تصنيع الآلات المصغرة, ثبت أيضًا أن التصنيع الدقيق هو تخصص فرعي أساسي في هندسة التصنيع, تنطوي على تصنيع مكونات مصغرة دقيقة. لديها مجموعة من التطبيقات في العديد من الصناعات التي تشمل الإلكترونيات والأجهزة الطبية. إلى جانب ذلك, لقد تطورت تقنيات التصنيع المصغرة بشكل هائل. يستكشف هذا المقال جوانب مختلفة من الآلات المصغرة بما في ذلك تقنيات التصنيع المختلفة, مواد, وتطبيقات التصنيع المصغر وقضاياه وعوامله التي تهمه.
ما هي الآلات المصغرة?
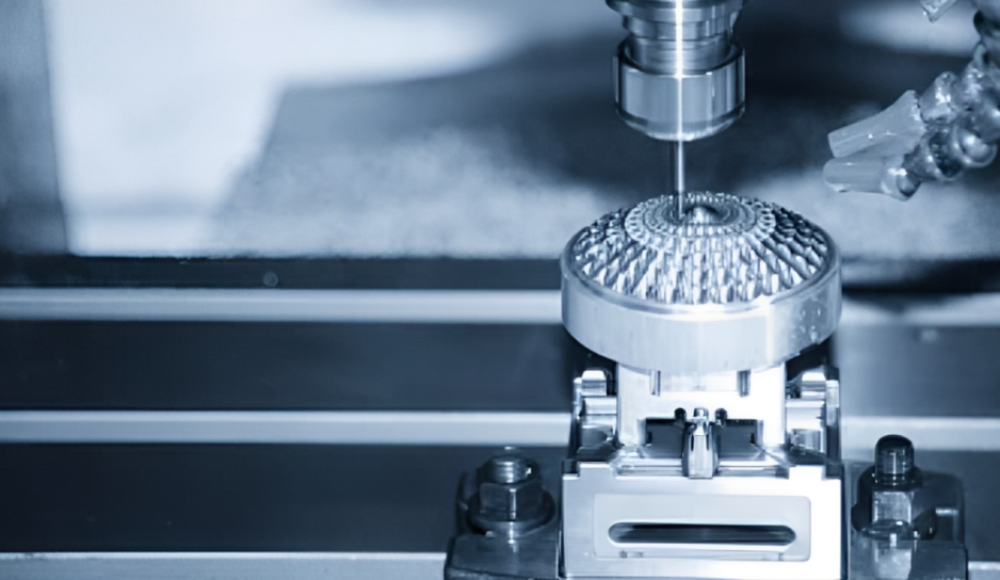
التصنيع المصغر أو الدقيق يعني تصنيع أجزاء صغيرة بأبعاد تقاس بالملليمتر وتنفيذ عمليات تصنيع متطورة. تتطلب هذه المعالجة دقة ودقة عالية. إلى جانب ذلك, إنه أمر بالغ الأهمية للصناعات التي تستخدم الأقسام المعقدة. تستخدم الآلات الدقيقة الأدوات والآلات التي تعمل بمقاييس دقيقة, ويستخدم تكنولوجيا التحكم العددي بالكمبيوتر في معظم عملياته. لكن, ويتميز بدقته, مستوى عال من التفاصيل, والمنتجات ذات الحجم المعقول.
عملية كاملة من الآلات المصغرة
مصغرة أو التصنيع الدقيق يتكون من عدة مراحل, والتي تم تطويرها خصيصًا لإنشاء أجزاء صغيرة دقيقة. فيما يلي نظرة عامة مفصلة عن العملية الكاملة للتصنيع المصغر:
1. التصميم والنماذج الأولية
- نمذجة CAD: بدءاً من صنع نموذج CAD للجزء الفعلي, الذي يحتاج إلى تصنيع. تم تطوير النموذج التالي بشكل صحيح مع المواصفات, الأحجام, والتفاوتات المدرجة بشكل مناسب.
- النماذج الأولية: يمكن إنشاء نموذج أولي مادي باستخدام تقنية النماذج الأولية السريعة, أي. 3الطباعة د. يساعد هذا في التحقق من التصميم قبل البدء فعليًا في عملية التصنيع.
2. اختيار المواد
- اختيار المادة المناسبة: إثبات الذات, اعتمادا على تطبيق الجزء المصغر, مواد مناسبة, أي. الألومنيوم, الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ, البلاستيك, إلخ.
- الإعداد المادي: يتم شراء المواد الخام للاستخدام وتأهيلها للوفاء بالمعايير المطلوبة وعمليات التصنيع المتوقعة.
3. إعداد الأدوات
- اختيار الأداة: اختيار الأدوات المناسبة - تعتمد المطاحن أو المثاقب الدقيقة باستخدام الحاسب الآلي على المادة كما أن تصميم الجزء أمر بالغ الأهمية أيضًا.
- إعداد الآلة: يتم تركيب الأدوات المناسبة للتصنيع المصغر على ماكينة CNC لضبط السرعة المناسبة, معدل التغذية, وعمق القطع.
4. عملية التصنيع
- عقد العمل: يتم تأمين المادة بشكل مثالي بواسطة أداة تثبيت أو ملزمة على الطاولة لتقليل أو إزالة أي حركة أثناء عملية التصنيع.
- التصنيع باستخدام الحاسب الآلي: يتم تشغيل عمليات التصنيع باستخدام الحاسب الآلي الدقيقة بواسطة برنامج تصميم لإنشاء المنتج المطلوب. قد تتضمن هذه العملية تقنيات مختلفة, مشتمل:
- طحن: يتضمن القطع بمطحنة Micro CNC النحت لإضافة أو تحقيق خصائص معينة في الميزات أو الأشكال.
- تحول: ربط المادة لتحويل الأسطوانة إلى الزاوية المطلوبة لقطع الأجزاء الدائرية.
- حفر: الحفر كما هو موضح في التصميم.
- معالجة التفريغ الكهربائي (موسيقى الرقص الإلكترونية): يكون شكل المادة المراد قطعها معقدًا أو عند قطع المواد الصعبة.
- يراقب: أثناء المعالجة, المشغلون قريبون دائمًا, مراقبة دقيقة لتحقيق النتائج الصحيحة.
5. عمليات ما بعد التصنيع
- إزالة الأزيز: ويشمل عملية تنعيم سطح المنتج. لذا, يمكن أن تكون آمنة وممتعة من الناحية الجمالية.
- التشطيب: المعالجات السطحية الاصطناعية مثل التلميع, أنودة, أو طلاء لجعل السطح يبدو جيدًا ويعمل بشكل أفضل.
6. رقابة جودة
- تقتيش: تتضمن تقنيات التصنيع أدوات قياس دقيقة مثل الفرجار, والميكرومتر. لذا, يمكنهم التأكد من أن الأجزاء تلبي التفاوتات والأحجام المطلوبة.
- اختبار: إجراء اختبارات وظيفية أو اختبارات الإجهاد لتحديد ما إذا كان الجزء يعمل بشكل جيد.
7. حَشد (إذا لزم الأمر)
- تكامل المكونات: في قضايا الشركات, ويمكن تجميع المكونات المصغرة مع غيرها لتشكل الجزء الأخير من تجميع معين.
- التكيف المصغر: وتكييفه بطريقة تجعله مناسبًا تمامًا وعمليًا داخل خط التجميع.
أهمية التفاوتات الصارمة في الآلات المصغرة/الصغرى باستخدام الحاسب الآلي
فيما يلي بعض الجوانب المهمة لفهم مدى أهمية التسامح المحكم في التصنيع باستخدام الحاسب الآلي المصغر.
- الوظيفة: تعتبر التفاوتات مهمة لأنه في معظم التصميمات، يجب أن تتوافق الأجزاء الصغيرة التي تشكل التجميع مع مكونات التزاوج لتكون فعالة.
- رقابة جودة: يحافظ على الاتساق بين التشغيل من جزء إلى جزء ومن التشغيل إلى التشغيل وهو أمر مهم بشكل خاص في الصناعات التي تحتاج إلى دقة عالية, أي. الفضاء والطبية.
- قابلية التبادل: يجب أن تكون الأجزاء قابلة للتبديل; إن اتباع خطة التسامح يعني أن الأجزاء من عمليات الإنتاج المختلفة سوف تتناسب بشكل جيد مع الأجزاء الأخرى.
- الحد من النفايات: تساعد الدقة العالية على تقليل المواد الخردة. إلى جانب ذلك, فهو يقلل التكلفة بشكل فعال ويزيد الإنتاج.
- تعزيز الأداء: تؤدي الدرجة العالية من الدقة في تحديد الشكل الدقيق للمكونات إلى أداء أفضل, بما في ذلك مقاومة التآكل وزيادة عمر خدمة المكونات.
المواد المتوافقة مع الآلات المصغرة/الصغرى باستخدام الحاسب الآلي
| مادة | كثافة (جم/سم3) | صلابة (روكويل) | التطبيقات النموذجية |
| سبائك الألومنيوم | 2.7 | ب70-80 | مكونات الفضاء الجوي, المساكن الإلكترونية |
| الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ | 7.9 | ب80-90 | الأجهزة الطبية, مهمات الربط, التروس الصغيرة |
| سبائك التيتانيوم | 4.5 | ب30-35 | أجزاء الفضاء الجوي, يزرع, مكونات عالية الأداء |
| البلاستيك (على سبيل المثال, ديلرين, بتف) | 1.4-2.0 | R80-90 | التروس, رمان, المساكن, العزل |
| نحاس | 8.9 | ب60-65 | موصلات كهربائية, المبادلات الحرارية |
| نحاس | 8.5 | ب60-70 | الصمامات, التجهيزات, الأجزاء الزخرفية |
| الكربون الصلب | 7.8 | C25-40 | أدوات, مكونات السيارات |
| نايلون مملوء بالزجاج | 1.4-1.5 | R80-90 | مركبات اساسيه, أجزاء مقاومة للاهتراء |
| سيراميك | 3.0-3.5 | ح60-70 | أدوات القطع, العوازل |
| سبائك المغنيسيوم | 1.8 | ب60-70 | أجزاء الفضاء الجوي, مكونات السيارات |
التقنيات المختلفة المستخدمة في الآلات المصغرة
لذا, دعونا نناقش التقنيات المختلفة المستخدمة في التصنيع الدقيق:
1. الطحن باستخدام الحاسب الآلي
الطحن باستخدام الحاسب الآلي يستخدم أدوات القطع للطحن أو التقشير ويعطي مخططات هندسية معقدة للأجزاء. تصميم القاطع دقيق للغاية ويمكن استخدامه في العديد من التطبيقات, أي. طحن الوجه والكفاف. إن مشكلة التفاوتات الصارمة خاصة في الأجزاء الصغيرة المُشكَّلة هي الجوهر الإجرائي للغاية لإعداد الآلات والبرمجة.
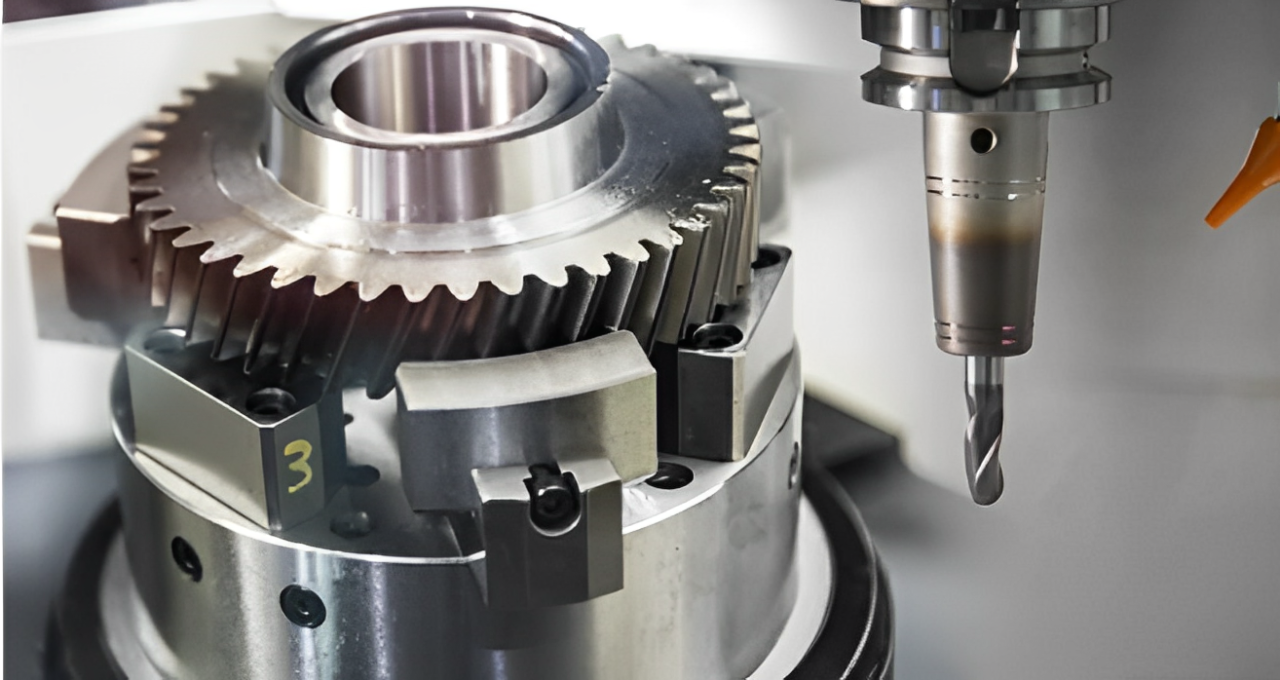
2. تحول باستخدام الحاسب الآلي
تحول باستخدام الحاسب الآلي يقوم بإنشاء أشكال دورانية للأجزاء الأسطوانية من خلال دوران قطعة العمل في المخرطة. هنا لا تدور الأدوات لإزالة المواد وتعمل بشكل جيد عند إنشاء أشكال التناظر مما يوفر سهولًا دقيقة للغاية ومصقولة. لكن, يقتصر تطبيقه على الشكل الهندسي.
3. معالجة التفريغ الكهربائي
موسيقى الرقص الإلكترونية يزيل المواد عن طريق الشرر الكهربائي وبالتالي فهو مناسب للعمل على الأشكال الصعبة في المواد الصلبة, أي. الصلب والتيتانيوم. هذه الطريقة جيدة بشكل خاص لتصميم القوالب والقوالب. لكن, إنها عملية تستغرق وقتًا طويلاً وقد يستغرق إعدادها وقتًا أطول مقارنةً بالتقنيات الأخرى.
4. القطع والنقش بالليزر
تقوم تقنية القطع بالليزر بتركيز أشعة الليزر على قطع المواد أو نقشها بتصميمات متقاربة للغاية. إنه الأفضل للألواح الرقيقة ولكنه ليس جيدًا للألواح السميكة أو تلك التي تحتاج إلى قطع الكثير من المواد.
5. الآلات الدقيقة
الآلات الدقيقة هي عملية تقصير, مكسور, أو تقليل أبعاد المكونات بمقياس أقل من 1 مم. تتضمن هذه الأعمال أدوات صغيرة لتصنيع ميزة صغيرة, وهو مفيد جدًا في تصنيع الأدوات الطبية. لكن, إنه مقيد بحقيقة أن هناك حاجة إلى أدوات ومعدات أكثر تقدمًا بسبب ساعات المعالجة الطويلة.
6. قطع المياه النفاثة
القطع بنفث الماء يستخدم الماء عالي الضغط مع جزيئات العقيق لقطع قطع العمل مع القليل من الحرارة. إنها مناسبة للأشكال المعقدة ولكنها ليست بدقة القطع بالليزر, وعادة, المواد تحتاج إلى مزيد من العلاج.
7. 3د الطباعة
في الطباعة ثلاثية الأبعاد, تتم إضافة أجزاء جديدة إلى التصنيع وتمكين النماذج الأولية السريعة للهندسة المعقدة. هناك مجموعة متنوعة من المواد التي يدعمها ولكنها قد تتطلب في بعض الأحيان المعالجة اللاحقة لتحقيق الدقة المحددة.
8. غرق EDM
يطبق غرق EDM أقطابًا كهربائية على شكل الاكتئاب والملامح الداخلية على المواد الصلبة. إنها توفر دقة كبيرة لتصنيع القوالب ولكنها قد تستغرق وقتًا طويلاً, ويجب أن يتم إعدادها بدقة.
العوامل الرئيسية التي يجب مراعاتها ضرورية للتصنيع المصغر
دعونا نناقش بعض العوامل الأساسية التي يجب مراعاتها عند المعالجة المصغرة:
- سرعة: لذلك من الضروري موازنة سرعات المغزل للحصول على دقة عالية وتجنب التشوه الحراري لقطعة العمل.
- معدل التغذية: تسمح معدلات التغذية الصحيحة بمعالجة المادة بالطريقة الصحيحة مع تأثيرات أقل أو معدومة على قطعة العمل.
- اختيار الأداة: من المهم اختيار الأداة الصحيحة, أي. المطاحن أو التدريبات CNC الصغيرة. أنها تؤثر بشكل كبير على تشغيل الآلات الدقيقة.
- استخدام المبرد: يساعد المبرد الصحيح في التحكم في الحرارة ويعزز متانة الأداة أثناء التشغيل الآلي.
- معايرة الآلة: تتطلب هذه العملية معايرة CNC أكثر تكرارًا للحصول على تصنيع الأجزاء المناسبة بأحجام مصغرة مختلفة.
إيجابيات وسلبيات الآلات الدقيقة / الدقيقة
وفيما يلي إيجابيات وسلبيات الآلات المصغرة:
مزايا:
- دقة عالية: يمكن تحقيق صنع القالب من خلال تصميمات دقيقة ذات خلوصات صغيرة ودقة عالية.
- قابلية التوسع: من السهل زيادة الإنتاج من نطاق صغير إلى نطاق واسع.
- براعه: يمكن استخدامه على أي مادة تقريبًا وفي كل المواقف تقريبًا.
- تقليل النفايات: إن تقليل كمية النفايات يعني تحسين التكاليف والبصمة البيئية المادية.
- قدرات الأتمتة: ويمكن ربط هذه التقنية بجهاز كمبيوتر لأتمتة عملية التصنيع, التنصت على المزيد من خطوط الإنتاج.
محددات:
- ارتفاع التكاليف الأولية: المعدات والأدوات المتطورة, على العموم, لها تكلفة عالية.
- الإعداد المعقد: يحتاج إلى إعداد خاص وقد يستغرق إعداده بعض الوقت.
- القيود المادية: قد تشكل بعض المواد تحديًا للآلة عند اعتماد مبدأ التصغير.
- متطلبات المهارة: يقوم الأفراد الماهرون بتشغيل عمليات تصنيع التصغير والإشراف عليها بكفاءة.
تطبيقات الآلات المصغرة
دعونا نلقي نظرة عامة على التطبيقات الشائعة للتصنيع المصغر:
- أجهزة طبية: إنتاج أجزاء صغيرة للمعدات الجراحية, يزرع العظام, ومعدات التشخيص.
- الفضاء الجوي: يعمل في صناعة المواد الخفيفة, تطبيقات عالية القوة للطائرات وسفن الفضاء.
- إلكترونيات: تصنيع موصلات كهرومغناطيسية مصغرة, الدوائر المطبوعة, وأجزاء لسلع الاتصالات المتنقلة.
- السيارات: إنتاج المكونات الدقيقة المستخدمة في تصنيع المحركات والمكونات الإلكترونية في المركبات.
- علم الروبوتات: مصغر & الأجزاء الميكانيكية الدقيقة المستخدمة في الروبوتات & الأنظمة الآلية.
خاتمة
ختاماً, تعد الآلات المصغرة أو الآلات الدقيقة قطاعًا فرعيًا مهمًا في قطاع التصنيع لأنها تسمح بإنشاء منتجات صغيرة ولكنها معقدة للغاية. قد تكون هذه المنتجات مطلوبة في العديد من الصناعات ذات التقنية العالية وقد فتحت إمكانات جديدة لزيادة حجم الفوائد المستمدة من الآلات المصغرة. وذلك لأن الصناعات مستمرة في التطور. لذا, وسيظل مجالًا حيويًا للعديد من الشركات المصنعة التي ترغب في اكتساب الإتقان في التصنيع الدقيق.
أسئلة مكررة
س1. ما هي أنواع الأجزاء التي تنتجها الآلات المصغرة عادة؟?
عادةً ما تتم المعالجة الدقيقة على أجزاء ذات أحجام في نطاق المليمتر وفي معظم الحالات أقل من 5 مم.
Q2. ما هي الصناعات التي تقوم بالتصنيع الدقيق بشكل أكثر فعالية؟?
الصناعات الدقيقة بما في ذلك الأجهزة الطبية, الفضاء الجوي, إلكترونيات, السيارات, وتستخدم الروبوتات الآلات المصغرة لأجزائها.
س3. ما الذي يجعل CNC الصغير مختلفًا عن CNC أو التصنيع التقليدي العادي?
يركز التصنيع باستخدام الحاسب الآلي الصغير على تصنيع أصغر, أرق, والمكونات الأكثر تعقيدًا ذات دقة تصنيع أعلى ودقة تحتاج إلى أدوات وطرق محددة.
س 4. ما هي المواد المستخدمة في التصنيع المصغر?
المواد المستخدمة عادة هي الألومنيوم وسبائكه, الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ, التيتانيوم, سبائك, البلاستيك, والنحاس.
س5. ما هي الصعوبات المصغرة?
المخاوف هي; دقة, حالة الأداة, يثبت, والمواد والأدوات.
س6. ما إذا كان من الممكن أتمتة الآلات المصغرة?
نعم, من الشائع أن يتم التحكم في الآلات المصغرة من خلال تقنية CNC، مما يساعد على تحسين الكفاءة والدقة.
س7. أين تتناسب التفاوتات في سياق التصنيع المصغر?
يعد تقليل الاختلافات أمرًا بالغ الأهمية في التصنيع المصغر لأن الأجزاء يجب أن تعمل كما تم تصميمها وتتناسب مع الأجزاء الأخرى في التجميعات.