Prototipagem rápida revolucionou a maneira como os produtos são desenvolvidos, ajudando empresas e inovadores a passar rapidamente do conceito para modelos prontos para produção. Serve como uma etapa inestimável no desenvolvimento de produtos, permitindo avaliação rápida de projetos, facilitando melhorias, e minimizando o risco antes do início da fabricação em grande escala.
Os principais benefícios da prototipagem rápida incluem cronogramas de desenvolvimento acelerados, custos reduzidos, e maior precisão do produto. Selecionar o método correto de prototipagem rápida pode influenciar diretamente o sucesso e a eficiência do seu projeto.
O que é um protótipo?
Um protótipo é um modelo preliminar ou amostra de um produto construído com a finalidade de testar um projeto., conceito, ou funcionalidade. Os protótipos desempenham várias funções essenciais:
Prova de conceito: Protótipos verificam se uma ideia de design é viável, prático, e atende aos objetivos pretendidos.
Validação de Projeto: Permite que designers e engenheiros identifiquem falhas, refinar a estética, e aprimorar a funcionalidade no início do processo.
Coleta de Feedback: Facilita a obtenção de feedback do usuário e do mercado antes de comprometer recursos substanciais na produção em massa.
Avaliação de Produção: Permite uma avaliação dos processos de fabricação, materiais, e considerações de custo envolvidas na produção em massa.
A prototipagem acelera a inovação, reduz a incerteza, e muitas vezes se mostra inestimável para garantir o sucesso do produto.
Opções de fabricação de prototipagem rápida
Vários métodos tornaram-se predominantes devido à sua velocidade, precisão, e adequação para diversas necessidades de projetos. Os três métodos proeminentes de prototipagem rápida incluem usinagem CNC, 3D impressão, e elenco de vácuo.
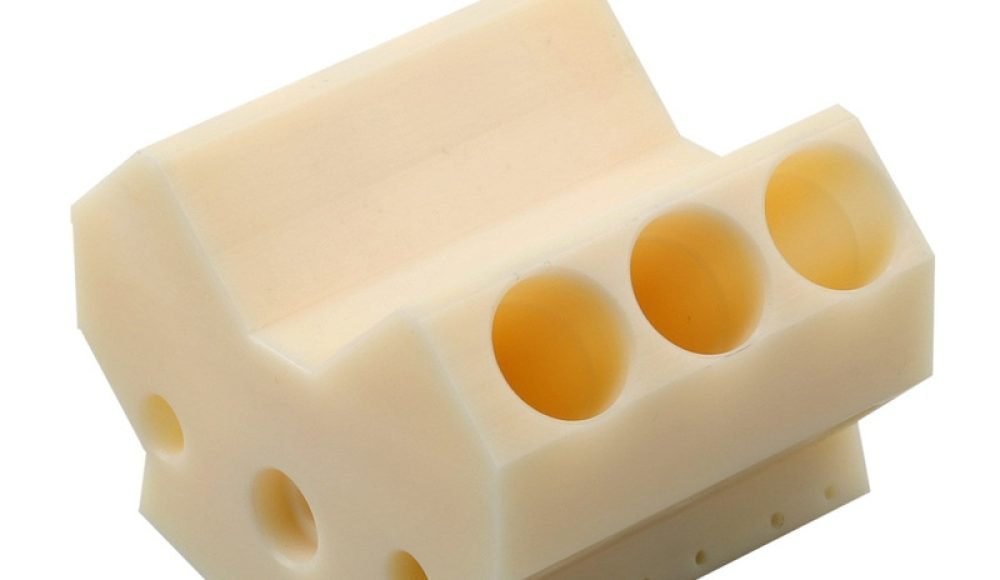
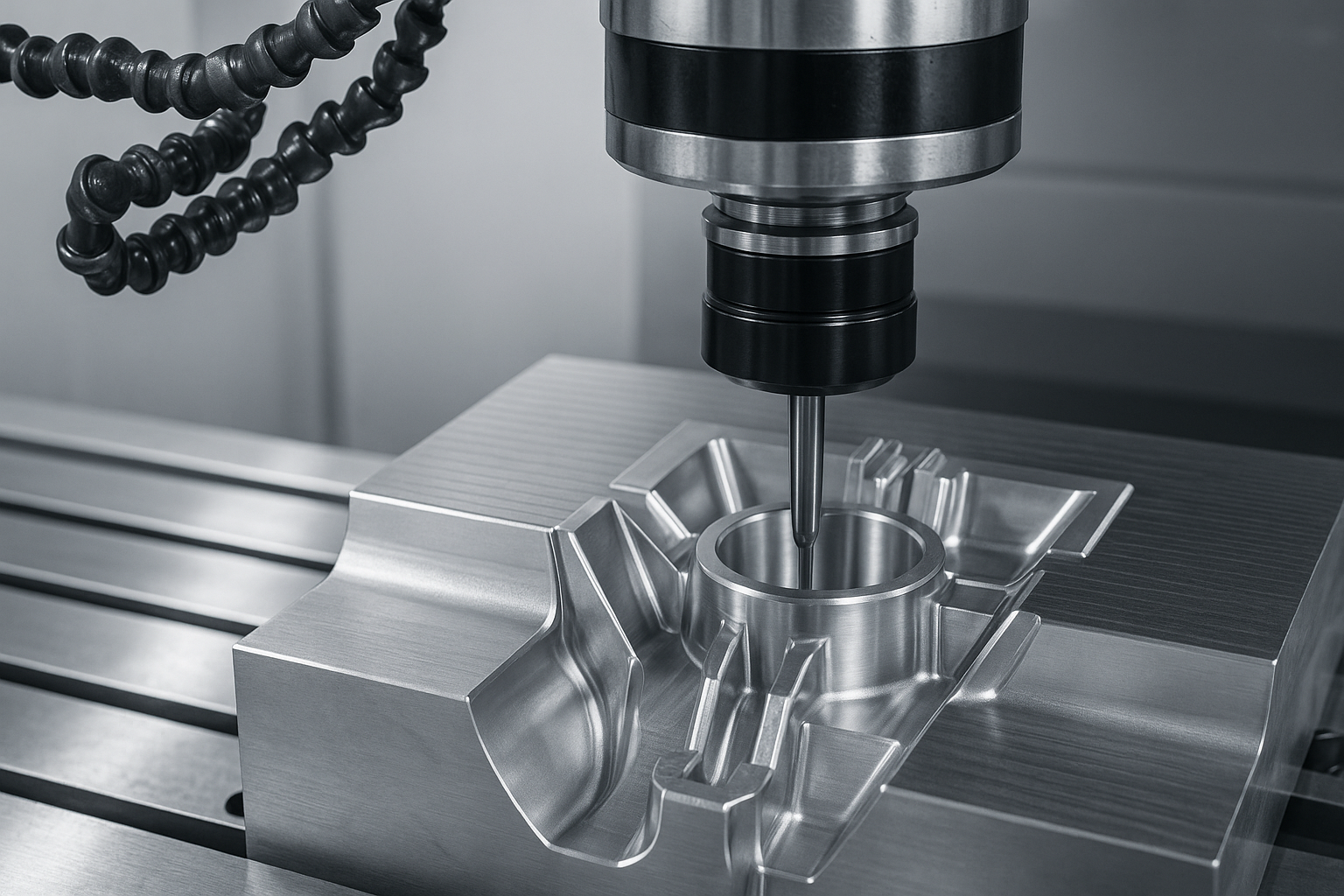
Usinagem CNC
CNC (Controle numérico do computador) a usinagem envolve o uso de máquinas de corte e modelagem controladas por computador para esculpir protótipos a partir de blocos sólidos de material, normalmente metal ou plástico.
Vantagens da usinagem CNC:
Precisão e Precisão Excepcionais: Capaz de atender tolerâncias extremamente restritas, tornando-o ideal para projetos altamente detalhados e exatos.
Tratamento de geometria complexa: O equipamento CNC pode criar com precisão formas e recursos complexos que a usinagem manual não consegue.
Durabilidade e versatilidade de materiais: Os protótipos CNC são robustos e se assemelham muito aos produtos finais em termos de resistência e propriedades do material.
Excelente acabamento superficial: Capaz de fornecer acabamentos de alta qualidade que requerem pós-processamento mínimo.
Aplicações típicas de prototipagem CNC:
Componentes mecânicos
Peças aeroespaciais e automotivas
Modelos complexos de engenharia
Durável, protótipos funcionais adequados para testes rigorosos
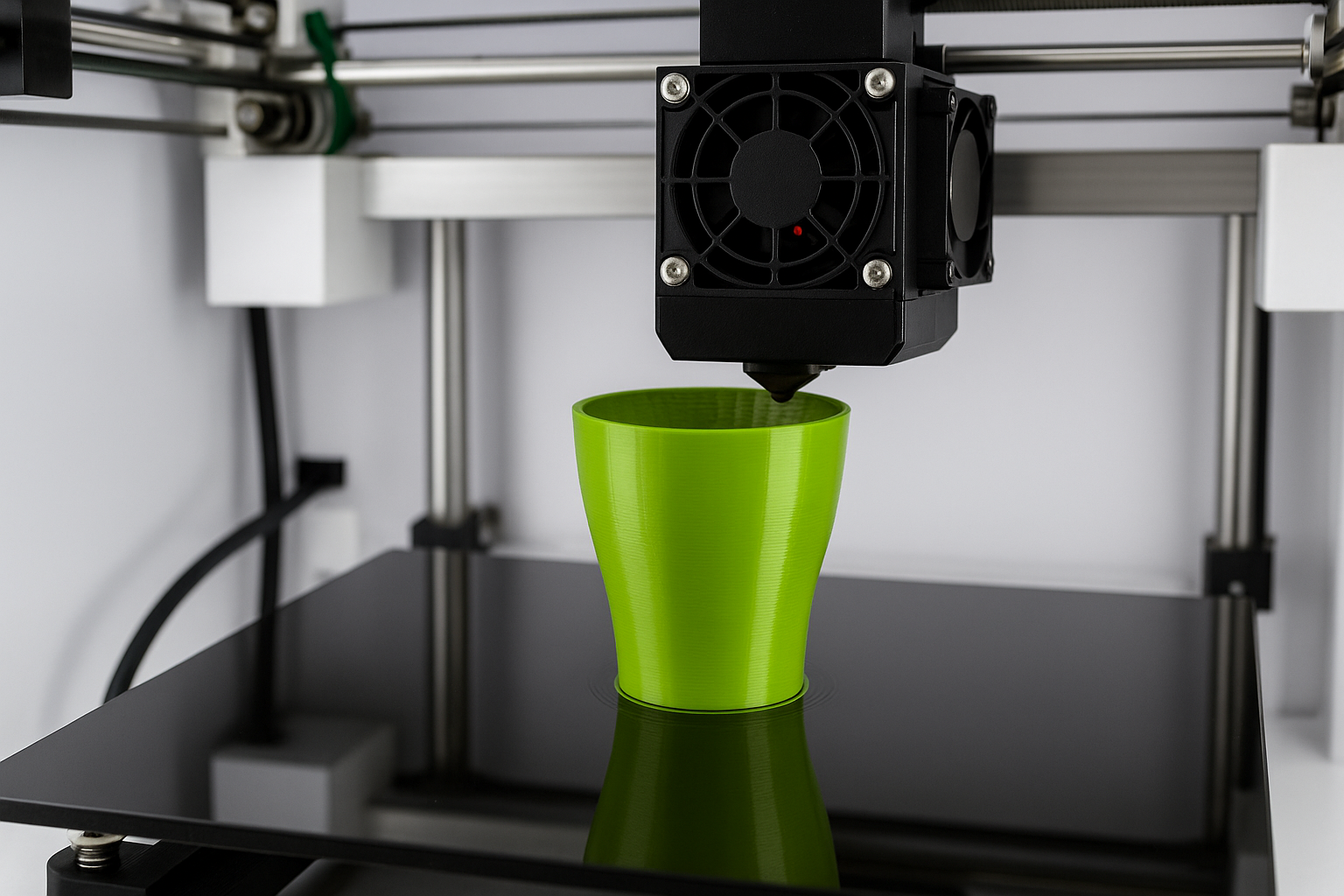
3Impressão D
3D impressão, também conhecida como manufatura aditiva, cria protótipos camada por camada usando design auxiliado por computador (cafajeste) arquivos. Este método tem visto um rápido avanço devido à sua acessibilidade e velocidade.
Vantagens da impressão 3D:
Velocidade e eficiência: Tempos de produção rápidos, permitindo processos de design iterativos em um curto espaço de tempo.
Custo-benefício: Relativamente barato, especialmente ao usar materiais plásticos padrão.
Alta precisão: Permite geometrias complexas e estruturas internas intrincadas, difíceis de alcançar pelos métodos tradicionais de fabricação.
Limitações da impressão 3D:
Resistência Material: Geralmente menor durabilidade em comparação com protótipos usinados em CNC.
Acabamento de superfície: Geralmente requer pós-processamento adicional para melhorar a suavidade da superfície.
Aplicações típicas de impressão 3D:
Modelos conceituais e projetos em estágio inicial
Próteses médicas e modelos dentários
Modelos arquitetônicos
Componentes funcionais de baixo estresse
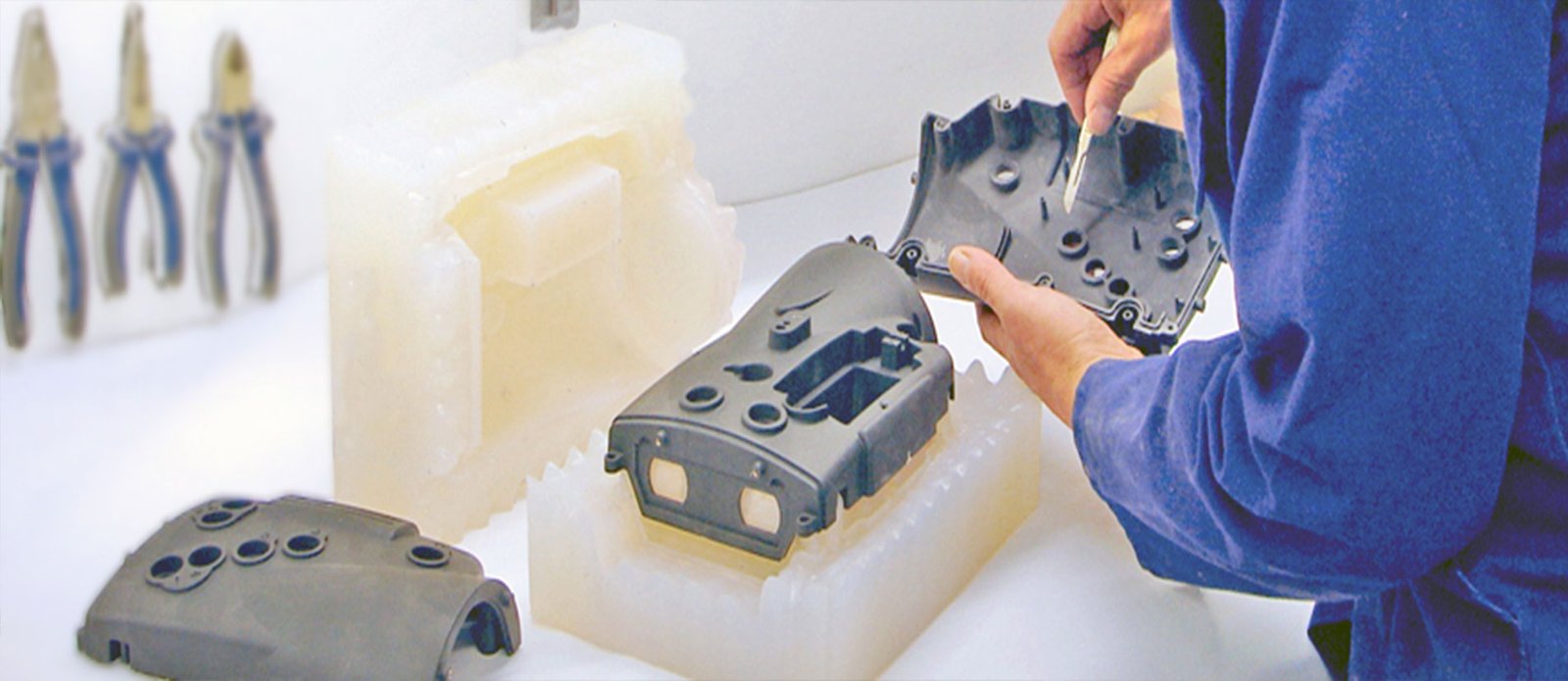
Elenco de vácuo
Fundição a vácuo, também conhecido como fundição de uretano, envolve a criação de um molde de silicone a partir de um padrão original (frequentemente criado por meio de usinagem CNC ou impressão 3D). Resina ou metal líquido é derramado no molde dentro de uma câmara de vácuo para eliminar bolhas de ar, resultando em precisão, peças fundidas sem defeitos.
Vantagens da fundição a vácuo:
Precisão e detalhe: Moldes replicam detalhes de protótipos originais, garantindo alta fidelidade.
Versatilidade de materiais: Capaz de produzir protótipos em vários materiais plásticos e elastoméricos que se assemelham muito aos materiais de produção final.
Adequado para corridas curtas: Ideal para pequenos lotes ou tiragens de produção limitadas devido à capacidade de reutilização do molde.
Limitações da fundição a vácuo:
Considerações de custo: Mais caro por peça em comparação com a impressão 3D, especialmente para pequenas quantidades, devido à intensidade do material e do trabalho.
Vida útil limitada do molde: Os moldes de silicone normalmente se degradam após um certo número de moldes, limitando sua reutilização.
Aplicações típicas de fundição a vácuo:
Pré-produção de pequenos lotes
Modelos visuais de alta qualidade
Protótipos de testes funcionais
Componentes que necessitam de grande semelhança com os produtos finais
Escolhendo a técnica correta de prototipagem
A seleção da técnica de prototipagem ideal depende de vários fatores, como:
Objetivo do protótipo: É principalmente funcional, visual, ou ambos?
Requisitos de materiais: Propriedades específicas do material (por exemplo., força, flexibilidade, resistência química).
Restrições orçamentárias: Equilibrando a relação custo-benefício com as necessidades de prototipagem.
Limitações de tempo: Com que rapidez o protótipo é necessário.
Necessidades de durabilidade: Se o protótipo passará por testes extensivos ou será puramente demonstrativo.
Aproveitar a experiência profissional garante que esses fatores sejam avaliados com precisão. Especialistas experientes em prototipagem podem recomendar o melhor processo com base em suas necessidades específicas de projeto, cronograma do projeto, orçamento, e considerações de produção.
Conclusão e apelo à ação
A prototipagem rápida é uma fase crítica do desenvolvimento de produtos, melhorando significativamente a viabilidade do produto e reduzindo riscos potenciais de produção. Usinagem CNC, 3D impressão, e fundição a vácuo oferecem vantagens exclusivas adaptadas a diferentes cenários de prototipagem.
Fazendo parceria com um fornecedor confiável de prototipagem com ampla experiência no setor, como o nosso, com mais 15 anos de conhecimento especializado – você pode garantir resultados da mais alta qualidade. Nosso conhecimento abrangente, equipamento avançado, e diversos recursos de materiais nos posicionam de forma única para recomendar e executar a melhor abordagem de prototipagem para suas necessidades específicas.
Quando você estiver pronto para seguir em frente, convidamos você a consultar nossos especialistas para orientação personalizada e uma estimativa precisa. Deixe-nos ajudar a dar vida às suas ideias rapidamente, precisamente, e com boa relação custo-benefício.
Aqui estão cinco seções de perguntas frequentes que você pode adicionar ao artigo para aprimorar o SEO e responder às dúvidas comuns dos leitores:
Perguntas frequentes
1. Quanto tempo normalmente leva a prototipagem rápida?
Os prazos de prototipagem rápida dependem da técnica escolhida e da complexidade do design. Usinagem CNC e impressão 3D podem entregar protótipos em poucos dias, enquanto a fundição a vácuo normalmente leva um pouco mais de tempo devido à preparação do molde, geralmente entre uma a duas semanas.
2. Qual técnica de prototipagem rápida é a mais econômica?
Para protótipos iniciais, especialmente aqueles que exigem iterações frequentes, 3D impressão geralmente fornece a solução mais econômica devido ao seu menor custo de configuração. Usinagem CNC e fundição a vácuo são econômicos para protótipos mais robustos ou quando a durabilidade e a precisão justificam investimentos iniciais ligeiramente maiores.
3. Os protótipos podem ser usados para testes funcionais??
Sim, protótipos feitos através de usinagem CNC e fundição a vácuo são particularmente adequados para testes funcionais rigorosos devido à resistência e precisão do material. 3Protótipos impressos em D são adequados para isqueiros, cenários de testes menos rigorosos.
4. Existem limitações nos materiais do protótipo?
A escolha do material varia de acordo com o método de prototipagem. A usinagem CNC oferece a mais ampla variedade, incluindo metais e plásticos de engenharia. 3A impressão D geralmente utiliza plásticos e resinas específicas, Considerando que os materiais de fundição a vácuo imitam de perto os plásticos e elastômeros de qualidade industrial, oferecendo boa flexibilidade de material.
5. Quão precisos são os protótipos rápidos em comparação com o produto final?
Todos os métodos de prototipagem rápida discutidos – usinagem CNC, 3D impressão, e fundição a vácuo – produza protótipos altamente precisos. A usinagem CNC normalmente oferece a mais alta precisão, seguido de perto pela fundição a vácuo e impressão 3D. A escolha depende dos requisitos de precisão do seu projeto e da aplicação pretendida.
Meta título: Técnicas rápidas de fabricação de protótipos: CNC, 3Impressão D & Elenco de vácuo
Meta Descrição: Aprenda sobre técnicas de prototipagem rápida, como usinagem CNC, 3D impressão, e elenco de vácuo. Descubra suas vantagens, limitações, aplicações, e como escolher o melhor método para o design do seu produto.
Leia mais:






1 pensei em “Técnicas rápidas de fabricação de protótipos: Usinagem CNC, 3Impressão D, e elenco de vácuo”