Na usinagem de precisão, specifying the proper hole geometry is crucial. The mechanical components get the proper fit and function using these parameters. Counterbore and spotface holes are among the most popular kinds of hole modification and they each have common but overlapping uses. Por isso, counterbore holes allow the fasteners to almost flush with the surface. Por outro lado, spotface holes will create a flat seating area for the bolt heads and washers.
Neste artigo, we will discuss the meaning of those definitions, aplicações, Métodos de usinagem, and symbols in engineering drawings and will compare them.
What is a Counterbore Hole?
A counterbore hole is a flat-bottomed cylindrical cavity that enlarges existing holes. Então, they can fit flat fasteners only at or below material surfaces. The primary agenda of counterbores is to create pockets for bolt heads, arruelas, e nozes. It helps them not protrude above the working surface.
Counterbores help achieve the required sizes. Accurate counterboring holes require cylindrical enlargements with parallel walls that evenly bear loads, covering both fixadores and workpieces. It is helpful for specialized equipment, such as drill bits with guided pilots.
Counterbores in Engineering Drawings
Engineering drawings represent counterbores using the ” ⌴” symbol, which looks like a square U. Specifications are a group of dimensions that outline the dimensions of the counterbore, ou seja, diâmetro, profundidade, and hole diameter size.
The drawing document directs technicians to make “⌀25 x 10 deep for M12 bolt” counterboring, which requires a 25 mm diameter bore cut to a depth of 10 mm to accommodate an M12 bolt. The notational system is specific and demonstrates to machining staff which specifications are required to provide proper fitment.
What is a Spotface Hole?
The surface feature called spotface forms even surfaces around holes. It enables the nuts and washer bolt heads to rest in even positions. Spotface gives a shallow cut through less material. It can create an even flat surface without going full-depth counterbore sizes. Spotface holes give fasteners a flush fit on odd and curved surfaces. Erase tools create spotface holes that make shallow cuts to save raw material but still have adequate contact areas.
Spotface Holes in Engineering Drawings
A spotface utilizes the same symbol as counterbores (“⌴”) yet requires additional notes of “SF” or “SPOTFACE” to differentiate it. Dimensioning spotface holes starts by specifying the diameter at the same value as the fastener head or washer and then moves to dimension the hole depth unless needed for functionality. Spotfaces appear in castings and rough surfaces. They play a vital role when designers need a flat uniform seating area.
A Detailed Comparison of Counterbore vs. Spotface:
The difference between counterbore and spotface holes carries over to their uses sizes applications, and machining processes with their related engineering standards.
1. Usar
Counterbores play their primary role by giving fasteners room under exterior surfaces for support and preventing hardware interference. Spotface holes create a smooth attachment area for fasteners on irregular or curved materials without altering the true material density.
2. Profundidade
Engineering drawings specify depth values for counterborings that are sufficiently deep to accommodate bolt heads or washers. Spotface hole depths remain low since they only require a few millimeters deep to meet surface levelness.
3. Aplicativo
The functional application of counterbores is encountered during the mounting of fasteners beneath material surfaces in mechanical assemblies along with aerospace structures and components of automotive engines. Spotfaces offer standard bearing surfaces on rough-machined and casted parts in machinery and heavy industrial equipment.
4. Processo de usinagem
Counterbore and spotface hole manufacturing operations include drilling and then milling operations. Counterbores require pilot-guided tools while spotfaces take similar tools when operators use depth control to prevent overremoval.
5. Engineering Specifications
Engineering drawings indicate these features using the same symbol “⌴” but spotfaces also have an added SF annotation. The diameter and depth dimensions denote counterbores in drawings but spotfaces usually need only diameter dimensions since depth is very little.
6. Structural Impact
Counterboring adversely impacts the structural integrity of parts. Since this production process removes significant amounts of material. Aqui, the workpiece is measured before commencing the machining operation. These parts use spotfaces to maintain their structural integrity very well since they remove a minimal material for flattening.
We can briefly differentiate them in the following table:
| Recurso | Counterbore | Spotface |
| Propósito | Recessing fasteners for flush-fitting | Creating a flat surface for fastener heads |
| Profundidade | It can be deep depending on the fastener | Very shallow, minimal material removal |
| Common Usage | Used in assemblies requiring flush-mounted bolts | Used on rough, elenco, or curved surfaces to ensure fastener stability |
| Symbol in Drawings | ⌴ with diameter and depth specifications | ( ⌴ )with the letters ‘SF’ inside it – with a diameter (depth often omitted) |
| Remoção de Materiais | Removes significant material | Removes minimal material |
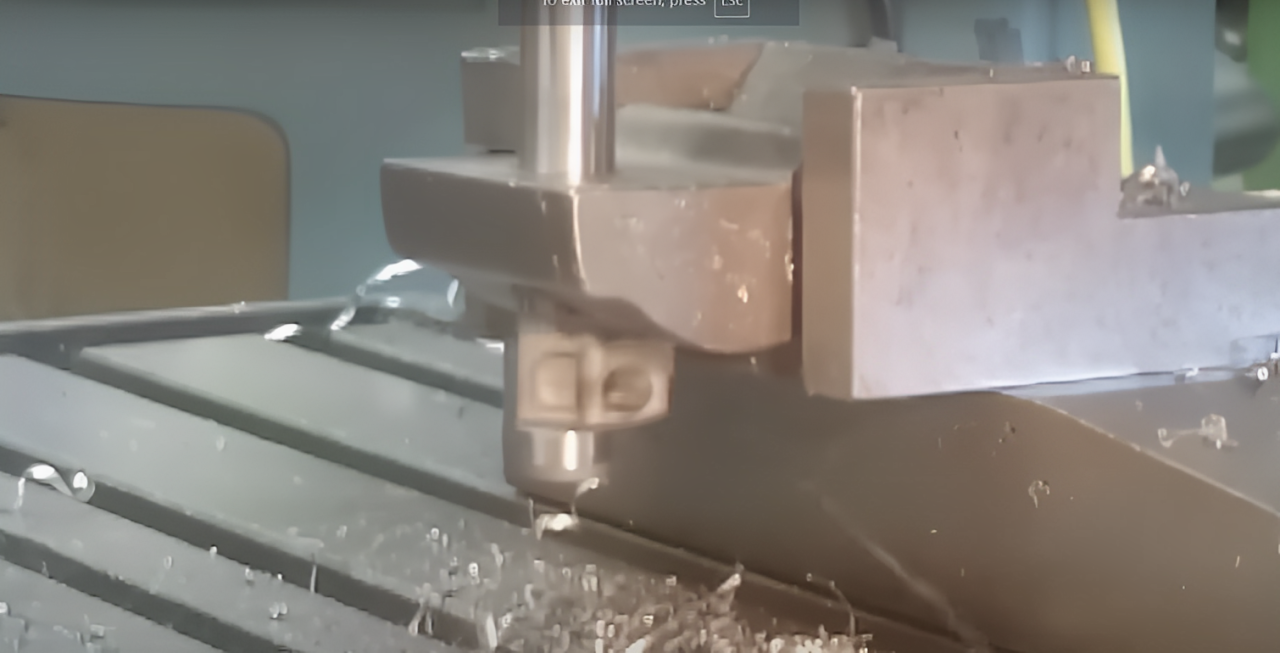
Counterbore and Spotface Machining
Both counterbore and spotface machining procedures entail precision cutting tools that produce clean, flat-bottomed holes. Drill presses and CNC milling machines typically produce accurate dimensions and surface finishes.
1. Counterbore Machining
- Utilizes a counterbore pilot cutter.
- Provides an accurately sized recess for fastener heads.
- Usually done after the initial hole was drilled.
2. Spotface Machining
- Utilizes a guided pilot spotfacing tool.
- Only remove sufficient material to provide a smooth, superfície plana.
- Typically utilized in castings or uneven surfaces.
Counterbore and Spotface Tools
Various cutting tools are utilized in the production of counterbore and spotface features, como:
- Counterbore Cutters: Piloted for precision alignment.
- Spotface Tools: They are the same as counterbore cutters but are designed for shallow material removal.
- Mills finais: Utilized in Usinagem CNC to produce accurate counterbore or spotface surfaces.
- Specialized Drill Bits: Certain drill bits have built-in counterbore or spotface capabilities.
General Manufacturing Considerations for Counterbore and Spotface
Manufacturers consider the following when designing parts with counterbores or spotfaces:
- Tipo de material: Harder materials can be accommodated with specialized tooling.
- Tolerance Requirements: Accurate precision for proper assembly.
- Fastener Specifications: Compatibility with screws and bolts.
- Acabamento de superfície: A flat, smooth surface is required for best fastener seating.
Identifying Spotface and Counterbore Symbols
Symbols in engineering are vital to precise manufacture. The symbol for counterbore/spotface is widespread, as are:
- Diameter notation (Ø).
- Counterbore depth notation.
- Spotface depth is usually only used if essential.
Qual é melhor? Counterbore Vs. Spotface Holes?
The appropriate use of counterbore or spotface holes depends solely on their functions, a designer needs. Counterbores prove effective for achieving structural integrity. They provide deeper holes required to hide or recess fasteners. Por outro lado, spotfaces find their best application when users require even fastener seating across nondescript and irregular or curved surfaces.
We use counterbores when designing for load-bearing, while spotfaces work best for achieving uniform force distribution. The selection process for a suitable hole modification technique begins with precise knowledge of application requirements.
Conclusão
Para concluir, the necessary machining features need proper fastener installation and load distribution including counterbores and spotfaces. The counterbores give recessed seating to bolts and screws. While spotfaces create planar faces on nonplanar materials. The shaft differences, aplicações, and machining allow engineers and machinists to make informed decisions.
Perguntas frequentes
- What is the main difference between a counterbore and a spotface hole?
The counterbore is deeper and will accommodate the fasteners. Por outro lado, a spotface has an extremely shallow depth with a plane surface for proper seating.
- Is a spotface an option instead of a counterbore?
Not always. These Spotfaces are too shallow to fully recess fasteners. They don’t recess far enough to make them suited to use where flush mounting is needed.
- Is spotface machining a tool requiring special tools?
No entanto, the depth of counterbore tools can be controlled for spotfaces creation.
- What industries do counterbores and spot faces come to play in?
The main industries included in it are; aeroespacial, automotivo, heavy machinery woodworking, e indústrias médicas.