亜鉛ダイキャスティングは、精密な製造における基礎プロセスです, 例外的な次元精度を提供します, 強さ, および費用対効果. From automotive components to medical devices, zinc alloys are used to create durable and complex parts with excellent surface finishes and tight tolerances.
This comprehensive guide explores the key aspects of zinc die casting—from the working principles and methods to leading machines, alloy properties, common applications, and the numerous advantages that make zinc a top choice for high-performance components.
亜鉛ダイカストとは?
Zinc die casting is a manufacturing process in which molten zinc is injected under high pressure into steel molds (死ぬ) to form precise, 繰り返し可能な部品. Due to zinc’s relatively low melting point (~420–450°C) and superior castability, the process allows for thin-walled, 複雑な, and high-strength parts.
Zinc alloys used in die casting—such as Zamak and ZA series—are engineered for enhanced mechanical properties including wear resistance, 寸法安定性, そして靭性. These alloys allow for the creation of parts with fine features, 厳しい許容範囲 (±0.001 in / 0.0254 んん), and excellent surface finishes suitable for plating or painting.
Zinc Die Casting Methods
概要
Die casting techniques rely on high-pressure injection to achieve complete mold filling and precise replication of mold geometry. Zinc’s superior fluidity and low melting point make it ideal for this process, enabling intricate designs and high repeatability.
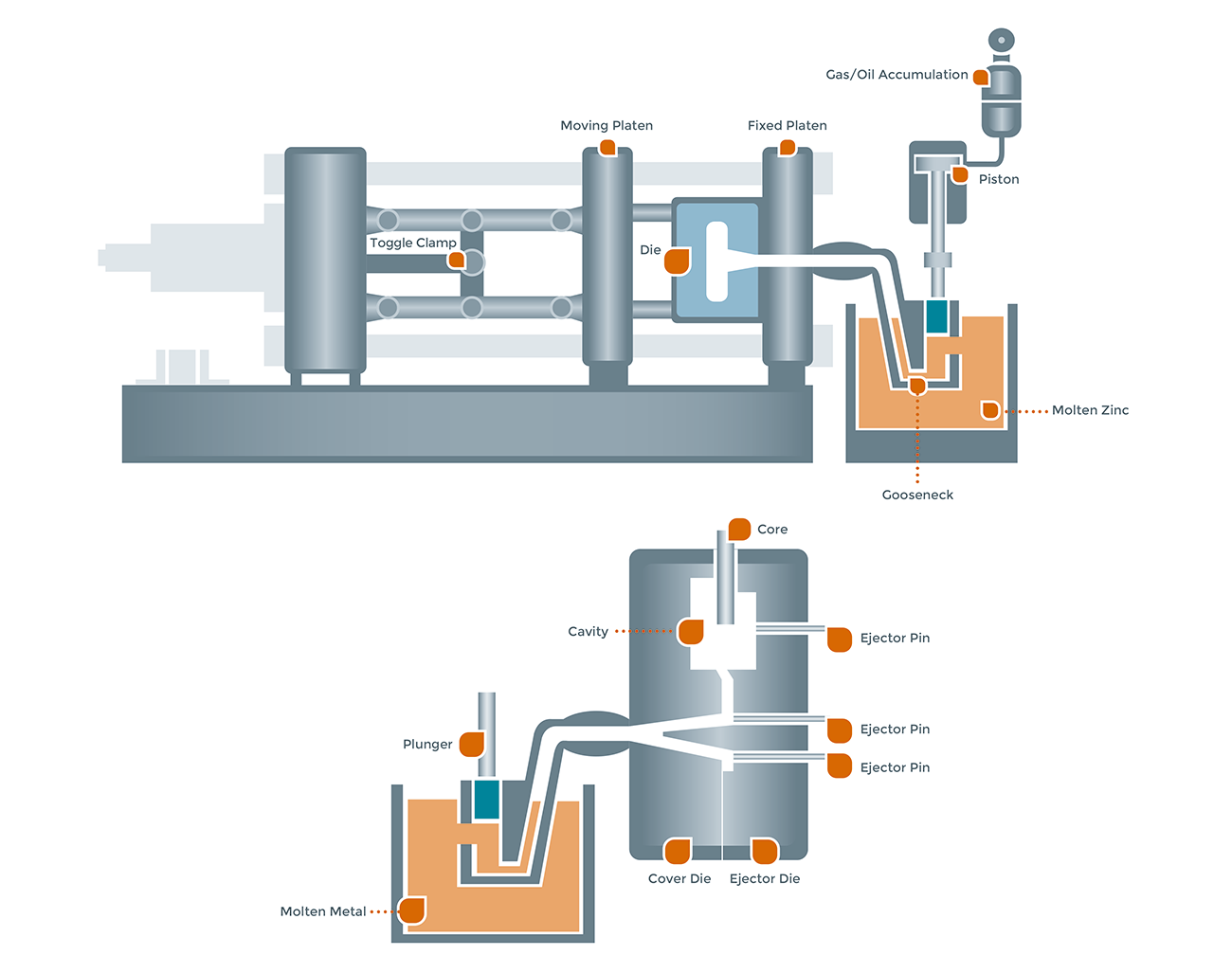
Hot Chamber Zinc Die Casting
Process Components:
Furnace: Integrated with the machine, continuously melting and feeding zinc alloy.
Gooseneck: Transfers molten zinc from the furnace to the die.
ノズル: Channels zinc into the die cavity.
Plunger: Provides injection force up to 5000 psi.
Die Types:
Single Die: For prototypes or small runs.
Multiple Die: For mass production, reduces cost per part.
Combination Die: Casts different parts in a single cycle.
Unit Die: Modular inserts for fast changeovers.
Process Steps:
Filling: Plunger draws molten zinc into the shot chamber.
注射: 高速, high-pressure injection into the die.
Pressure Hold: Maintains pressure during solidification.
冷却: Rapid heat dissipation for fast cycle times.
Ejection and Finishing: Part is ejected and finished via trimming, 研磨, またはコーティング.
Hot chamber casting is preferred for small to medium-sized parts requiring high volume and tight tolerances.
Cold Chamber Zinc Die Casting
Used when zinc alloys with higher melting points or special compositions are required.
コンポーネント:
Separate Furnace: External, provides better alloy control.
Shot Chamber: Preheated chamber minimizes defects.
Hydraulic Plunger: Forces molten zinc into the mold.
Process Steps:
ひしゃく: Zinc alloy is poured into the chamber.
注射: Hydraulic plunger injects zinc into the die.
冷却 & 排出: Mold cools and part is ejected.
仕上げ: Surface treatments as required.
Cold chamber casting is ideal for larger, denser components and provides more flexibility in alloy use.
Leading Zinc Die Casting Machines
High-performance die casting requires precision equipment. Below are notable machines used globally:
Urpe CC25
Integrated furnace, 42 kN force
Ideal for continuous production and mid-sized parts
Manual to fully automatic modes
Frech ZL60
Modular hot chamber system
Suits a wide range of part sizes
Real-time monitoring, エネルギー効率
BuhlerPrince HMT1600
Heavy-duty machine for industrial zinc castings
Large platen, closed-loop controls
Multi-stage injection system
Techmire ZDC-2000
Compact, multi-slide machine
Suited for high-mix, 低容量の実行
Exceptional speed and precision
Frech ZP 8
High-capacity hot chamber machine
Built-in die spraying and process control
Servo injection system
Each machine offers unique features in terms of clamping force, shot speed, オートメーション, and alloy compatibility.
Zinc Alloys Used in Die Casting
Zinc die casting alloys are engineered to deliver performance across diverse industrial applications. それらには以下が含まれます:
Zamak Series
重荷 2: High hardness and creep resistance.
重荷 3: Most common, excellent dimensional stability.
重荷 5: 強い, better corrosion resistance than Zamak 3.
ZA 8: 高級アルミニウム, used in hot chamber processes.
Specialty Alloys
ACuZinc5: High copper content for wear resistance.
EZAC: Developed for creep resistance and thermal stability.
ZA-12: Gravity or cold chamber suitable, for high-strength parts.
GDSL: Ultra-thin casting, wall thickness as low as 0.3 んん.
Selection depends on strength, 延性, 耐食性, creep performance, and application-specific requirements.
Applications of Zinc Die Casting
Zinc’s castability and strength allow its use across several industries:
自動車
Seat belt gears, door locks, airbag housings
Rearview mirror frames, windshield wipers
Structural brackets and transmission parts
医療機器
Housing for diagnostic tools
Gears and joints for surgical tables
EMI shielding in monitoring equipment
Locks and Hardware
Smooth finishes and high durability for tubular locks
Used in both commercial and residential security systems
エレクトロニクス
Enclosures with EMI/RFI shielding
Heat sinks with detailed integrated fins
Customized Components
Fully tailored designs with complex geometries
Thin-walled precision parts for assemblies
Advantages of Zinc Die Casting
Tooling Cost Efficiency
P20 steel used for zinc dies (対. H13 for aluminum), reducing cost
Die lifespan: 1,000,000+ shots—10x that of aluminum
Mechanical Performance
高強度, 剛性, and creep resistance
Strong impact resistance even at low temperatures
Dimensional Precision
公差: ±0.001 in
Wall thickness as low as 0.006 で (0.15 んん)
Negates need for machining in most cases
導電率
Excellent thermal and electrical performance
Suitable for shielding applications (EMI, RFI, ESD)
複雑な形状
Sharp edges, 薄い壁, integrated features
Perfect for functional-mechanical assemblies
優れた表面仕上げ
Ready-to-use surfaces with minimal secondary work
Compatible with chromating, 絵画, and plating
High Production Rate
150–200% faster cycle times than aluminum
Hot chamber process combines melting and injection
Efficient Assembly Integration
Combination dies for multi-part casting
Reduces labor and assembly steps
結論
Zinc die casting remains one of the most cost-effective and versatile manufacturing solutions in the industrial world. By leveraging the material’s low melting point, excellent castability, 機械的強度, and fine detail reproduction, industries can achieve high-volume, precision production at reduced costs.
Whether you’re sourcing lightweight automotive components, intricate electronic enclosures, or long-lasting structural elements, zinc die casting offers a unique blend of speed, 精度, and strength that few other processes can match.
For optimal results, manufacturers should select the right casting method (hot or cold chamber), appropriate alloy, and suitable machine. Partnering with experienced die casting providers ensures product quality, long-term performance, and competitive market positioning.
続きを読む:
キャスティングとダイ. CNC加工: Which Is Right for Your Part?
ホットチャンバー対. Cold Chamber Die Casting Comparison