دائمًا. مواد مثل الألومنيوم عمومًا أكثر بأسعار معقولة وتوفر توازنًا جيدًا بين القابلية للآلات, قوة, والمتانة, جعلهم خيارًا شائعًا. لكن, مواد عالية الأداء مثل التيتانيوم أو نظرة خاطفة يمكن أن يكون أغلى بكثير, سواء من حيث تكاليف المواد ووقت الآلات.
قبل اتخاذ قرار بشأن المادة, تأكد من موازنة الأداء مع التكلفة. أحيانا, سيتم أداء مادة أقل تكلفة تمامًا لتطبيقك, السماح لك بالتوفير على كل من تكاليف المواد ونفقات الآلات.
نصائح عند استخدام عمليات CNC للآلة مواد مختلفة
اختر الأدوات المناسبة للوظيفة
لا يتم إنشاء جميع أدوات القطع على قدم المساواة. تتطلب مواد مختلفة أنواعًا مختلفة من الأدوات لتحقيق أفضل النتائج. على سبيل المثال, معادن أصعب مثل التيتانيوم و الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ سيحتاج إلى أدوات كربيد أو سيراميك لأنهم يمكنهم تحمل الحرارة والضغط المتمثل في قطع المواد الأكثر صعوبة. لمواد ليونة مثل الألومنيوم أو البلاستيك, يمكنك في كثير من الأحيان الابتعاد عن استخدام أدوات فولاذية عالية السرعة.
- نصيحة: قم دائمًا بمطابقة مادة الأداة الخاصة بك مع المواد التي تقوم بتصنيعها. هذا يساعد في تقليل ارتداء الأدوات ويضمن تخفيضات أكثر سلاسة.
التحكم في سرعة القطع ومعدل التغذية
تعد سرعة القطع ومعدل التغذية أمرًا ضروريًا لتحقيق النتائج المرجوة. إذا كانت سرعة القطع سريعة جدًا بالنسبة لمواد معينة, يمكن أن يتسبب في ارتداء الأداة بشكل أسرع, درجة حرارة, أو حتى كسر. على الجانب الآخر, إذا كان معدل التغذية بطيئًا جدًا, يمكن أن يؤدي إلى عدم كفاءة التشغيل وزيادة وقت الإنتاج.
- نصيحة: لمواد ليونة مثل الألومنيوم, استخدم سرعات قطع أسرع وارتفاع معدلات التغذية. لمواد أصعب مثل التيتانيوم أو فُولاَذ, تقليل سرعة القطع ومعدل التغذية لتجنب تراكم الحرارة المفرط وارتداء الأدوات.
استخدم المبرد المناسب
يعد استخدام سائل التبريد أثناء تصنيع CNC ضروريًا لتقليل تراكم الحرارة ومنع الأضرار التي لحقت الأداة وقطعة العمل. مواد مختلفة تولد مستويات مختلفة من الحرارة, لذلك يمكن أن يختلف نوع المبرد والمبلغ المستخدم.
- نصيحة: يستخدم المبردات القائمة على الماء لمواد ليونة مثل الألومنيوم و البلاستيك, لأنها يمكن أن تساعد في منع التلف الحراري. لمواد أصعب مثل الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ و التيتانيوم, قد ترغب في استخدام المبردات القائمة على الزيت لتحسين التبريد والتزييت.
انتبه إلى سمك المواد
يؤثر سماكة المادة التي تقوم بتصنيعها على مدى سرعة وكفاءة جهاز CNC الخاص بك. مواد أكثر سمكا, خاصة مثل المعادن الصلب الكربوني و الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ, سوف تتطلب المزيد من الآلات القوية والأدوات الأقوى للوصول إليها. على الجانب الآخر, مواد أرق مثل البلاستيك أو صفائح الألومنيوم سوف يتطلب طاقة أقل ويمكن تصحيحه بسرعة أكبر.
- نصيحة: قم دائمًا بضبط مسارات عمق القطع والأدوات وفقًا لسمك المادة. للمواد الأكثر سمكا, قلل من عمق كل قطع لتجنب توتر الجهاز والأدوات.
النظر في خصائص المواد قبل اختيار استراتيجية الآلات
كل مادة لها مجموعة من الخصائص الخاصة بها - بعضها أكثر هشاشة, البعض الآخر أكثر مرونة, ويمكن للبعض التوسع أو التعاقد عند التعرض للحرارة. سيساعدك فهم هذه الخصائص على تحديد أفضل استراتيجية للآلات للمادة.
- نصيحة: للمواد عرضة لتزييف, مثل البلاستيك يحب بولي كلوريد الفينيل أو أسيتال, استخدم سرعات القطع المنخفضة وتجنب التخفيضات العميقة لتقليل حركة المواد. لمواد مثل التيتانيوم, التي تتوسع بسبب الحرارة, استخدم معدل تغذية أبطأ وتأكد من معايرة جهازك جيدًا لتجنب أي تشوهات.
ضمان العمل المناسب
يعد الاحتفاظ بموادك في مكانه أمرًا بالغ الأهمية, خاصة عند تصنيع الأشكال المعقدة. إذا لم يتم عقد الشغل بشكل صحيح, يمكن أن تتحرك أثناء الآلات, مما يؤدي إلى ضعف التسامح, عيوب السطح, أو حتى الأجزاء التالفة. بعض المواد أكثر عرضة للتشوه أو التحول, لذلك يحتاجون إلى رعاية إضافية.
- نصيحة: استخدم قوية وموثوقة تجهيزات العمل, مثل المشابك أو أنظمة تشاك فراغ, لعقد أجزائك في مكانها بشكل آمن. لمواد ليونة مثل البلاستيك, استخدم أساليب عمل أكثر ليونة لتجنب إتلاف الجزء.
اختر جهاز CNC المناسب
ليس كل آلة CNC مناسبة لكل مادة. مواد أكثر ليونة, يحب الألومنيوم, يمكن تشكيلها بسهولة مع آلات CNC قياسية 3 محاور. لكن, مواد أصعب, مثل التيتانيوم أو فُولاَذ, قد يتطلب 5-آلات محور CNC لمزيد من المرونة ودقة أفضل.
- نصيحة: للتخفيضات المعقدة أو المفصلة للغاية في المواد الصعبة, النظر في استخدام 5-محور CNC الآلات. سيسمح هذا النوع من الآلات بمزيد من زوايا الهجوم وتحكم أفضل في عملية القطع.
الانتهاء من الأهمية
يمكن أن تحدث النهاية على سطح الجزء الخاص بك, سواء من حيث الجمال والوظائف. بعض المواد, يحب الألومنيوم و الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ, سيكون له سطح ناعم بشكل طبيعي بعد الآلات, بينما الآخرين, يحب البلاستيك أو التيتانيوم, قد تتطلب عمليات إضافية بعد ذلك مثل تلميع أو أنودة لتحقيق النهاية المطلوبة.
- نصيحة: ضع دائمًا في الاعتبار السطح المطلوب في الاعتبار عند اختيار مادة. إذا كانت هناك حاجة إلى نهاية لامعة أو سلسة, تأكد من أن المواد التي تختارها مواتية لهذا النوع من النهاية. بعض المواد, يحب نحاس أو الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ, يمكن أن يكون مصقول بسهولة, بينما الآخرين, يحب برونزية, قد تتطلب خطوات إضافية.
حساب تكلفة المواد وتوافرها
تكلفة المواد هي دائمًا اعتبارًا رئيسيًا. التيتانيوم و الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ, في حين ممتازة لبعض التطبيقات, يمكن أن تكون أغلى بكثير من المواد مثل الألومنيوم أو نحاس. بالإضافة إلى ذلك, بعض المواد متوفرة بسهولة من غيرها, والتي يمكن أن تؤثر على أوقات الرصاص.
- نصيحة: اختر المواد التي تتناسب مع ميزانية مشروعك. لو الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ أكثر من ميزانيتك, يعتبر الألومنيوم أو الصلب الكربوني كبدائل لأجزاء أقل أهمية.
فهم التأثير البيئي
بعض المواد لها تأثير بيئي كبير, إما من خلال التعدين, يعالج, أو التخلص. مواد مثل البلاستيك, إذا لم يتم إعادة تدويرها بشكل صحيح, يمكن أن تسهم في الهدر. لكن, مثل المعادن الألومنيوم و الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ غالبًا ما تكون قابلة لإعادة التدوير.
- نصيحة: كلما كان ذلك ممكنا, اختر مواد قابلة لإعادة التدوير أو لها تأثير بيئي الحد الأدنى. الألومنيوم, على سبيل المثال, تم إعادة تدويرها على نطاق واسع ولديها بصمة بيئية أقل مقارنة بمواد مثل بلاستيك.
احصل على مواد تصنيع CNC المناسبة لمشاريعك
يعد اختيار المادة المناسبة أمرًا ضروريًا لمشروع تصنيع CNC الخاص بك. إذا كنت غير متأكد من المواد الأكثر ملاءمة لاحتياجاتك, فكر في طلب المشورة المهنية من مقدمي خدمات الآلات CNC الذين يقدمون خيارات وخبرات مواد شاملة.
ما هي الآثار المترتبة على تكلفة مواد الآلات المختلفة?
إن اختيار المادة المناسبة لآلات CNC لا يتعلق فقط بالقوة والأداء - إنه أيضًا يؤثر على ميزانيتك. بعض المواد رخيصة وسهلة الجهاز, في حين أن البعض الآخر مكلف ويتطلب أدوات خاصة أو وقت معالجة إضافي.
ما الذي يدفع تكلفة مواد الآلات?
- سعر المواد الخام- بعض المواد, مثل الألومنيوم, متوفرة على نطاق واسع وبأسعار معقولة, بينما الآخرين, مثل التيتانيوم, أكثر تكلفة بكثير.
- القدرة على التصنيع- مواد ليونة (مثل النحاس والألمنيوم) آلة أسرع, تقليل ملابس العمل وارتداء الأدوات. المواد الصلبة (مثل الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ أو inconel) تتطلب أدوات أبطأ وأدوات خاصة, زيادة التكاليف.
- ارتداء أداة- بعض المواد أدوات القطع الباهتة بسرعة, مما يؤدي إلى ارتفاع تكاليف الأدوات.
- الخردة والنفايات- قد تؤدي المواد الأكثر صعوبة إلى مزيد من النفايات بسبب كسر الأدوات أو أخطاء الآلات.
- متطلبات التشطيب- بعض المعادن, مثل النحاس, تبدو رائعة بشكل طبيعي, بينما الآخرين, مثل الصلب الكربوني, تتطلب الطلاء أو التلميع, إضافة تكلفة إضافية.
مقارنة التكلفة لمواد الآلات الشائعة
| مادة | تكلفة المواد الخام | تكلفة التصنيع | تأثير التكلفة الإجمالية | أفضل حالات الاستخدام |
| الألومنيوم | قليل | قليل | $$ | الفضاء الجوي, السيارات, إلكترونيات |
| نحاس | واسطة | منخفض جدا | $$ | أجزاء دقيقة, السباكة, كهربائي |
| الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ | واسطة | عالي | $$$ | طبي, تجهيز الأغذية, أجزاء مقاومة للتآكل |
| التيتانيوم | عالية جدًا | عالية جدًا | $$$$$ | الفضاء الجوي, يزرع الطبية |
| الكربون الصلب | قليل | واسطة | $$ | الأجزاء الهيكلية, أدوات |
| البلاستيك (عضلات المعدة, بوم, نايلون) | قليل | منخفض جدا | $ | النماذج الأولية, مكونات خفيفة الوزن |
| إنكونيل (سبيكة النيكل) | عالية للغاية | عالية للغاية | $$$$$$ | محركات طائرة, تطبيقات الحرارة الشديدة |
كيفية موازنة التكلفة والأداء
✅ اذهب للألمنيوم أو النحاس إذا أردت بسعر معقول, مواد سهلة للآلة.
✅ استخدم المواد البلاستيكية للنماذج الأولية منخفضة التكلفة لا تحتاج إلى قوة عالية.
✅ النظر في الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ متى مقاومة التآكل أمر بالغ الأهمية, لكن كن مستعدًا لزيادة تكاليف الآلات.
✅ التيتانيوم و inconel نكون مواد مميزة- استخدمهم فقط عندما يكون ذلك ضروريًا للغاية بسبب ارتفاع سعرها وصعوبة الآلات.
💡 نصيحة محترف: إذا كان الجزء الخاص بك لا يحتاج إلى قوة متطرفة أو مقاومة للحرارة, التمسك بالألمنيوم أو الفولاذ الطري لتوفير تكاليف المواد والآلات.
خاتمة
Machining CNC هي عملية تصنيع متعددة الاستخدامات بشكل لا يصدق تستوعب مجموعة واسعة من المواد. سواء كنت تعمل مع المعادن, البلاستيك, أو المركبات, مفتاح النجاح هو اختيار المواد الصحيحة بناءً على تطبيق الجزء, ملكيات, ومتطلبات الآلات. من خلال فهم الخصائص المادية وتحديات الآلات, يمكنك تحسين عملية اختيار المواد, تقليل التكاليف, وتحقيق أجزاء عالية الجودة.
الأسئلة الشائعة
- ما هي العوامل التي يجب مراعاتها عند اختيار مادة CNC?
النظر في تطبيق الجزء, وزن, دقة, ملكيات, والتكلفة.
- أي سبيكة الألومنيوم هي الأفضل لآلات CNC?
يستخدم الألومنيوم 6061-T6 بشكل شائع في تصنيع CNC نظرًا لقابليته الممتازة وقوته.
- أي البلاستيك الأكثر قابلية للآلية?
اسيتال, نظرة خاطفة, و PVC توفر قابلية كبيرة للآلات والاستقرار الأبعاد.
- ما هو أصعب معدن للمطحنة?
التيتانيوم هي واحدة من أصعب المعادن في مطحنة, غالبًا ما تتطلب أدوات وتقنيات متخصصة.











1 فكرت في "مواد التصنيع باستخدام الحاسب الآلي, كل ما تحتاج إلى معرفته”