No mundo da precisão de Usinagem CNC, every variable counts. Among these, Pés de superfície por minuto (Sfm) plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency, precisão, and longevity of both the tool and the workpiece. Se você é fresagem, perfuração, girando, ou moagem, understanding and properly applying SFM is essential for optimal performance.
This in-depth guide breaks down everything you need to know about SFM—what it is, como funciona, how to calculate it, and how it affects your machining results.
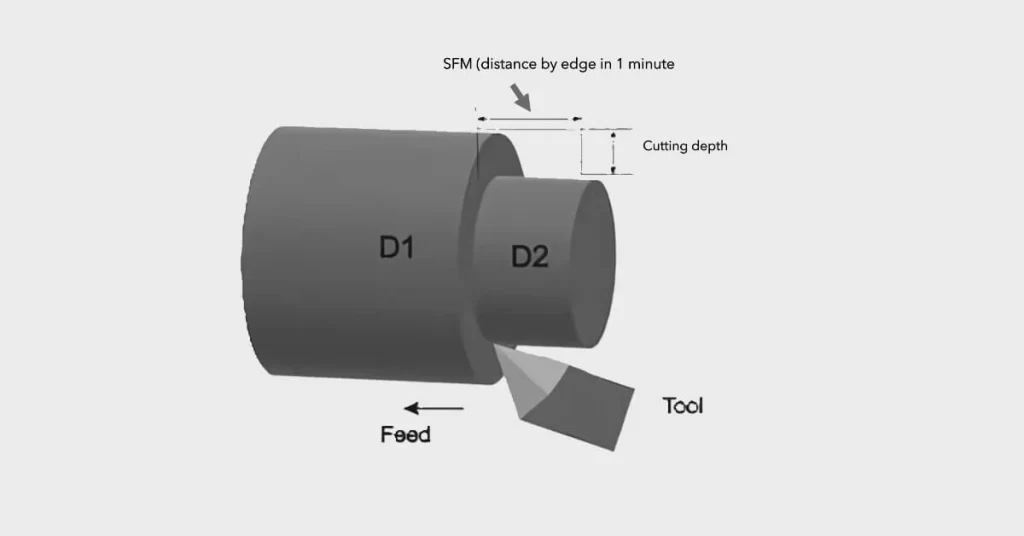
What is SFM (Pés de superfície por minuto)?
Pés de superfície por minuto (Sfm) refers to the linear speed at which a cutting tool moves across the surface of the workpiece. Diferente Revolutions Per Minute (RPM), which only tells you how fast the tool or spindle is rotating, SFM measures how fast the cutting edge is actually moving through the material.
🔍 Why It Matters:
SFM is material-dependent—you need different SFM settings for aluminum, aço, plásticos, etc..
It directly affects Desgaste da ferramenta, tempo de usinagem, geração de calor, e acabamento superficial.
Unit of Measurement: SFM is typically expressed in feet per minute (ft/min).
How Does SFM Impact Machining Processes?
🧱 1. It Controls How Fast You Can Cut
When you set the right surface speed, your tool moves across the material at just the right pace.
Too fast? You’ll burn up the tool.
Too slow? You waste time and might get a rough finish.
The sweet spot helps remove material quickly without stressing your machine or tool.
🧰 2. It Helps Your Tools Last Longer
Nobody wants to change tools every few minutes, certo?
A good SFM keeps things cool and controlled—less heat = longer tool life. High SFM can make the tool dull faster, especially on tough metals. But with the right setting, your tools stay sharp and your jobs stay on track.
✨ 3. It Affects Surface Finish
Want a part that looks and feels smooth? Then your surface speed matters.
If you go too fast, the part might overheat, expand slightly, or get a scorched surface.
If you go muito lento, the tool may rub instead of cutting, leaving behind a rough or uneven finish.
The right SFM gives you that limpar, brilhante, professional surface—no sanding needed.
🔥 4. It Controls Heat Buildup
Machining always creates heat, but too much of it causes problems like:
Tool damage
Warped parts
Chips sticking instead of clearing
By choosing the right SFM—and using coolant when needed—you can manage the heat and avoid thermal issues before they start.
Applications of SFM in Machining Processes
🧰 Milling
Milling uses rotating tools to remove material. The SFM value influences how fast you can cut. A higher SFM (with proper feed rate) improves efficiency and surface finish.
🌀 Drilling
Drilling into tough materials (por exemplo., aço) requires carefully controlled SFM to avoid bit overheating and wear. Correct speed also prevents hole misalignment and burnishing.
🔁 Turning
In lathe operations, SFM dictates how fast the rotating part engages the stationary cutting tool. Too fast causes overheating; too slow leads to rough cuts.
⚙️ Grinding
For cylindrical or surface grinding, the grinding wheel’s speed (measured in SFM) affects both the finish and wheel life. Proper SFM ensures efficient, sharp cuts and prevents wheel glazing.
How to Calculate SFM in Machining
O formula for calculating SFM is:
SFM=π×D×RPM12\text{Sfm} = \frac{\pi \times D \times RPM}{12}
Onde:
D = Diameter of the tool or workpiece (in inches)
RPM = Revolutions Per Minute
12 = Converts inches per minute to feet per minute
📌 Example:
If you’re using a 3-inch diameter end mill at 900 RPM:
SFM=3.1416×3×90012=706.86 ft/min\text{Sfm} = \frac{3.1416 \times 3 \times 900}{12} = 706.86 \, \texto{ft/min}
Tools and Software for SFM Calculation
To save time and reduce errors, machinists use specialized tools and software:
🛠 Tools:
Machinist’s Calculator – Great for shop-floor conversions and feed/speed calculations.
Online SFM Calculators – Free and accessible from any browser.
CNC Machine Control Panels – Often come with built-in calculators.
Software de câmera – Integrates SFM calculations with toolpaths.
🧠 Recommended Software:
G-Wizard – Speed/feed calculator with built-in material/tool database.
FSWizard – Real-time calculator for speeds, Feeds, and SFM.
HSMAdvisor – Advanced tool for balancing SFM, taxas de alimentação, and cutting depths.
Machinist’s Calculator Pro – App version with robust calculation capabilities.
Effects of Too High or Too Low SFM
🔺 Too High SFM – When You’re Cutting Too Fast
Going too fast might sound like a good thing—get the job done quicker, certo? But in machining, faster isn’t always better.
Here’s what can go wrong:
🔥 1. Superaquecimento
When the cutting edge moves too quickly, it creates a ton of friction and heat. That heat builds up fast, and if your coolant can’t keep up, your tool can start to burn out.
💥 2. Tool Wear and Breakage
High SFM causes your tool edges to dull more quickly. Em alguns casos, it can even chip or snap your cutting tool if the material is tough enough.
✨ 3. Bad Surface Finish
Excess heat or vibration caused by high speeds can leave you with a rough, inconsistente, ou até burned surface—not a good look for any machined part.
💸 4. Custos mais elevados
More broken tools = more replacements = more money out of your pocket.
🔻 Too Low SFM – When You’re Cutting Too Slow
Playing it safe and going too slow might seem like a smart move, but that can backfire too.
🧊 1. Rubbing Instead of Cutting
If the tool moves too slowly, it may not “slice” the material properly. Em vez de, it just rubs against it, building up heat and wearing down your tool without actually cutting much.
⌛ 2. Slower Production
Lower speeds mean longer cycle times. If you’re machining hundreds of parts, that adds up fast.
🧱 3. Poor Finish
Slow speeds often cause conversa, vibração, e rougher edges—not the smooth finish you want.
🌡️ 4. Heat Buildup (Sim, Even When Slow!)
Surprisingly, going too slow can still generate heat—just in a different way. Instead of slicing cleanly, the tool struggles and rubs, which creates friction and heat anyway.
Recommended SFM Settings for Common Materials
| Material | HSS Tools (Sfm) | Carbide Tools (Sfm) |
| Alumínio | 250–400 | 600–1000 |
| Latão | 300–600 | 800–1200 |
| Ferro fundido | 60–120 | 400–800 |
| Aço suave | 70–150 | 300–600 |
| Inconel | 10–30 | 50–200 |
| Cobre | 100–300 | 500–1000 |
| Plástico | 300–800 | 800–2000 |
| Titânio | 30–70 | 100–300 |
Observação: Use coated tools and coolant for tough materials.
Factors That Influence SFM Selection
🔧 Type of Operation
Different processes demand different speeds. Milling might allow for higher SFM than drilling or turning, depending on cutter engagement.
🪚 Tool Material
HSS: Budget-friendly but lower SFM capacity
Carboneto: Withstands higher speeds
Cerâmica / CBN: For extreme conditions
🔩 Workpiece Material
Harder materials require lower SFM to reduce heat and friction.
🏭 Machine Capabilities
Your CNC machine’s RPM limits and rigidity affect what SFM you can achieve without causing vibration or instability.
💦 Coolant & Lubrificação
Coolant reduces heat and improves surface finish, allowing for slightly higher SFM safely.
Conclusão
SFM is not just a number—it’s a critical part of your machining strategy. Whether you’re running a quick prototype or a full production job, getting the right surface speed can make the difference between success and costly rework.
No Precisão máxima, we use advanced software and expert knowledge to fine-tune SFM and every other parameter for precision CNC machining. Let us help you optimize your next project for performance, custo, e qualidade.