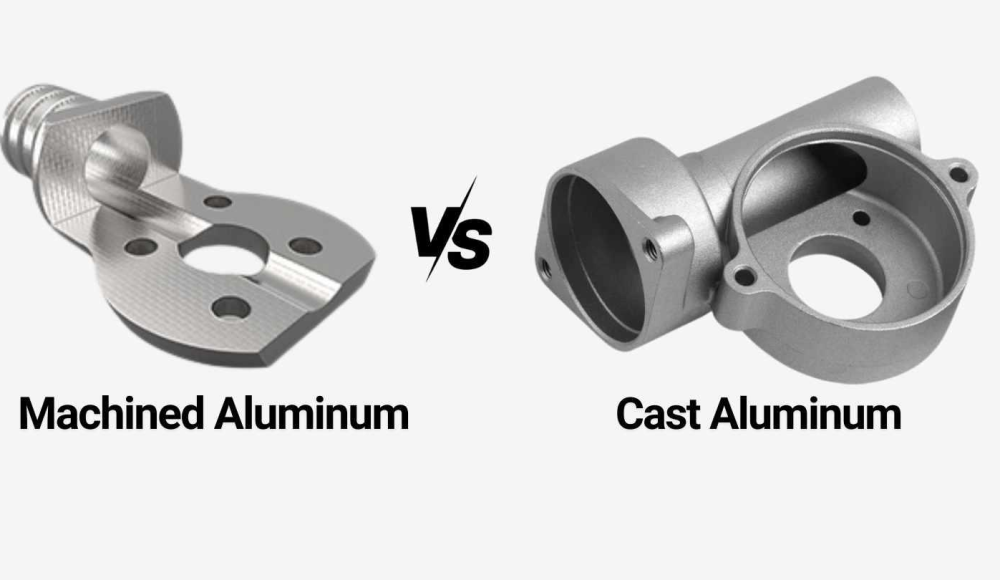
アルミニウム is one of the most widely used metals in modern manufacturing, valued for its lightweight, 耐食性, and excellent mechanical properties. When producing aluminum parts, two primary methods are commonly used—casting and machining. But how do they compare, and which one is best for your specific needs?
This article will explore the differences between cast aluminum and machined aluminum, their advantages, デメリット, and the factors to consider when choosing the right method for your project.
導入
Aluminum’s prominence in industries such as aerospace, 自動車, エレクトロニクス, and construction stems from its unique properties. The choice between casting and machining aluminum parts depends on factors like design complexity, 生産量, precision requirements, コストの考慮事項.
What is Machined Aluminum?
Definition and Process
Machined aluminum parts are created by removing material from a solid block of aluminum using cutting tools controlled by computer numerical control (CNC) 機械. This subtractive manufacturing process allows for high precision and is ideal for producing complex geometries with tight tolerances.
Common Machining Techniques
- CNCフライス加工: Involves rotating cutting tools to remove material from the workpiece, enabling the creation of intricate shapes and features.
- CNC旋削加工: The workpiece is rotated while a stationary cutting tool shapes it, which is commonly used for producing cylindrical parts.
- 掘削: Utilizes rotating drill bits to create precise holes in the aluminum workpiece.
- 研削: Employs abrasive wheels to achieve fine surface finishes and precise dimensions.
Industries That Use Machined Aluminum
- 航空宇宙: Components such as aircraft structural parts and housings.
- 自動車: エンジン部品, ヒートシンク, およびサスペンションコンポーネント.
- 医学: Surgical instruments and prosthetic devices.
- エレクトロニクス: Computer casings and precision connectors.
Machining is preferred in applications requiring high precision, 強さ, and excellent surface finishes.
What is Cast Aluminum?
Definition and Process
Cast aluminum parts are produced by pouring molten aluminum into molds, where it solidifies into the desired shape. This process is well-suited for creating complex geometries and is cost-effective for high-volume production runs.
Common Casting Methods
永久鋳型鋳造
- ダイカスト: Molten aluminum is injected under high pressure into steel molds, allowing for rapid production of precise parts.
- 真空ダイカスト: A vacuum assists in drawing molten aluminum into the mold, reducing air entrapment and improving part quality.
- インベストメント鋳造: Utilizes wax patterns to create molds for producing intricate and detailed components.
Expendable Mold Casting
- 砂型鋳造: Employs sand-based molds that are destroyed after each use, making it suitable for large parts and lower production volumes.
- Lost Wax Casting: Involves creating a wax model, coating it with a refractory material to form a mold, then melting away the wax and pouring in molten aluminum.
Industries That Use Cast Aluminum
自動車: エンジンブロック, トランスミッションのケース, と車輪.
工事: Architectural components and structural supports.
アプライアンス: Parts for stoves, washing machines, and kitchen equipment.
Casting is advantageous for producing complex shapes and is cost-effective for mass production.
Key Differences Between Machined and Cast Aluminum
| カテゴリ | アルミ削り出し | 鋳造アルミニウム |
| Material Types | Common alloys include 6061, 7075, そして 2024, known for their strength and machinability. | Typically uses alloys like A356, A380, そして A390, chosen for their casting properties and mechanical characteristics. |
| 生産速度 | Suitable for low to medium production volumes; setup is quick, but machining time increases with part complexity. | Efficient for high-volume production once molds are created; initial mold fabrication can be time-consuming and costly. |
| 表面仕上げ | Achieves smooth and customizable finishes directly from the machining process; additional polishing can enhance appearance. | May exhibit surface imperfections; often requires post-processing such as machining or polishing to achieve desired finish. |
| 精度 & 公差 | Capable of achieving tight tolerances, making it ideal for components where precision is critical. | Generally offers lower precision due to factors like mold wear and metal shrinkage during cooling; suitable for parts where exact tolerances are less critical. |
| 強さ & 耐久性 | Machined parts maintain the material’s inherent strength and are free from internal defects, providing high reliability. | Cast parts may contain porosity or inclusions, potentially reducing strength; しかし, they are adequate for many applications. |
| コストに関する考慮事項 | Higher cost per unit due to machining time and tool wear; no need for expensive molds, making it cost-effective for small batches or prototypes. | Lower cost per unit in mass production, but initial investment in mold creation is substantial; cost-effective for large quantities. |
| ベストアプリケーション | Ideal for aerospace components, 医療機器, and precision instruments where high accuracy and material integrity are paramount. | Suited for automotive parts, 消費財, and structural components where complex shapes and cost efficiency are prioritized over extreme precision. |
Pros and Cons of Machined Aluminum
長所
- 高精度: CNC machining allows for exact dimensions and tight tolerances, essential for critical applications.
- 優れた表面仕上げ: Produces parts with excellent surface quality, reducing the need for additional finishing processes.
- マテリアルの完全性: Maintains uniform material properties without internal defects, ensuring consistent performance.
- 柔軟性: Since no molds are needed, CNC machining can easily accommodate design modifications and small production runs.
- Wide Material Selection: A variety of aluminum alloys, including high-strength grades like 7075, can be used for machining.
短所
- Higher Cost for Large Production Runs: While great for small batches, CNC machining becomes expensive when scaling up due to extended production times and tool wear.
- 材料廃棄物: Since CNC machining is a subtractive process, a significant amount of material is cut away, leading to higher material costs compared to casting.
- Limited Design Complexity: While CNC machining can produce intricate shapes, some extremely complex geometries (such as internal cavities) are better suited for casting.
Pros and Cons of Cast Aluminum
長所
大量生産に向けたコスト効率の高い製品: Once the mold is made, casting enables high-volume production at a low per-unit cost.
Excellent for Complex Shapes: Cast aluminum can achieve intricate geometries that would be difficult or impossible to machine.
Lower Material Waste: Casting uses only the required amount of molten aluminum, 材料の無駄を最小限に抑える.
Good Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Cast aluminum components are strong enough for many applications while remaining lightweight.
短所
Lower Precision: Cast parts often require additional machining to meet tight tolerances.
表面の欠陥: 気孔率, 収縮, and rough textures can occur, requiring secondary finishing processes.
初期費用が高い: Creating molds for casting is expensive and time-consuming, making it less ideal for small production runs or prototyping.
When to Choose Machined Aluminum vs. 鋳造アルミニウム
| Requirement | 最良の選択 | Reason |
| 高精度 & 厳しい公差 | アルミ削り出し | CNC machining achieves superior accuracy, making it ideal for aerospace, 医学, そして精密工学. |
| 複雑な形状 & Intricate Shapes | 鋳造アルミニウム | Casting allows for highly complex designs that would be difficult to machine. |
| Small Production Runs | アルミ削り出し | No need for expensive molds; CNC machining is cost-effective for low-volume projects. |
| Large-Scale Manufacturing | 鋳造アルミニウム | Casting is more cost-effective for high-volume production. |
| 強い, High-Performance Parts | アルミ削り出し | Machining preserves material integrity, producing stronger and more reliable components. |
| Cost Efficiency for Simple Parts | 鋳造アルミニウム | Casting is more economical for producing basic components with minimal machining. |
結論
Both machined aluminum and cast aluminum have their place in manufacturing. CNC machining excels in precision, 強さ, および表面の品質, making it ideal for high-performance applications. 一方で, casting is the go-to choice for producing large quantities of complex parts at a lower cost.
Choosing the right method depends on your project’s requirements, 予算, および生産量. If you need high accuracy and strength, machining is the better option. If cost and design complexity are more important, casting is the way to go.
If you’re unsure which process best fits your needs, consulting with an expert manufacturer can help you make the right decision.
もっと詳しく知る & Get a Quote
For more information on CNC machining and aluminum casting, visit:
🔗 Xometry – CNC Machining Services
🔗 PHB Corp – Die Casting Explained
🔗 LeClaire Manufacturing – Sand Casting vs. ダイカスト
Would you like to add any additional details or modify specific sections? 😊