A moagem de CNC pode parecer complexa, Mas em sua essência, É um maneira precisa e automatizada de remover o material de uma peça de trabalho usando uma roda de moagem rotativa. Neste guia abrangente, Vamos explorar a moagem do CNC em profundidade, incluindo sua história, princípios de trabalho, tipos de processos de moagem, materiais, indústrias que dependem disso, e as vantagens que ele oferece.
Introdução à moagem do CNC
O que é moagem de CNC?
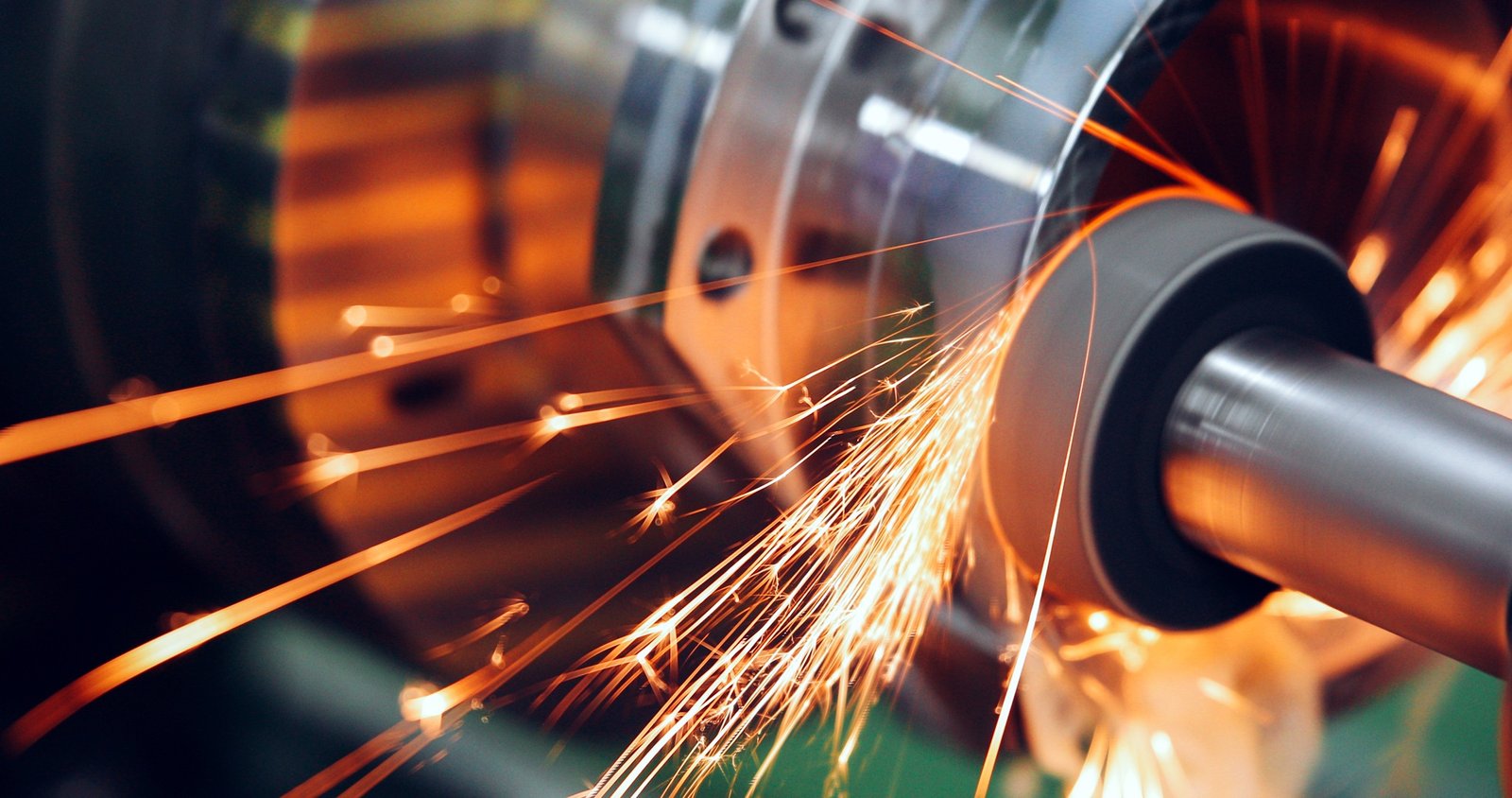
CNC (Controle Numérico Computadorizado) retificação é um processo de usinagem que usa um rebolo giratório de alta velocidade para remover material de uma peça de trabalho. Ao contrário da retificação manual convencional, A retificação CNC é automatizada, significando todos os aspectos do processo - como profundidade de corte, taxa de alimentação, e velocidade da roda - é controlada com precisão por programação de computador.
Por que o CNC está moendo importante?
- Garante extrema precisão e repetibilidade na usinagem.
- Produz Acabamentos de superfície superiores para componentes de alto desempenho.
- Capaz de lidar Materiais difíceis de máquinas, como titânio e cerâmica.
- Reduz erro humano, aumentando a eficiência e a produtividade.
A retificação CNC é usada em indústrias onde tolerâncias apertadas e finos acabamentos superficiais são críticos, tornando-o uma parte essencial da fabricação moderna.
História da moagem do CNC
Técnicas de moagem precoce
Antes da tecnologia CNC, moagem era feito manualmente usando pedras abrasivas e primeiras retificadoras. Esses métodos eram lentos, trabalho intensivo, e faltou precisão.
Inovação pós-Segunda Guerra Mundial
Depois da Segunda Guerra Mundial, indústrias como aeroespacial e automotiva precisavam usinagem de alta precisão para tecnologias avançadas. A introdução do controle numérico inicial (NC) máquinas abriram caminho para retificação automatizada.
Pioneiros de usinagem CNC
John T.. Parsons e Frank L.. Stulen foi fundamental no desenvolvimento da tecnologia CNC nas décadas de 1940 e 1950, lançando as bases para as atuais retificadoras CNC.
Avanços na moagem da CNC
- 1970década de 1980: Introdução de microprocessadores e controles digitais.
- 1990década de 2000: Integração CAD/CAM para programação automatizada.
- Hoje: Máquinas retificadoras CNC acionadas por IA e habilitadas para IoT melhoram a precisão e a eficiência.
Como funciona a moagem de CNC
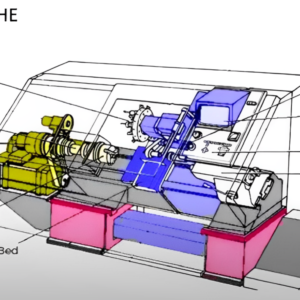
As principais partes de uma máquina de retificação de CNC
Antes de mergulharmos no processo, é importante entender os principais componentes que tornam possível a retificação CNC:
🔹 Rebolo – Esta é a ferramenta de corte que remove material da peça. Ele gira em alta velocidade e vem em diferentes formas e materiais, Dependendo do trabalho.
🔹 Sistema de controle CNC – Este é o cérebro da máquina, controlando cada movimento com extrema precisão. Segue um design pré-programado para orientar o processo de moagem.
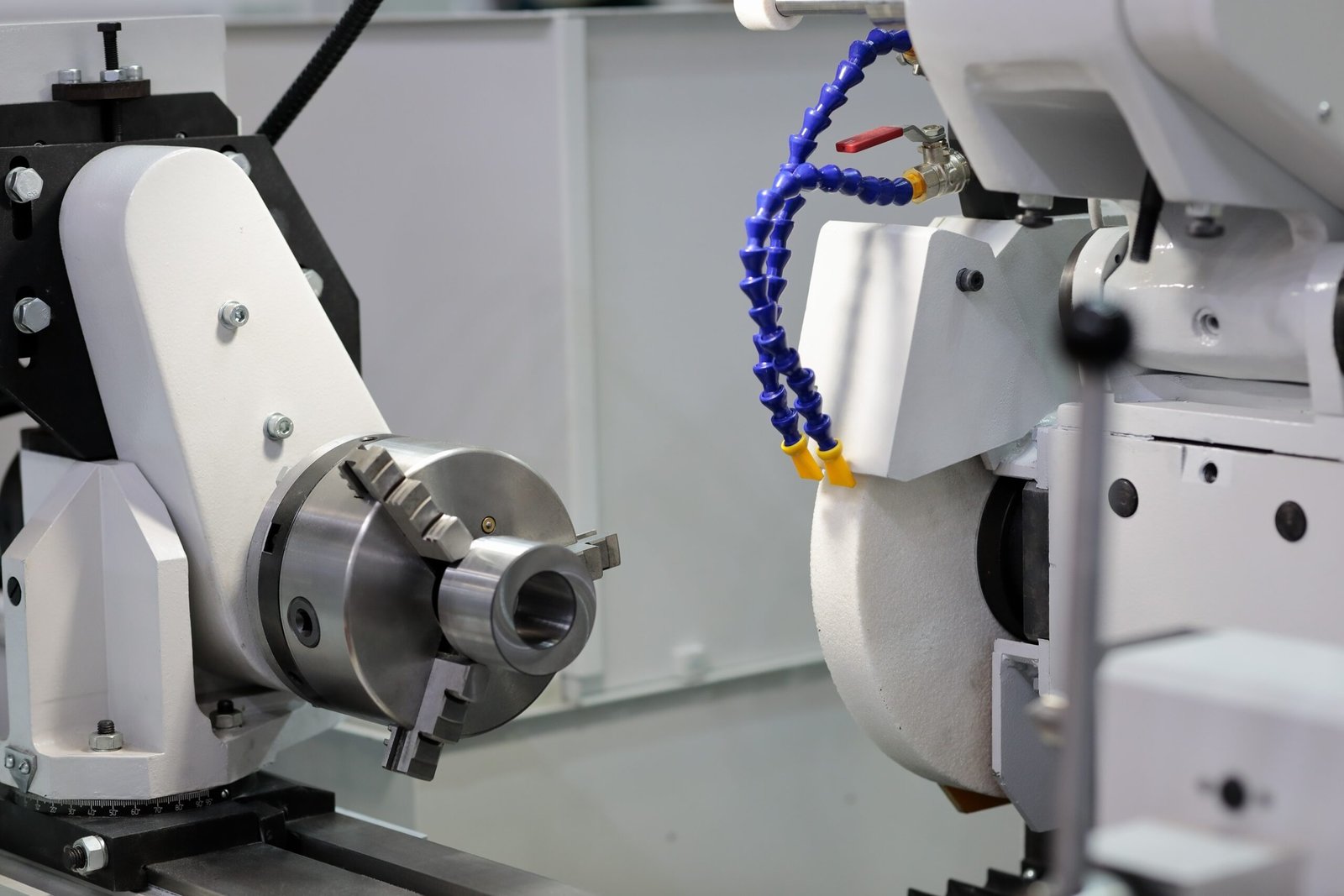
🔹 Fixação da peça - O mecanismo de retenção que mantém o material no lugar durante a moagem. Garante estabilidade e evita erros de movimento.
🔹 Sistema de refrigeração – Evita o superaquecimento e reduz o atrito, mantendo a área de moagem fria. Também ajuda a prolongar a vida útil da ferramenta.
🔹 Servomotores & Acionamentos de eixo - Esses mova o rebolo e a peça de trabalho em diferentes direções para obter a forma e o acabamento perfeitos.
Processo de retificação de CNC passo a passo
Etapa 1: Programando a máquina CNC
Tudo começa com um Blueprint digital. Um CAD (Design auxiliado por computador) o modelo da peça é criado, e o software CNC converte-o em um conjunto de instruções (Código G) para a máquina seguir.
✔ Define o caminho do rebolo.
✔ Define velocidades e profundidade de corte.
✔ Garante precisão automatizando movimentos.
💡 Pense nisso como fazer um bolo: A receita (Código G) diz à máquina exatamente o que fazer, passo a passo!
Etapa 2: Protegendo a peça de trabalho
O material que precisa ser lixado é preso no lugar para impedir o movimento. A dispositivo elétrico forte e estável garante precisão, para que o rebolo possa remover o material com precisão.
✔ Evita vibrações e erros.
✔ Mantém a peça firmemente no lugar.
💡 Imagine tentar fatiar um tomate em uma tábua instável – você precisa de estabilidade para cortes perfeitos!
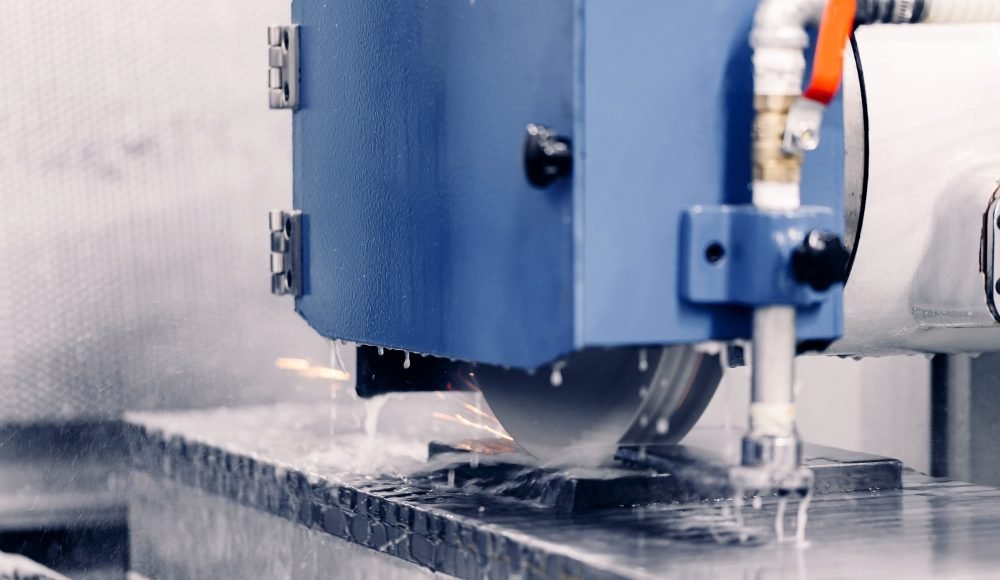
Etapa 3: A moagem começa
O sistema CNC agora move o rebolo em direção à peça de trabalho na velocidade e ângulo certos. Como a roda gira em alta velocidade, remove pequenos pedaços de material, moldar a peça de trabalho de acordo com o projeto programado.
✔ O rebolo pode se mover lado a lado, para cima e para baixo, e para frente/para trás.
✔ Algumas retificadoras CNC podem até girar a peça para 360-moagem de grau.
✔ O material é removido camada por camada, garantindo um acabamento suave e preciso.
💡 Pense nisso como lixar madeira – mas muito mais preciso e controlado!
Etapa 4: Resfriamento e Lubrificação
A moagem gera Muito calor devido ao atrito. Para proteja a peça de trabalho e o rebolo, refrigerantes e lubrificantes são pulverizados na área de moagem.
✔ Reduz o superaquecimento e evita a distorção do material.
✔ Mantém o rebolo afiado e eficaz.
✔ Melhora o acabamento superficial final.
💡 Assim como o motor de um carro precisa de refrigerante para evitar superaquecimento, As retificadoras CNC usam refrigerantes para se manterem em ótima forma!
Etapa 5: Inspeção e acabamento final
Assim que a moagem estiver concluída, a parte é medido e inspecionado para ter certeza de que atende às especificações exigidas.
✔ Se a peça corresponde ao projeto, é bom ir! 🎉
✔ Se ajustes são necessários, a máquina CNC pode fazer pequenas correções.
✔ Algumas peças sofrem adicional polimento ou tratamento térmico Para durabilidade extra.
💡 Pense nisso como o controle de qualidade em uma fábrica – cada produto deve passar pela verificação final antes do envio!
Principais tipos de processos de moagem CNC
Moagem de superfície - para superfícies perfeitamente planas
🔹 Melhor para: Criando suave, superfícies planas em metal, cerâmica, e materiais compósitos.
🔹 Como funciona:
✔ Uma rotação Roda de moagem se move sobre a superfície da peça de trabalho, raspar camadas minúsculas para torná -lo perfeitamente suave.
✔ A peça de trabalho é mantido no lugar em uma mesa magnética ou acessório enquanto a roda se move para frente e para trás.
✔ A máquina garante alta precisão, fazendo peças exatamente nivelado e livre de pontos difíceis.
🔹 Onde é usado:
✅ Automotivo - blocos de motor, componentes de freio.
✅ Tool & Die a fazer - morre de precisão, ferramentas de corte.
✅ Máquinas industriais - peças de máquina plana, placas de metal.
💡 Pense nisso como lixar uma mesa de madeira, mas com extrema precisão!
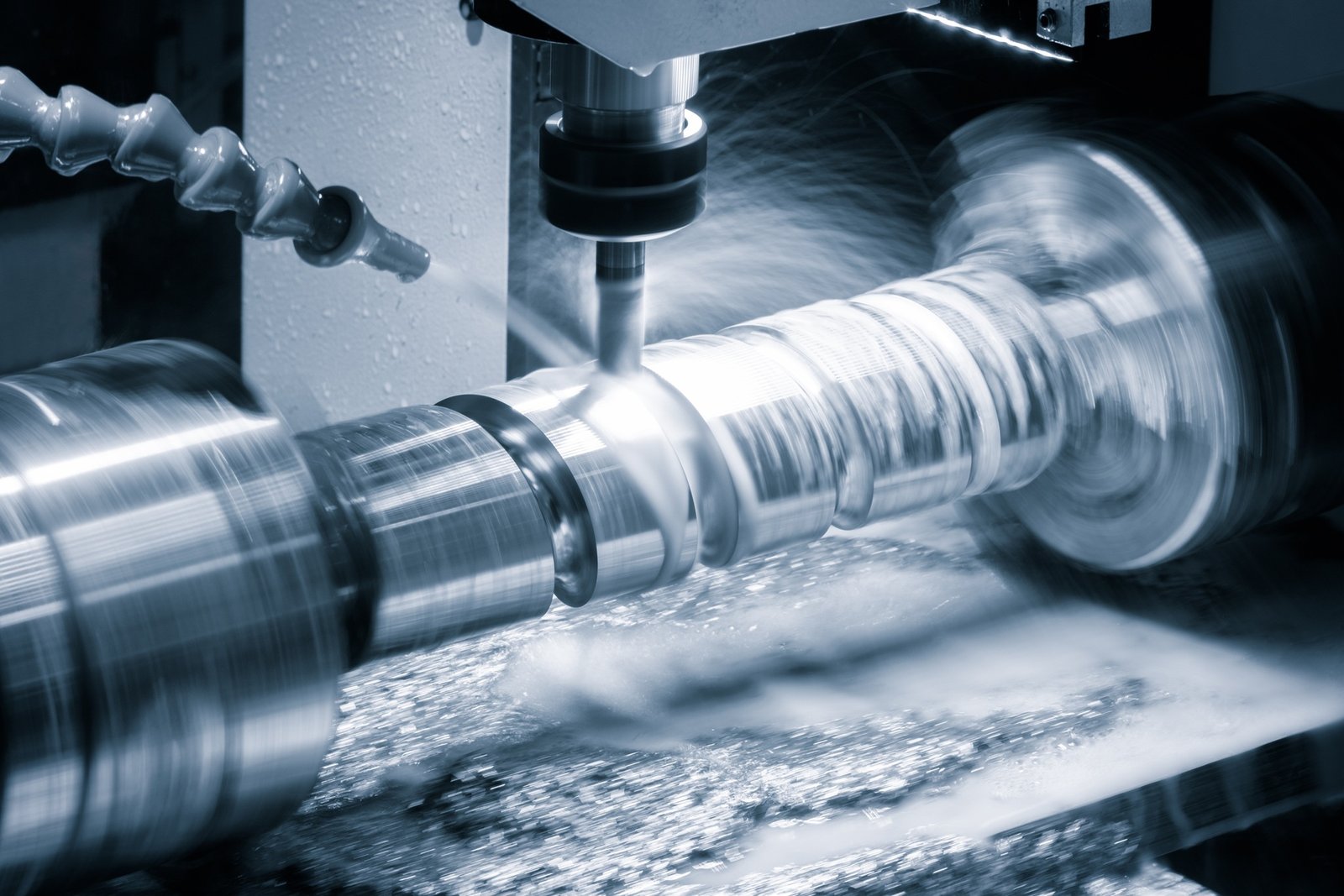
Rotagem cilíndrica - para peças perfeitamente redondas
🔹 Melhor para: Modelagem objetos cilíndricos como eixos, varas, e rolamentos.
🔹 Como funciona:
✔ A peça de trabalho gira Enquanto a roda de moagem se move através de sua superfície.
✔ Isso garante um uniforme, forma circular com um acabamento incrivelmente suave.
✔ Os controles CNC permitem Ajustes precisos de diâmetro até a menor fração de um milímetro.
🔹 Onde é usado:
✅ Aeroespacial – Eixos de motores de aeronaves.
✅ Automotivo – Eixos de transmissão, pistões.
✅ Industrial – Cilindros Hidráulicos, rolos de rolamento.
💡 Imagine apontar um lápis uniformemente por todos os lados – é assim que funciona o desbaste cilíndrico!
Moagem sem centro - mais rápida e mais eficiente
🔹 Melhor para: Produção de alta velocidade de pequeno, peças redondas como alfinetes, parafusos, e buchas.
🔹 Como funciona:
✔ Ao contrário da retificação cilíndrica, a peça de trabalho não é mantido no lugar por uma braçadeira ou acessório.
✔ Em vez disso, é apoiado por um lâmina de descanso de trabalho e guiado entre um Roda de moagem e a roda reguladora.
✔ A roda reguladora controla a velocidade e alimentação, garantindo tamanho e forma consistentes.
🔹 Onde é usado:
✅ Produção em massa – Pequenas peças metálicas, pinos de precisão.
✅ Automotivo – Injetores de combustível, componentes da válvula.
✅ Médico – Pinos cirúrgicos, pequenas peças de implante.
💡 Pense em um cachorro-quente rolando em uma grelha – é assim que a moagem sem centro mantém as peças em movimento enquanto as tritura uniformemente!
Rotagem interna - para orifícios precisos e superfícies internas
🔹 Melhor para: Esmerilhamento dentro uma parte oca, como tubos, rolamentos, e cilindros do motor.
🔹 Como funciona:
✔ Um pequeno Roda de moagem está inserido no diâmetro interno da peça de trabalho.
✔ A roda entra e sai, moldando a superfície interna para precisão perfeita.
✔Ideal para peças que devem se encaixar perfeitamente, como caixas de rolamentos ou cilindros hidráulicos.
🔹 Onde é usado:
✅ Aeroespacial – peças para motores a jato.
✅ Automotivo – Furos de cilindro, cubos de engrenagem.
✅ Médico – Tubo médico de precisão.
💡 Pense nisso como usar um mini tambor de lixa dentro de um cano para alisar as paredes!
Moagem de engrenagem - Criando dentes de engrenagem de precisão
🔹 Melhor para: Fazendo engrenagens de alta precisão para motores, transmissões, e máquinas.
🔹 Como funciona:
✔ Um rebolo especializado molda cada dente da engrenagem.
✔ O processo garante tamanho exato do dente, espaçamento, e ângulos, evitando ruído e vibração.
✔ Produz engrenagens que dure mais e funcione com mais suavidade.
🔹 Onde é usado:
✅ Automotivo – Transmissões de carros e caminhões.
✅ Industrial – Maquinaria Pesada, Robótica.
✅ Aeroespacial – Trem de pouso de aeronaves, turbinas.
💡 Pense nisso como afiar uma lâmina de serra, mas muito mais preciso e durável!
Moagem de alimentação de fluência - para profundo, Cortes pesados
🔹 Melhor para: Removendo grandes quantidades de material em uma única passagem.
🔹 Como funciona:
✔ Usa um taxa de alimentação muito lenta mas um profundidade de moagem profunda para cortar materiais resistentes.
✔ Ideal para Materiais difíceis de máquinas Como titânio, Inconel, e aço ferramenta.
✔ Produz menos calor e estresse, evitando que os materiais se deformem ou quebrem.
🔹 Onde é usado:
✅ Aeroespacial – Lâminas de turbina, componentes de aeronaves.
✅ Médica – Próteses, implantes ortopédicos.
✅ Energia – Peças da usina, componentes de turbinas eólicas.
💡 Pense nisso como usar um cinzel para esculpir grandes seções em vez de raspar pequenas camadas!
Griping de gabarito - para orifícios e contornos super precisos
🔹 Melhor para: Modelagem de furo ultraprecisa e acabamentos de superfície afinados.
🔹 Como funciona:
✔ Usa um de alta velocidade, rebolo pequeno fazer pequenos ajustes para a forma de uma peça.
✔ Frequentemente usado para Bolores, morre, e componentes aeroespaciais.
✔ pode alcançar tolerâncias extremamente apertadas (até ±0,001mm!).
🔹 Onde é usado:
✅ Tool & Fabricação de Matrizes – Moldes de Injeção, Stamping morre.
✅ Aeroespacial – Componentes de motor de precisão.
✅ Eletrônica – Peças micromecânicas, Componentes semicondutores.
💡 Imagine esculpir com um lápis afiado a laser – trata-se de detalhes e precisão extremos!
Qual processo de retificação do CNC é adequado para você?
Aqui está uma comparação rápida para ajudá-lo a decidir:
| Tipo de moagem | Melhor para | Benefício principal |
| Moagem de superfície | Superfícies planas | Suave, acabamento preciso |
| Retificação Cilíndrica | Peças redondas (veios, rolos) | Alta precisão, forma uniforme |
| Moagem sem centro | Pequenas peças redondas (alfinetes, parafusos) | Rápido, produção em alto volume |
| Moagem Interna | Dentro de furos e tubos | Preciso, superfícies internas lisas |
| Moagem de engrenagens | Engrenagens para motores/máquinas | Corte perfeitamente os dentes da engrenagem |
| Moagem de alimentação lenta | Metais rígidos, cortes profundos | Remove grandes quantidades de material |
| Moagem de gabarito | Pequeno, ajustes detalhados | Precisão ultra-alta (±0,001 mm) |
Materiais usados na moagem CNC
Seja metal, plástico, cerâmica, ou mesmo materiais compósitos, A retificação CNC pode moldá-los com alta precisão e acabamentos superficiais perfeitos.
Mas nem todos os materiais são igualmente fáceis de lixar – alguns são macios e fáceis de moldar, enquanto outros são superduros e requerem rebolos especiais.
Metais - os materiais mais comuns para a moagem CNC 🏗️
Os metais são de longe os materiais mais utilizados na retificação CNC. Eles são fortes, durável, e usado em quase todos os setores, da indústria aeroespacial a dispositivos médicos.
Aqui está uma análise dos metais mais comumente moídos:
🔹 Aço - forte e confiável
✔ Usado em: Automotivo, aeroespacial, maquinaria industrial
✔ Tipos: Aço carbono, aço inoxidável, aço para ferramentas
✔ Por que é usado:
✅ Super forte e durável.
✅Pode ser tratado termicamente para maior resistência.
✅ Versátil – usado em tudo, desde engrenagens até ferramentas cirúrgicas.
⚠️ Desafio: Aços mais duros desgastar os rebolos rapidamente.
💡 Pense no aço como o “burro de carga” da manufatura – ele está em toda parte!
🔹 Aço inoxidável-resistente e resistente à corrosão
✔ Usado em: Dispositivos médicos, processamento de alimentos, peças marítimas
✔ Por que é usado:
✅Não enferruja nem corrói.
✅Ótimo para higiênico aplicações (como ferramentas médicas).
✅Pode ser polido até acabamento espelhado.
⚠️ Desafio: Aço inoxidável endurece o trabalho, tornando difícil moer.
💡 Imagine tentar lixar um material super resistente, superfície brilhante - isso é aço inoxidável!
🔹 Alumínio - leve e fácil de moer
✔ Usado em: Aeroespacial, automotivo, eletrônicos
✔ Por que é usado:
✅ Macio e fácil de usinar.
✅Não enferruja.
✅Pode ser polido até acabamento suave.
⚠️ Desafio: A suavidade pode levar ao entupimento dos rebolos.
💡 Se o aço é o campeão dos pesos pesados, o alumínio é o atleta ágil – leve e rápido!
🔹 Titanium - super forte, mas difícil de moer
✔ Usado em: Aeroespacial, implantes médicos, veículos de alto desempenho
✔ Por que é usado:
✅ Incrivelmente forte, mas leve.
✅ Altamente resistente ao calor.
✅ Usado em aplicações críticas onde o fracasso não é uma opção.
⚠️ Desafio: O titânio tem baixa condutividade térmica, Então isso aquece rapidamente, dificultando a moagem.
💡 Pense no titânio como um metal de super-herói – forte, mas precisa de manuseio especial!
🔹 Cobre & Latão – Macio e Suave
✔ Usado em: Componentes elétricos, encanamento, peças decorativas
✔ Por que é usado:
✅ Excelente condutividade (usado em peças elétricas).
✅ Fácil de moer e forma.
✅Pode ser polido até Alto brilho.
⚠️ Desafio: Materiais macios como latão podem obstruir os rebolos.
💡 Afiar latão é como afiar um lápis macio – é fácil, mas requer um toque cuidadoso!
Cerâmica – Dura, mas Frágil 🏺
Cerâmica são incrivelmente difícil, tornando-os ótimos para resistente ao desgaste peças, mas eles também são frágil e pode rachar se não for manuseado com cuidado. A retificação CNC é uma das apenas maneiras de moldá-los com precisão.
🔹 Cerâmica comum usada em retificação CNC:
✔ Alumina (Óxido de Alumínio) – Usado em eletrônica e ferramentas de corte.
✔ Carboneto de Silício – Encontrado em aplicações de alta temperatura e abrasivos.
✔ Zircônia – Usada em implantes médicos e coroas dentárias.
💡 Pense na cerâmica como o vidro – superduro, mas pode quebrar se você não tomar cuidado!
Plásticos – fáceis de moer, mas sensíveis ao calor 🔬
Os plásticos são comumente usados em médico, automotivo, e eletrônicos de consumo, Mas eles têm que ser terra na velocidade certa para Evite derreter.
🔹 Plásticos comuns para retificação CNC:
✔ Policarbonato - forte, resistente a impactos, usado em equipamentos de proteção.
✔ Acrílico - usado em lentes e displays ópticos.
✔ PTFE (Teflon) -baixo atrito, usado em aplicações médicas e industriais.
💡 Moer plásticos é como cortar manteiga com uma faca quente - muito calor, e derrete!
Materiais Compósitos – O Melhor dos Dois Mundos 🔗
Compostos se combinam Dois ou mais materiais Para criar algo ainda melhor. Eles são forte, leve, e resistente ao calor, mas eles Use ferramentas de moagem rapidamente.
🔹 Exemplos de materiais compósitos:
✔ Fibra de carbono - super forte, usado em equipamentos aeroespaciais e esportivos.
✔ Fibra de vidro - usado em barcos, carros, e materiais de construção.
💡 A moagem de compósitos é complicada - como tentar marcar metal e plástico ao mesmo tempo!
Metais Exóticos e Preciosos – Alto Valor, Alta Precisão 💎
Algumas indústrias, como joia, eletrônicos, e aeroespacial, requer a moagem de cru, metais caros.
🔹 Metais preciosos comuns:
✔ Ouro - usado em eletrônicos e detalhes finos.
✔ Prata - Ótimo para condutividade elétrica.
✔ Platina - encontrada em implantes médicos e jóias.
💡 Esses materiais são caros, Então, todo pouquinho de resíduos importantes!
Qual material é certo para você?
Aqui está um rápido comparação de diferentes materiais de moagem CNC:
| Material | Força | Facilidade de moagem | Uso comum |
| Aço | 🟢 Super Strong | 🔴 Difícil de moer | Engrenagens, ferramentas, aeroespacial |
| Alumínio | 🟡 Leve | 🟢 Fácil de moer | Automotivo, eletrônicos |
| Titânio | 🔴 ULTRA-FLONG | 🔴 Difícil de moer | Implantes médicos, aeroespacial |
| Latão & Cobre | 🟢 Soft & suave | 🟢 Muito fácil | Elétrica, encanamento |
| Cerâmica | 🔴 extremamente difícil | 🟡 precisa de moagem especial | Médico, eletrônicos |
| Plásticos | 🟡 Flexível & sensível ao calor | 🟢 Fácil (Mas assista ao calor!) | Médico, automotivo |
| Compósitos | 🟢 forte & leve | 🔴 Hard to Moafing Tools | Aeroespacial, equipamento esportivo |
| Metais preciosos | 🟢 Valioso & resistente à corrosão | 🟡 Reting de delicada necessária | Joia, eletrônicos de ponta |
Indústrias que usam retificação CNC
🏭 Aeroespacial - Blades de turbina, Componentes do trem de pouso.
🚗 Automotivo - Peças do motor, engrenagens, componentes de freio.
⚕️ Dispositivos médicos - Ferramentas cirúrgicas, implantes, próteses.
🔬 Eletrônicos - As bolachas semicondutoras, micro-componentes.
🔧 Ferramenta & Die Making - Moldes, ferramentas de corte, morre.
Vantagens da retificação CNC
Precisão e exatidão insanas 🎯
Um dos o maior vantagens da moagem do CNC é o seu super alta precisão. Ao contrário da moagem manual, o que depende da habilidade do operador, A moagem do CNC é controlado por computador, garantindo Precisão perfeita todas as vezes.
✅ pode segurar tolerâncias tão apertadas quanto ± 0,001 mm - Isso é mais fino que um cabelo humano!
✅ Cria perfeito, acabamentos suaves sem arestas ou imperfeições.
✅ Ideal para Indústrias de alta precisão como aeroespacial, médico, e automotivo.
💡 Se você precisar de peças que se encaixam perfeitamente, A moagem de CNC é a sua melhor aposta!
Super Consistente e Repetível 🔄
Já tentou cortar algo à mão e obter duas peças que não combinam? Que nunca acontece com moagem CNC!
✅ Cada parte sai exatamente o mesmo, seja é o primeiro ou o 10.000º peça.
✅ Não erros humanos - A máquina segue perfeitamente as instruções programadas.
✅Ótimo para produção em massa onde a consistência é fundamental.
💡 Imagine fazer 1,000 engrenagens, tudo idêntico até o micrômetro – a retificação CNC torna possível!
Lida com materiais duros e resistentes 💪
Alguns materiais, como titânio e cerâmica, são super difícil e pode destruir ferramentas de corte normais. Mas retificação CNC? Sem problemas!
✅Pode moer Aço endurecido, carboneto, titânio, e até vidro.
✅Funciona em materiais resistentes ao calor e resistentes ao desgaste com as quais outras ferramentas lutam.
✅ Usos rebolos especiais para cortar os materiais mais duros com facilidade.
💡 Se outros métodos de usinagem tiverem dificuldades, A retificação CNC pode lidar com o desafio!
Funciona para formas complexas e pequenos detalhes 🛠️
A retificação CNC não é apenas para superfícies planas ou peças simples-pode criar intrincado, formas detalhadas que outras máquinas não podem.
✅Pode moer furos internos, superfícies curvas, e pequenos sulcos com extrema precisão.
✅ Perfeito para ferramentas personalizadas, implantes médicos, e peças aeroespaciais complexas.
✅ Usos técnicas de moagem especializadas como retificação centerless para formatos exclusivos.
💡 Se sua peça tiver ângulos estranhos, tolerâncias apertadas, ou curvas complexas, A retificação CNC pode fazer isso acontecer!
Alta velocidade e eficiência ⚡
Retificação CNC automatiza o processo, o que significa que as peças são feitas mais rápido e com menos desperdício.
✅ Não há necessidade de ajustes constantes – basta configurar o programa e deixá-lo rodar.
✅ Reduz tempo de configuração e trabalho humano, reduzindo custos de produção.
✅Pode lidar múltiplas operações de retificação em uma configuração, economizando tempo.
💡 Mais velocidade + mais eficiência = custos mais baixos e prazos de entrega mais rápidos!
Menos desgaste das ferramentas = custos mais baixos 💰
Ferramentas de corte tradicionais desgastar rápido, especialmente em metais duros. Mas rebolos em retificação CNC durar muito mais tempo porque são feitos para trabalhos de alta resistência.
✅ Os rebolos são projetado para durabilidade, significado menos substituições.
✅ Não acúmulo excessivo de calor, reduzindo danos à ferramenta e à peça.
✅ Menos desperdício = mais economia de custos a longo prazo.
💡 Os rebolos são como corredores de maratona – duram muito mais do que as ferramentas de corte normais!
Funciona em uma ampla variedade de materiais 🌍
A retificação CNC não se limita apenas metais- ele pode lidar plásticos, cerâmica, compósitos, e até vidro.
✅Funciona em macio, frágil, ou materiais ultraduros.
✅Pode moer ligas resistentes ao calor usadas em aplicações aeroespaciais e médicas.
✅ Ideal para materiais delicados que exigem suavidade, cortes precisos.
💡 Quer seja alumínio, fibra de carbono, ou aço endurecido, A retificação CNC dá conta do recado!
Melhor acabamento superficial = não é necessário trabalho extra ✨
Um grande bônus da retificação CNC é o acabamento super suave isso cria. Muitas peças saem pronto para usar, sem polimento ou acabamento extra.
✅ Folhas semelhante a um espelho superfícies com rugosidade zero.
✅ Reduz a necessidade de etapas de acabamento secundário, economizando tempo e dinheiro.
✅ Perfeito para peças estéticas ou componentes de alto desempenho que precisam de uma superfície impecável.
💡 Se suas peças precisam ter aparência E funcionar perfeitamente, A retificação CNC é o caminho a percorrer!
Pode ser totalmente automatizado = menos mão de obra necessária 🤖
As retificadoras CNC podem ser totalmente automatizado, o que significa que eles correr 24/7 com supervisão mínima.
✅Pode ser integrado à robótica Para linhas de produção totalmente automatizadas.
✅ Reduz a dependência de operadores qualificados, cortando custos de mão -de -obra.
✅ pode ser executado durante a noite ou durante os fins de semana para maximizar a produtividade.
💡 Deixe as máquinas fazer o trabalho enquanto você se concentra na inovação!
Retificação CNC vs.. Moagem Tradicional – Uma Comparação Rápida
| Recurso | Retificação CNC ✅ | Moagem tradicional ❌ |
| Precisão 🎯 | ±0,001 mm (super preciso) | Depende da habilidade do operador |
| Consistência 🔄 | 100% repetível | Pequenas variações possíveis |
| Velocidade ⚡ | Rápido e automatizado | Mais devagar, Ajustes manuais necessários |
| Opções de material 🔩 | Funciona em metais duros, cerâmica, compósitos | Melhor para materiais mais suaves |
| Desgaste da ferramenta 🛠️ | Rodas de moagem duram mais | Ferramentas de corte se desgastam mais rápido |
| Acabamento da superfície ✨ | Acabamento semelhante ao espelho | Pode precisar de polimento extra |
| Complexidade 🏗️ | Pode criar complexo, formas complexas | Melhor para formas mais simples |
| Custos de mão -de -obra 💰 | Totalmente automatizado, baixos custos de mão -de -obra | Requer operadores qualificados |
Fatores de custo em retificação CNC
💰 Custo da máquina:
- Máquinas de nível básico: $10,000+
- Máquinas de gama média: $50,000- US $ 200.000
- Máquinas de precisão de ponta: $500,000+
⏳ Fatores de tempo:
- Peças simples: Alguns minutos por peça.
- Partes complexas: Várias horas para moagem complexa.
Projeto & Dicas operacionais para retificação CNC
🔹 Escolha a roda de moagem certa - Selecione com base na dureza do material.
🔹 Otimizar a taxa de alimentação & Velocidade - impedir o desgaste da ferramenta e superaquecimento.
🔹 Use refrigerantes & Lubrificantes - Aprimore a vida da ferramenta e a qualidade da superfície.
🔹 Manutenção regular da máquina -garantir precisão e desempenho a longo prazo.
🔹 Evite designs excessivamente complexos - Simplifique as geometrias para usinagem eficiente.
Conclusão
A moagem de CNC é um processo essencial na fabricação moderna, fornecendo precisão incomparável, eficiência, e repetibilidade. Seja para aeroespacial, automotivo, ou aplicações médicas, A moagem de CNC garante a produção de componentes de alta qualidade que atendem a tolerâncias estritas.
Ao entender o processo, materiais, e fatores de custo envolvidos, Os fabricantes podem otimizar suas operações de moagem para máxima eficiência e produtividade.
Perguntas frequentes
1️⃣ Como você pode melhorar a eficiência da moagem do CNC?
Manter regularmente a máquina, Use técnicas adequadas, Escolha a roda de moagem certa, e otimize os parâmetros de corte para obter os melhores resultados.
2️⃣ Quanto tempo leva o processo de moagem do CNC?
A velocidade de moagem depende da dureza do material, velocidade do fuso (12,000-24,000 RPM), e profundidade de corte, com tarefas simples levando minutos e peças complexas levando horas.
3️⃣ Quanto custa uma máquina de moagem CNC?
Modelos básicos começam em $10,000, enquanto as máquinas de precisão de ponta podem exceder $500,000, com custos adicionais para manutenção, ferramentas, e software.
4️⃣ Quais são as principais especificações de uma máquina de moagem CNC?
As especificações típicas incluem o tamanho da tabela (200mm × 500mm+), velocidade do fuso (1400-24,000 RPM), Tamanho da roda de moagem (355 × 40 × 127mm), e energia motor (750W-5000W).
5️⃣ Quais são os diferentes tipos de moagem de CNC?
Os principais tipos incluem moagem de superfície (Peças planas), Moagem cilíndrica (veios), Moagem sem centro (produção em massa), Moagem interna (orifícios de precisão), e moagem de ferramentas (Ferramentas de resharpening). 🚀
Links externos recomendados (Backlinks para aprendizado adicional)
Visão geral da moagem do CNC - https://www.mmsonline.com/articles/the-evolution-of-cnc-grading
Tipos de rodas de moagem - https://www.nortonabrasives.com/en-us/Grinding-wheels
Análise de custo de moagem CNC - https://www.thefabricator.com/the-ins-ands-of-cnc-grinding
Materiais usados na moagem de precisão - https://www.engineeringclicks.com/materials-in-grinding
Moagem de superfície vs.. Retificação Cilíndrica - https://www.machinemfg.com/grinding-machine-types-and-uses






9 pensamentos "Retificação CNC: O guia final para usinagem de precisão”