軍事請負業者や防衛機器サプライヤーは、比類のない精度を提供する CNC テクノロジーに依存しています。, 再現性, 極端な動作環境に耐えることができるミッションクリティカルなコンポーネントを製造する能力. 戦闘機やレーダー システムから海軍艦艇や先進兵器まで, CNC 加工は軍事生産のほぼすべての分野をサポートしています.
多くの従来の製造方法とは異なり、, CNC 加工により、部品が安全のために必要な非常に厳しい公差を確実に満たすようになります, パフォーマンス, そしてステルス. 同時に, これらの技術の多くは航空宇宙などの民間部門に波及しています。, 自動車, および海事産業 - CNC の二重用途の価値を実証.
防衛製造における CNC 加工
CNC加工 20世紀半ばに初めて開発されたサブトラクティブ製造プロセスです, そしてその役割は21世紀に大きく拡大しました. 今日のシステムははるかに先進的です, 組み込む:
自動化, 事前にプログラムされたコントロール 正確さと一貫性のために.
製造および組み立てのための設計 (DFMA) 生産を合理化するための原則.
マルチ軸の機械加工 複雑な形状の場合.
最小限の手動介入, 人的エラーの削減と効率の向上.
その結果、厳格な軍用仕様を満たす高性能コンポーネントの生産が迅速化されます。, 防衛サプライヤーがあらゆる部品の耐久性と信頼性を確保しながら、緊急の需要に迅速に対応できるようにします。.
軍事および防衛における CNC 加工の 5 つの主な用途
1. 航空宇宙
軍用航空宇宙部品は、ほとんどの民間航空機よりもはるかに厳しい公差を達成する必要があります, 特にステルス システムでは、わずかな表面の不一致でもレーダーの不可視性が損なわれる可能性があります。.
ステルス機 (F-35 ライトニング II): ロッキード・マーティンは、高度な 5 軸フライス盤を使用して、炭素繊維複合材のスキンと構造部品を極めて正確に加工しています。. 組み立て精度により、レーダー波が反射されるのではなく確実に偏向されます。, ステルス能力の維持.
ステルス爆撃機 (B-2 スピリット): ノースロップ・グラマンは、胴体外板の穴あけとトリミングに CNC テクノロジーを採用しています。, 従来の方法と比較して生産時間を 3 分の 1 に短縮.
無人航空機 (uavs): ゼネラル・アトミックスのプレデター・ドローンはコア切断に CNC 加工を使用しています, 軽量設計と耐久性を両立.
防衛航空宇宙メーカーは重要な CNC 要件を特定しました:
機械加工プロセスの絶対的な再現性.
工作機械の素早い応答性.
安定した, 振動のない基礎.
温度に敏感な許容範囲を維持するための厳格な環境制御.
CNC技術なし, 現代の航空機の複雑さとステルス性能を達成することは不可能でしょう.
2. 探知およびレーダー システム
レーダーと探知システムは航空機などの脅威を特定し追跡するために不可欠です, ドローン, そしてミサイル. これらのシステムには、スムーズなコンポーネントが必要です。, 精密に機械加工された表面と過酷な気象条件でも一貫したパフォーマンス.
レーダーアンテナ & 見つけました: CNC加工により曲線を実現, 強風や嵐の中での精度と耐久性に必要な空気力学的構造.
電子部品: マイクロ波アンテナ, 導波路, 回路基板ハウジングは、電気的性能と構造的信頼性を確保するために CNC フライス加工と旋削加工を使用して製造されています。.
モバイル統合: 多くのレーダーシステムは車両や船舶に搭載されています, 軽量でありながら頑丈なケーシングと CNC 加工が可能になる支持構造が必要.
民間の航空交通管制システムも同様のコンポーネントを使用しています, しかし、軍事用途では衝撃に対するより高い耐性が求められます, 振動, 電磁干渉.
3. 軍用車両
CNC 加工は装甲車両および非装甲車両の製造において重要です, 戦場の状況でも信頼性の高いパフォーマンスを保証.
装甲戦車 (例えば, ルクレール MBT): CNC 加工によるタレットリングの製造, 銃の防盾, エンジン部品, およびサスペンションシステム, 安全性と機能性を確保するには、すべてが完璧な精度で組み合わされる必要があります。.
実用車: さらに軽い車両も, 兵員輸送車や輸送トラックなど, 耐久性とメンテナンスの容易さのために CNC 製造部品が必要です.
正確なフィット感と仕上がりを保証することで, CNC 加工により車両の耐用年数が延長されます, メンテナンス効率の向上, 戦闘環境での迅速なアップグレードをサポートします.
軍艦, 潜水艦, 海軍支援船には何千もの精密機械加工部品が組み込まれています. CNC テクノロジーは、過酷な海洋環境において性能と耐食性の両方を提供します。.
推進 & 力: シャフト, タービン, プロペラは高精度で製造されており、効率と静かな動作を保証します。, ステルス潜水艦にとって重要.
兵器 & 通信システム: CNC 加工によりミサイル システムのハウジングを製造, レーダーアレイ, およびソナーシステム.
耐久性: CNC 加工によって適用されたカスタム表面仕上げにより、塩水による腐食や機械的摩耗から部品を保護します.
CNC 加工の適応性により、海軍技術者は海軍技術の進化に合わせて新しい設計を迅速にプロトタイプし、展開することができます。.
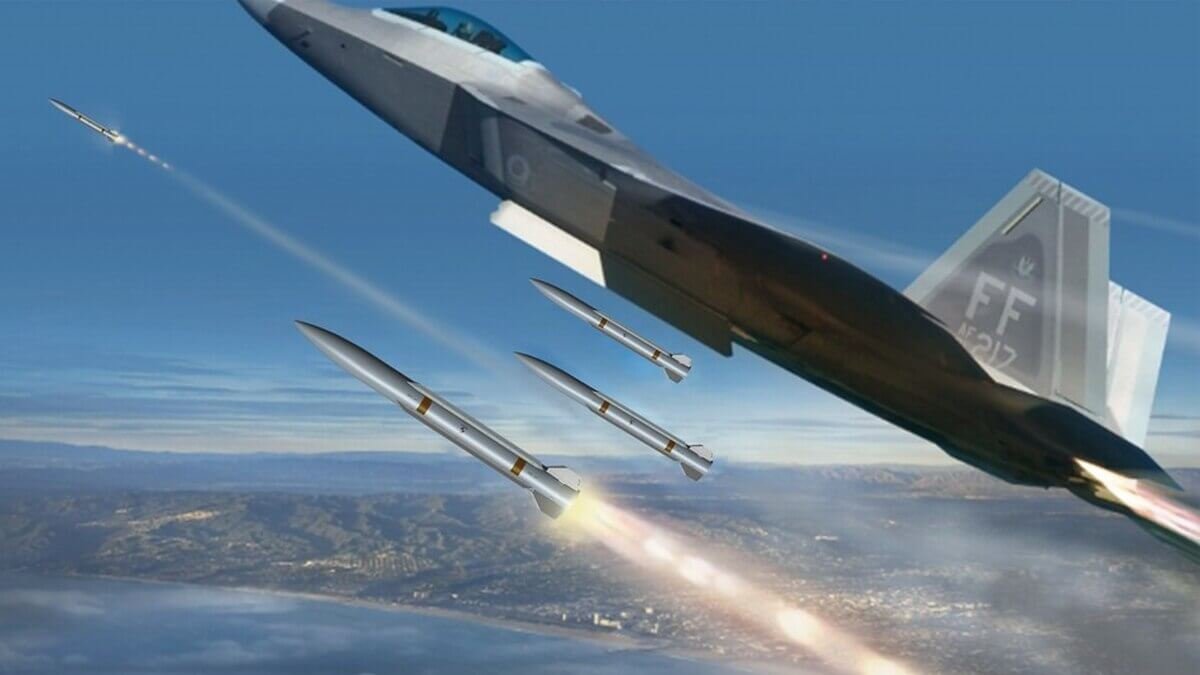
5. 武器システム
CNC 加工は長い間兵器開発の中心となってきました。, 銃器からミサイルシステムまで.
トマホークミサイル: 1990 年代にゼネラル ダイナミクス社が 4 軸 CNC 加工で製造したもの, レイセオンが製造する最新バージョンは現在、多軸ロボット CNC システムを使用して、単一の自動プロセスで 20 フィートのミサイル外板を加工しています。.
安全性 & 耐久性: CNC 加工により、ミサイルハウジングは発射時の極度のトルクに耐えることができます。, 潜水艦配備における高圧だけでなく.
自動化の利点: ロボット CNC システムにより手作業への依存が軽減されます。, コストを削減し、生産をスピードアップしながら、作業者の安全性を向上させます。.
この精度の組み合わせ, 効率, 耐久性と耐久性に優れた CNC 加工は武器製造に不可欠です.
トップス 精密工業: 軍事用 CNC 機能
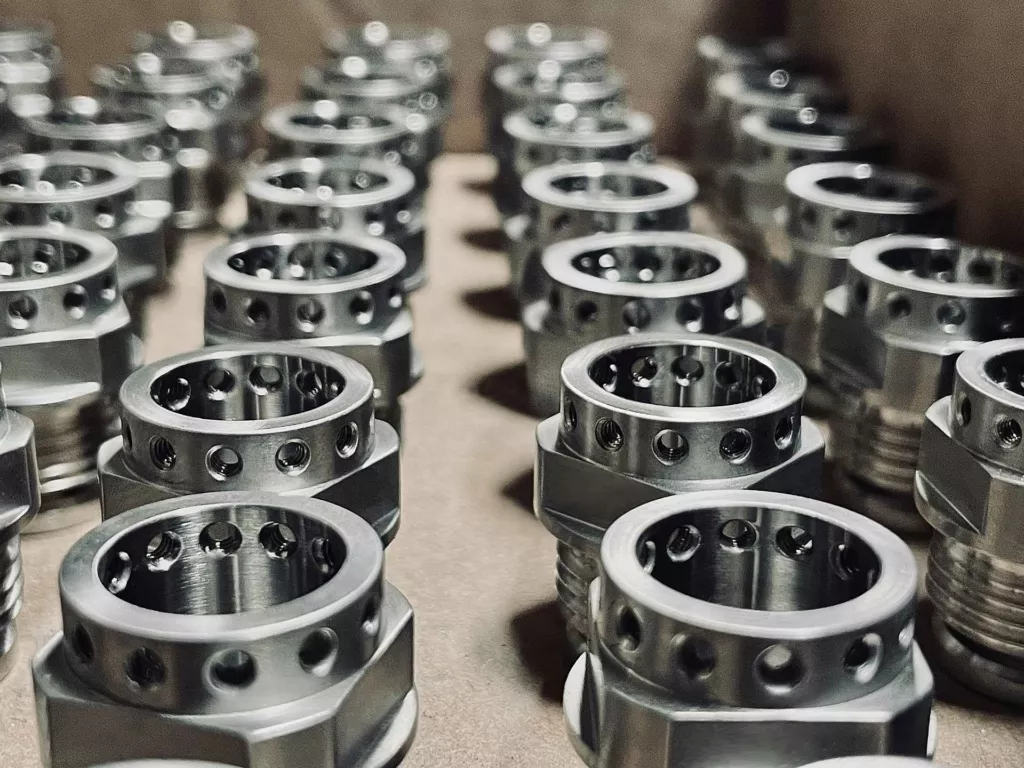
防衛請負業者は、トップス プレシジョンなどの専門会社に精密加工作業を委託することがよくあります。, 広範な CNC 機能を提供します, 含む フライス加工, 旋回, そして 放電加工 (放電加工).
ストウブの軍用グレードのコンポーネントの例としては、次のようなものがあります。:
アクチュエーターアーム 暗視ゴーグル用 (ワイヤー放電加工機).
ブレードカッター 安全ケーブル用 (5-軸CNC).
タレットの爪とロックコンポーネント (3-軸および4軸CNC).
ピボットボール 航空機用 (CNC旋削とスポット溶接).
プレナムベース 燃料の流れのために (ワイヤー放電加工機).
リリースクリップ 武器アセンブリ用 (3-軸CNC).
シェルレセプタクル 耐熱コネクタ用 (フライス加工).
これらの例は、小さなものからあらゆるものにわたる CNC 加工の多用途性を示しています。, 手持ち式軍事機器から大規模な航空宇宙および海軍システムまで.
結論
CNC 加工は、現代の防衛産業と軍事産業を支える最も重要な技術の 1 つです。. 極めて高い精度で部品を製造する能力, 再現性, 耐久性により、メーカーは航空宇宙特有の要求を満たすことができます。, レーダーシステム, 地上車両, 海軍艦艇, そして先進的な兵器.
防御を超えて, CNC テクノロジーは民生産業に影響を与え続けています, 現代のエンジニアリングと製造の基盤としての価値を証明. 軍事サプライヤー向け, 経験豊富な CNC 加工会社と提携することで、精度と信頼性だけでなく、進化する防衛上の課題に直面した際の費用対効果と革新性も確保します。.