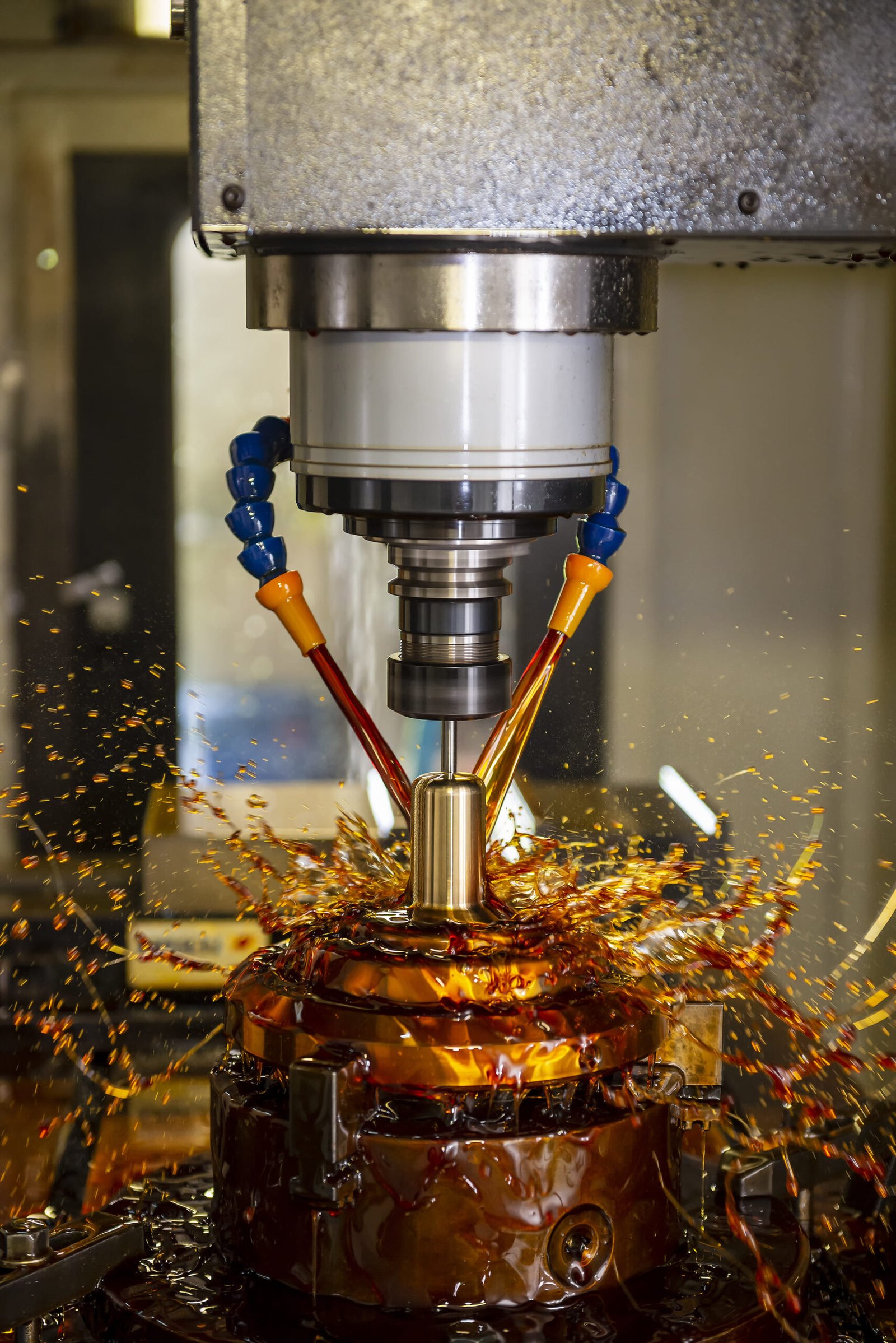
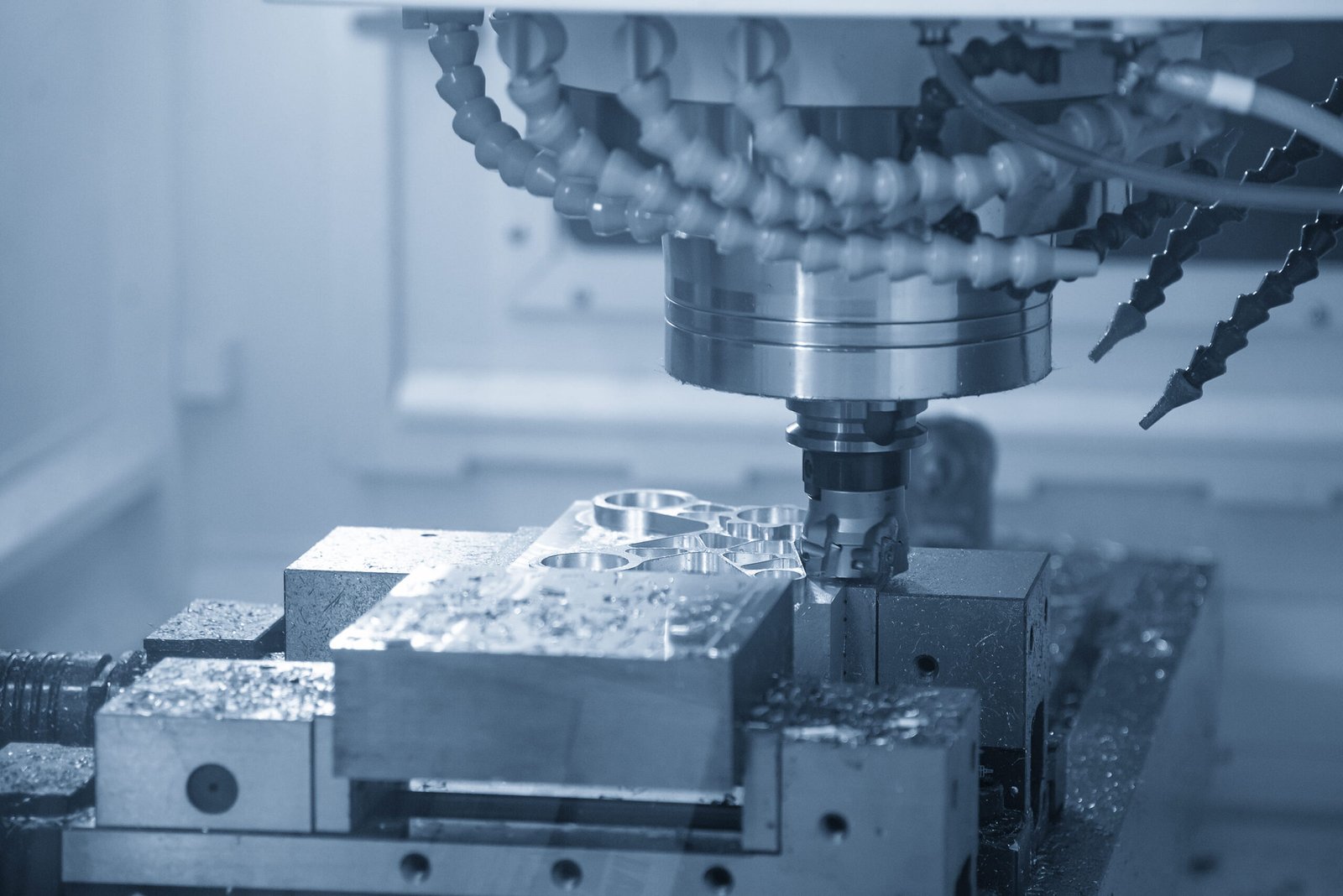
De fato, A fresagem CNC desempenha um papel muito significativo na indústria de manufatura. Ele usa máquinas controladas por computador que giram de acordo com as demandas do computador e realizam operações de corte rotativo multiponto. A fresagem CNC consiste em ferramentas de corte altamente avançadas e ajuda a cortar material excessivo das peças de trabalho. Então, neste artigo, lidaremos especificamente com ferramentas de fresagem CNC, maquinaria, e processos que envolve. além disso, trataremos de seu uso em diversas indústrias e suas alternativas no mercado.
Como você definiria o fresamento CNC?
Como outra fabricação de chapa metálica, A fresagem CNC é igualmente significativa. Como o próprio nome sugere, CNC significa Controle Numérico Computadorizado. Então, é um processo informatizado que controla todas as suas ferramentas de corte, ou seja. ferramentas de corte rotativas multiponto. Isso ajuda a cortar o excesso de material das peças de trabalho. além disso, ajuda a projetar peças e produtos personalizados. Esses produtos têm diversas aplicações em diferentes indústrias. Além disso, A fresagem CNC é flexível e pode usar vários materiais.
O que é uma fresadora CNC?
As máquinas que realizam operações de fresagem CNC são máquinas CNC. Estas são ferramentas de corte usadas especificamente para cortar o material do metal. As fresadoras tradicionais operam manualmente. Enquanto as fresadoras CNC são informatizadas. Eles são mais precisos e precisos. além disso, essas máquinas controlam os projetos e a função da ferramenta com um computador. Esta é a razão, por que a fresagem CNC agora é usada em muitas indústrias para fabricar peças personalizadas.
O que uma máquina de moagem CNC faz?
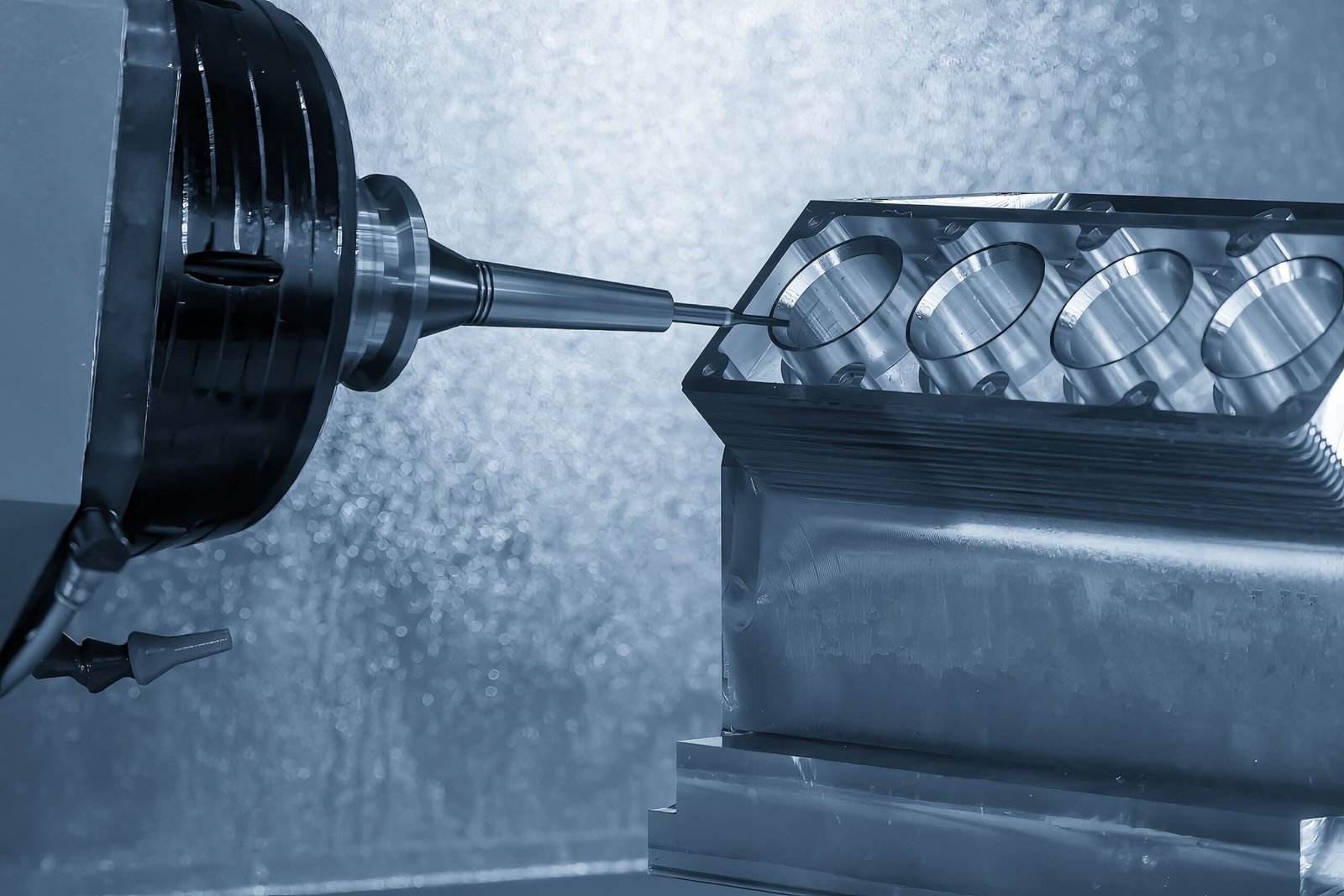
Por causa do controle computadorizado, as fresadoras CNC podem realizar diferentes operações de usinagem. Eles podem incluir perfuração, corte, e moldar. Aqui a peça de trabalho é fixada no ponto estacionário. Embora as ferramentas de corte sejam rotativas. Em seguida, essas ferramentas de corte giram em torno da peça de trabalho e ajudam a obter a forma e o tamanho necessários. Então, essas máquinas podem operar em eixos multidirecionais, ou seja. (X, S, e Z). Adicionalmente, se você lida com tecnologias mais avançadas. Essas fresadoras CNC podem girar em cinco ou mais eixos. Este recurso fornece flexibilidade na fabricação de peças personalizadas.
Qual é a diferença Bentre 3 eixos, 4-eixo, e máquinas de moagem de 5 eixos?
As máquinas de moagem CNC podem ser classificadas com base no número de eixos que operam junto, e quanto mais eixos uma máquina tiver, quanto mais complexo e versátil se torna na produção de partes complexas. Abaixo está uma explicação detalhada das diferenças entre 3 eixos, 4-eixo, e máquinas de moagem de 5 eixos:
1. 3-Máquina de moagem do eixo
- A 3-Máquina de moagem do eixo CNC é o tipo mais comum usado na fabricação e opera em três eixos lineares: X, S, e Z. Nesta configuração, A peça de trabalho é mantida no lugar enquanto a ferramenta de corte se move ao longo desses três eixos para remover o material da superfície.
- Vantagens: 3-As máquinas de eixo são simples de operar e programar, E eles são capazes de produzir peças com geometrias mais simples e cortes precisos. Eles são altamente econômicos para operações básicas de moagem, como furos de perfuração, slots, e contornos simples.
- Limitações: Enquanto as máquinas de 3 eixos são eficientes para tarefas básicas, Eles são limitados quando se trata de usinagem de recursos complexos, como undercuts, Contornos complexos, ou cortes de vários ângulos.
2. 4-Máquina de moagem do eixo
- A 4-Máquina de moagem do eixo CNC estende as capacidades de uma máquina de 3 eixos, adicionando um quarto eixo (geralmente o eixo a ou rotação ao redor do eixo x). Isso permite que a peça de trabalho gire como está sendo usinada, Fornecendo mais flexibilidade às peças da máquina com recursos em vários lados ou ângulos.
- Vantagens: 4-a moagem de eixos permite formas mais complexas, como peças com buracos, slots, ou ranhuras em lados diferentes. Reduz a necessidade de reposicionar a peça de trabalho manualmente, aumentando tanto a precisão quanto a eficiência.
- Limitações: 4-As máquinas de eixo são mais caras que as máquinas de 3 eixos, e eles exigem programação e configuração mais complexas. Embora sejam mais versáteis do que as máquinas de 3 eixos, Eles ainda não conseguem lidar com geometrias muito complexas ou cortes de vários ângulos.
3. 5-Máquina de moagem do eixo
- A 5-Máquina de moagem do eixo CNC é o tipo mais avançado de máquina de moer, capaz de mover a ferramenta de corte ou peça de trabalho ao longo de cinco eixos: X, S, Z, A, e B. Essas máquinas podem girar a peça de trabalho em várias direções, permitindo geometrias complexas, contornos profundos, e reduzidos a serem criados sem ter que reposicionar a parte.
- Vantagens: 5-a moagem de eixos é ideal para peças altamente complexas e complexas, como componentes aeroespaciais, implantes médicos, e lâminas de turbinas. Permite usinagem de alta precisão, maior flexibilidade, e a capacidade de cortar formas complicadas em uma única operação. Adicionalmente, 5-As máquinas de eixo melhoram o acabamento da superfície e reduzem os tempos de ciclo.
- Limitações: 5-As máquinas de eixo são as mais caras e requerem operadores altamente qualificados. A programação é mais complexa, E o tempo de configuração pode ser mais longo em comparação com máquinas de moagem de 3 ou 4 eixos. No entanto, Sua capacidade de produzir peças de alta precisão os torna um investimento valioso para indústrias que exigem projetos complexos.
Processo completo passo a passo de fresagem CNC
Então, aqui está o processo completo e passo a passo de fresamento CNC.
1. Projetando Parte
A fresagem CNC começa com o projeto da peça metálica. Geralmente é projetado usando software CAD. Aqui, você inclui todas as especificações, dimensões, e formas e características geométricas no design. Além disso, se você usa software CAD avançado. Eles fornecem mais precisão a projetos complexos e, em última análise, criam peças complexas. Então, aqui os engenheiros devem considerar alguns fatores. Eles podem incluir, propriedades dos materiais, acesso à ferramenta, e restrições de usinagem. Este design é a primeira parte mais crítica. Porque garantem que as peças finais cumprem todos os requisitos funcionais.
2. Programação de Máquinas CNC
Depois de projetar a peça em CAD. A próxima etapa é importá-lo para o software CAM. Ajuda a traduzir o design CAD em uma sequência de instruções para a máquina CNC. Em seguida, ele gera código em linguagem de programação numérica. Diz às máquinas como cortar e mover. além disso, também controla a velocidade da máquina e o caminho em que ela cortará. Aqui é importante otimizar o caminho de corte. Então, pode reduzir o tempo de usinagem e o desperdício de material. Então, os programadores ajustam os parâmetros de corte, ou seja. velocidade do fuso, taxa de alimentação, e profundidade de corte.
3. Configuração de máquinas CNC
Nesta etapa, os engenheiros preparam as máquinas CNC para operação. Aqui o material da peça é fixado adequadamente à mesa da máquina. Esta mesa é estacionária e evita movimentos durante a usinagem. Então, é importante manter as dimensões e integridade da peça. Além disso, aqui as ferramentas de corte ideais são selecionadas. Em seguida, eles instalam no porta-ferramentas da máquina. Depois disso, o engenheiro realiza calibrações da máquina e as define em pontos zero como referência para todas as medições. Os operadores verificam os protocolos de segurança e também verificam a configuração da máquina CNC.
4. Fase de Usinagem
Aqui as máquinas CNC seguem rigorosamente as instruções de programação das plataformas. Para realizar esta operação, as ferramentas de corte começam a girar a uma velocidade muito alta. Em seguida, eles removem progressivamente o material da peça. Depois disso, a peça de trabalho atinge a forma e dimensões específicas. Então, essas máquinas são giradas em vários eixos, ou seja. X, S, e Z). Essas máquinas também possuem mais duas dimensões para lidar com peças complexas.
5. Acabamento da peça
Uma vez que o material é cortado da peça de trabalho, geralmente requer acabamento. Geralmente é feito para atender às especificações finais e padrões de qualidade. Esta etapa pode incluir rebarbação para cortar as arestas vivas. Também inclui as rebarbas à esquerda do processo de corte. Além disso, também inclui polimento da superfície da peça. Ele suaviza a peça e aumenta as propriedades da superfície, como resistência à corrosão e dureza. O processo incluído no acabamento é a anodização, pintura, ou chapeamento também pode ser aplicado.
Quais são os diferentes tipos de fresamento CNC?
A fresagem CNC pode ser de diferentes tipos. Então, vamos discuti-los em detalhes
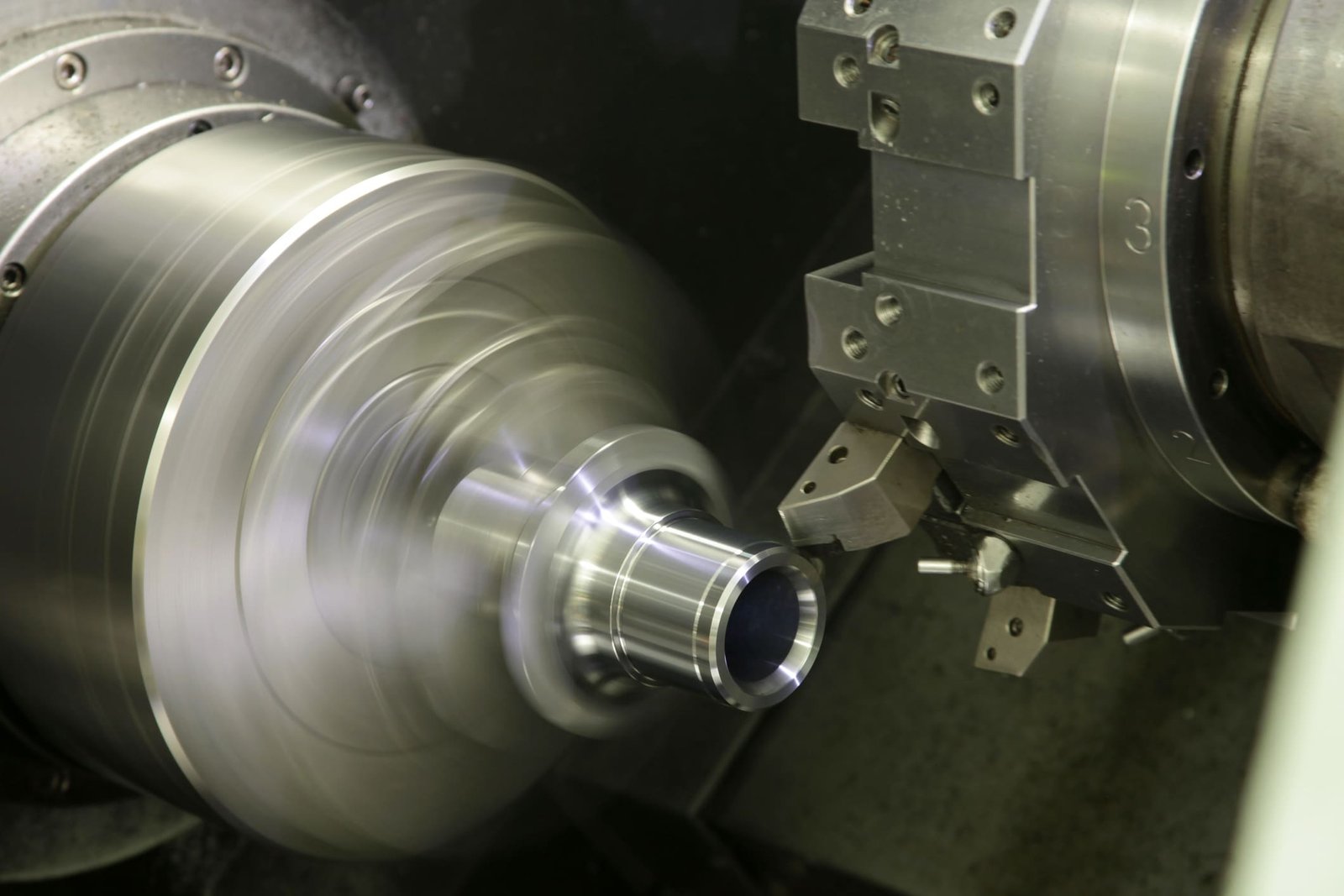

Corta a superfície plana perpendicular ao eixo do cortador. Aqui o cortador gás várias arestas de corte. Eles se movem ao redor da peça de trabalho e proporcionam um acabamento liso. Geralmente é feito em máquinas verticais. Então, eles são amplamente utilizados na fabricação de grandes superfícies. Eles podem incluir um bloco ou a face de uma peça.
Ajuda a cortar os diferentes recursos em algum ângulo em relação ao plano vertical ou horizontal da peça de trabalho. Aqui o cortador se inclina em algum ângulo. Sua mesa é rotativa para fornecer configurações precisas. O fresamento angular é geralmente usado na criação de recursos comuns, ou seja. Ranhuras em V, juntas em cauda de andorinha, e outras características angulares de peças ou conjuntos interligados.
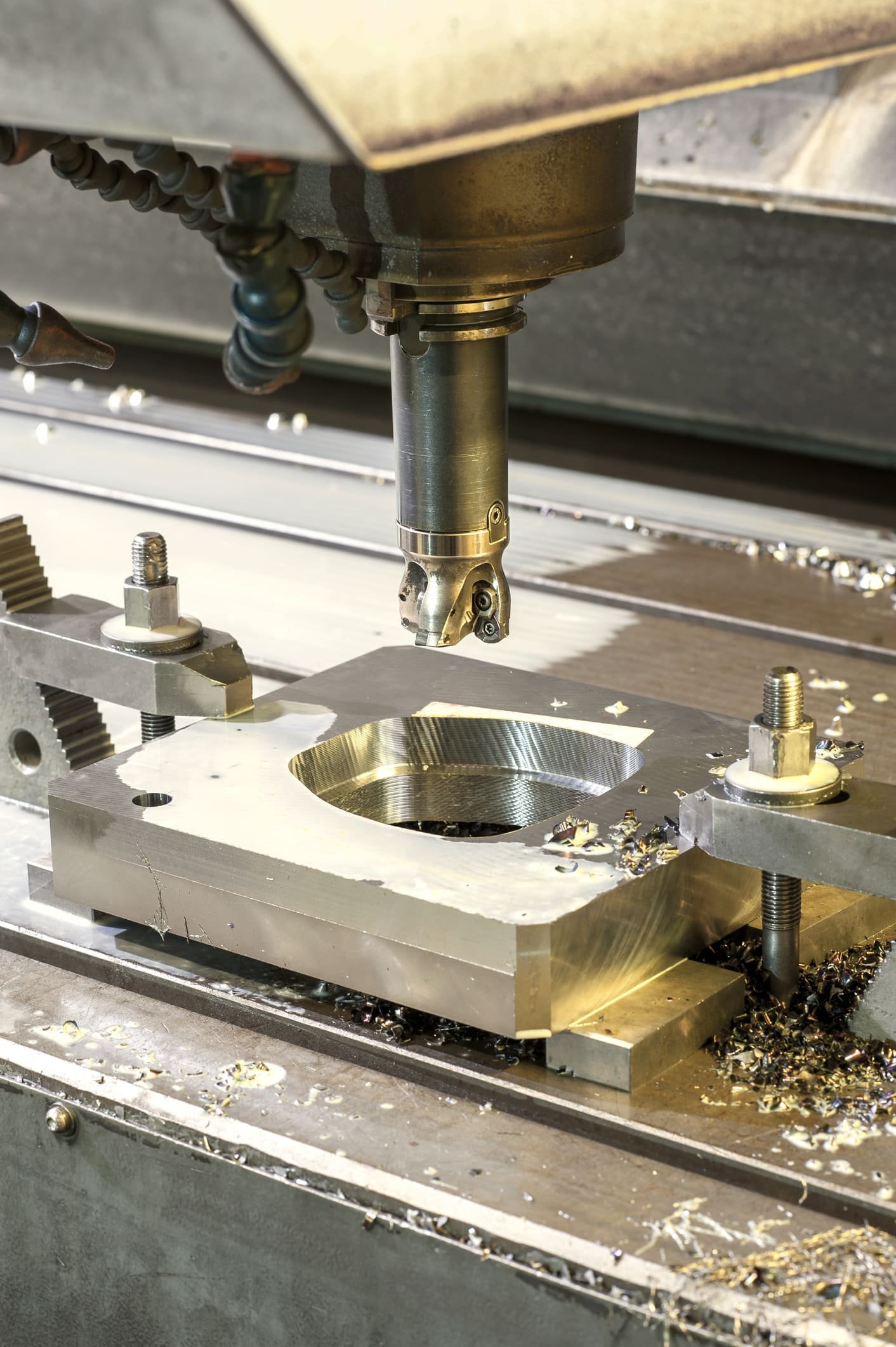
Ele usa cortadores moldados e ajuda a criar contornos e curvas complexos em uma peça de trabalho. Este processo é altamente adequado para peças personalizadas. Por isso, contém fresadoras horizontais e verticais. Então, pode cortar os perfis, ou seja. engrenagens, câmeras, e componentes de molde intrincados. Além disso, é amplamente utilizado nas indústrias por sua adequação personalizada.
Quais materiais são usados na fresagem CNC?
Aqui estão alguns materiais comumente usados por fresamento CNC. Então, vamos discuti-los aqui.
| Tipo de material | Materiais Específicos | Propriedades |
| Metais | Alumínio | Leve, usinável |
| Aço | Forte, durável | |
| Latão | Resistente a corrosão, condutor | |
| Cobre | Excelente condutividade | |
| Titânio | Alta resistência, resistente à corrosão | |
| Plásticos | abdômen | Difícil, resistente a impactos |
| Policarbonato | Resistente a impactos, transparente | |
| Nylon | Resistente ao desgaste, resistente a produtos químicos | |
| Acrílico | Claro, resistente às intempéries | |
| Compósitos | Fibra de vidro | Alta relação resistência-peso, resistente à corrosão |
| Polímeros Reforçados com Fibra de Carbono (PRFC) | Relação resistência/peso muito elevada, duro | |
| Madeira | Madeiras nobres | Durável, estética |
| Madeiras macias | Leve, fácil de usinar |
Tipos de fresadoras CNC
Baseado em diferentes formas e aplicações. Múltiplo Fresadoras CNC agora estão disponíveis no mercado. Então, vamos discutir essas máquinas em profundidade.
1. Fresadoras horizontais
Em tais máquinas, o fuso é montado horizontalmente, mas paralelo à mesa de trabalho. Toda esta configuração ajuda as máquinas a realizar operações de fresamento, colocando as fresas no eixo horizontal. Então, essas máquinas são altamente compatíveis para lidar com operações pesadas e em grande escala. Além disso, eles fornecem estabilidade e potência para cortar materiais duros. Essas máquinas têm uma alta taxa de remoção e podem conter diversas ferramentas. Então, eles são usados para fazer ranhuras de corte, engrenagens, e formas complexas.
2. Fresadoras verticais
As fresadoras verticais montam o fuso verticalmente e giram a ferramenta de corte. Aqui a peça de trabalho é colocada na horizontal e pode se mover em várias direções. Essas máquinas são altamente adequadas para fabricar peças detalhadas e precisas. Então, eles têm várias aplicações em perfuração, ranhura, e corte de componentes de pequeno e médio porte. além disso, eles são perfeitos para engenharia de precisão, prototipagem, e produção de pequenos lotes.
3. 5-Fresadoras de eixo
Tais máquinas permitem a movimentação das ferramentas de corte em cinco eixos, simultaneamente, ou seja. (X, S, Z, A, e B). Então, eles podem fazer peças complexas facilmente. Esta é a razão, eles têm mais flexibilidade e podem criar várias formas em apenas uma configuração. Esses 5-máquinas de eixo agora são usados em diferentes aplicações, ou seja. aeroespacial, automotivo, médico, e indústrias de fabricação de moldes para fabricação de pás de turbinas, implantes ortopédicos, e moldes intrincados.
4. Fresadoras de cama
Aqui o fuso é montado em um eixo giratório e pode girar. Enquanto a mesa de trabalho está parada. Eles são amplamente utilizados na fabricação de peças grandes e pesadas. Eles podem lidar com peças que precisam de suporte estável e vibrações mínimas. Então, essas máquinas são estáveis e comumente usadas na fabricação de peças, como a construção naval, construção, e fabricação de blocos de motor, quadros estruturais, e moldes grandes.
Aplicações de fresagem CNC
Aqui estão as diversas aplicações do processo de fresagem CNC. Vamos discuti-los em detalhes.
- Aeroespacial: Isso é amplamente utilizado na fabricação de componentes de precisão para aeronaves e espaçonaves..
- Automotivo: A fresagem CNC ajuda a fabricar peças de motor e componentes de transmissão.
- Médico: No setor médico, A fresagem CNC ajuda a fabricar instrumentos cirúrgicos e implantes.
- Eletrônicos: É usado para fazer caixas e gabinetes.
- Fabricação: A fresagem CNC também é adequada para fazer protótipos e peças personalizadas.
Benefícios e limitações da fresagem CNC
Aqui estão algumas vantagens e desvantagens das fresadoras CNC.
| Aspecto | Benefícios | Limitações |
| Precisão | Alta precisão e repetibilidade | Requer calibração e manutenção adequadas |
| Versatilidade | Produz formas complexas e detalhes intrincados | Habilidades avançadas de programação necessárias |
| Eficiência | Produção mais rápida, menos trabalho manual | Alto tempo de configuração inicial |
| Consistência | Peças idênticas em grandes quantidades | Risco de grandes lotes de defeitos se ocorrerem erros |
| Flexibilidade | Facilmente reprogramável para diferentes peças | Operadores e programadores qualificados são necessários |
| Faixa de materiais | Máquinas com uma variedade de materiais | Ferramentas especializadas necessárias para materiais muito duros |
| Custos trabalhistas | Necessidade reduzida de trabalho manual | Altos custos iniciais e de manutenção |
| Segurança | Risco reduzido de acidentes manuais | Requer protocolos de segurança rígidos |
| Escalabilidade | Adequado para produção de baixo e alto volume | Alto volume precisa de várias máquinas e espaço |
| Controle de qualidade | Monitoramento avançado de qualidade | Manutenção regular necessária |
| Geometrias Complexas | Produz peças complexas com tolerâncias restritas | Tempos de usinagem mais longos para peças complexas |
| Redução de resíduos | O corte preciso reduz o desperdício de material | Alguns resíduos materiais ainda estão presentes em processos subtrativos |
O que pode dar errado?
Enquanto o moinho de CNC oferece muitos benefícios, Existem vários fatores que podem dar errado durante o processo de moagem. Esses problemas podem levar a defeitos na parte final, Custos aumentados, e atrasos na produção. Abaixo estão alguns dos problemas comuns que podem ocorrer durante as operações de moagem do CNC:
1. Erros de configuração da máquina
- A configuração incorreta da máquina CNC é uma das fontes mais comuns de problemas. Isso pode incluir alinhamento inadequado da peça, Seleção incorreta da ferramenta, ou falha em calibrar adequadamente a máquina. Esses erros podem levar a resultados de usinagem inadequados, como dimensões imprecisas, Desgaste da ferramenta, ou até danos à máquina.
- Para evitar isso, É essencial ter um operador bem treinado que possa configurar e verificar cuidadosamente a máquina antes de iniciar o processo de moagem.
2. Problemas materiais
- A qualidade do material que está sendo fresada também pode afetar o resultado final. Materiais que não são uniformes ou têm defeitos, como rachaduras ou inclusões, pode causar problemas durante a usinagem. Esses defeitos podem levar a peças mais fracas, tem acabamentos superficiais ruins, ou não estão dentro da especificação.
- Usar materiais de alta qualidade e realizar uma inspeção completa antes da moagem pode ajudar a minimizar esses problemas.
3. Desgaste e dano da ferramenta
- A moagem do CNC envolve o uso de ferramentas de corte que podem se desgastar ao longo do tempo devido ao contato contínuo com a peça de trabalho. Se as ferramentas não forem substituídas ou mantidas regularmente, Pode resultar em acabamentos superficiais ruins, imprecisões dimensionais, e aumento do desgaste da ferramenta. Esse, por sua vez, pode levar a custos de produção e atrasos mais altos.
- Manutenção regular, Inspeção da ferramenta, e a seleção adequada de ferramentas com base no material usinado pode ajudar a prolongar a vida útil da ferramenta e manter a qualidade da usinagem.
4. Erros de programação
- A moagem da CNC depende de programação precisa para executar as operações desejadas. Se houver um erro na programação, como instruções incorretas do código G ou coordenadas imprecisas, Pode resultar em partes que não atendem às especificações. Isso pode incluir peças muito grandes, Muito pequeno, ou com recursos nos locais errados.
- Verificar minuciosamente os testes de programação e execução de simulação antes da moagem real pode ajudar a identificar possíveis problemas antes que eles afetem a produção.
5. Superaquecimento
- As máquinas de moagem CNC operam em alta velocidade, gerando calor significativo durante o processo de usinagem. Se a máquina não estiver devidamente resfriada, pode causar superaquecimento, levando a expansão térmica e imprecisões dimensionais. O superaquecimento também pode acelerar o desgaste da ferramenta e danificar o material.
- Usando o líquido de arrefecimento durante o processo de moagem, garantir a ventilação adequada, e monitorar a temperatura da máquina pode ajudar a evitar problemas de superaquecimento.
6. Acabamento superficial ruim
- Um acabamento superficial ruim pode ocorrer se as ferramentas de corte não forem nítidas o suficiente, Se a velocidade de usinagem for muito alta ou muito baixa, ou se o material não for apoiado adequadamente durante a moagem. Isso pode resultar em bruto, superfícies irregulares ou rebarbas excessivas que precisam de trabalho de acabamento adicional.
- Para evitar acabamentos superficiais ruins, É essencial selecionar os parâmetros de corte certos, Use ferramentas apropriadas, e verifique se a peça de trabalho está presa com segurança.
7. Problemas de ferramentas e acessórios
- As ferramentas e acessórios usados para manter a peça de trabalho no local durante a moagem do CNC também podem levar a problemas. Se a peça de trabalho não estiver presa, pode mudar durante o processo de usinagem, resultando em partes com dimensões inconsistentes. De forma similar, As ferramentas incorretas ou desgastadas podem levar a cortes ruins e desgaste excessivo de ferramentas.
- Garantir o design adequado do acessório e usar as ferramentas certas para cada trabalho pode ajudar a minimizar esses problemas.
Processos alternativos para operações de moagem
Enquanto a moagem do CNC é um dos métodos mais populares para usinagem de peças, Existem vários processos alternativos que podem ser usados, dependendo dos requisitos específicos da peça e do material. Esses processos alternativos são frequentemente escolhidos para suas vantagens únicas em determinadas aplicações:
1. Torneamento CNC
A torção do CNC é usada para criar peças cilíndricas ou cônicas, girando a peça de trabalho contra uma ferramenta de corte estacionária. É ideal para peças que têm simetria rotacional, como eixos, parafusos, e acessórios. A torção do CNC é tipicamente mais rápida que a moagem do CNC e é particularmente eficiente para a produção de alto volume de peças redondas.
2. Corte a laser
O corte a laser usa um feixe de laser focado para cortar materiais com alta precisão. É especialmente útil para cortar materiais finos, como chapha metal, plásticos, e madeira. O corte a laser fornece bordas de alta qualidade e é altamente eficiente para geometrias simples e complexas, Mas geralmente é limitado a materiais mais finos em comparação com a moagem do CNC.
3. Corte por jato de água
O corte a jato de água usa um fluxo de água de alta pressão (frequentemente misturado com partículas abrasivas) Para cortar os materiais. É ideal para materiais que não podem suportar o calor gerado por laser ou corte de plasma, como compósitos, cerâmica, e metais sensíveis. O corte a jato de água oferece alta precisão e pode ser usado em uma ampla variedade de materiais, incluindo metais, plásticos, e pedra.
4. Usinagem por descarga elétrica (Música eletrônica)
O EDM é um processo de usinagem de precisão que usa descargas elétricas (faíscas) Para remover o material da peça de trabalho. Esse processo é ideal para criar formas intrincadas e detalhes finos em materiais duros ou duros, como aços de ferramentas e carboneto. O EDM é amplamente utilizado para criar moldes, morre, e peças com geometrias complexas que são difíceis de alcançar através dos métodos tradicionais de usinagem.
5. 3Impressão D (Fabricação aditiva)
3D impressão, ou fabricação aditiva, é um processo que constrói a camada de peças por camada usando materiais como plástico, metal, ou cerâmica. É particularmente vantajoso para produzir protótipos, peças de baixo volume, e peças com geometrias complexas que seriam difíceis ou impossíveis de usinar usando a moagem CNC. 3A impressão D também é mais econômica para pequenas execuções de produção e reduz o desperdício de materiais em comparação com processos subtrativos.
6. Carimbo e socos
Estampagem e os socos são processos onde um dado é usado para cortar, forma, ou formar materiais. Esses processos são mais comumente usados para chapa metal e são eficientes para produzir altos volumes de peças. Carimbo e perfuração geralmente são mais rápidos e mais econômicos que a moagem da CNC ao lidar com materiais finos e formas simples.
7. Fundição
Fundição envolve derramar material líquido (geralmente metal ou plástico) em um molde para criar uma parte. Esse processo é frequentemente usado para produzir peças com formas complexas difíceis de fazer a máquina. O elenco pode ser uma alternativa econômica à moagem CNC para produção de alto volume, especialmente para peças feitas de materiais como alumínio, ferro, ou bronze.
CNC Milling vs CNC girando
Enquanto ambos Fresamento CNC e Torneamento CNC são processos de fabricação subtrativos que envolvem a remoção do material de uma peça de trabalho para criar uma peça acabada, Eles são diferentes em sua operação e aplicações adequadas. Aqui está uma comparação de ambos os métodos:
1. Fresagem CNC
- Processo: A moagem do CNC envolve o uso de uma ferramenta de corte rotativa que se move ao longo de vários eixos para remover o material de uma peça de trabalho estacionária. A máquina -ferramenta é movida em várias direções (geralmente 3, 4, ou 5 eixos) Para moldar a parte. O moinho de CNC é altamente versátil e pode ser usado para produzir uma grande variedade de formas, incluindo superfícies planas, contornos, buracos, e formas 3D complexas.
- Formulários: O moinho de CNC é usado para fazer peças com formas irregulares, geometrias complexas, e peças que requerem vários recursos ou bolsos profundos. É adequado para produzir componentes com contornos complexos, rostos, buracos, ou recursos 3D, como em indústrias como aeroespacial, automotivo, e dispositivos médicos.
- Vantagens:
- Capacidade de criar formas complexas e recursos 3D.
- Versatilidade para trabalhar com uma ampla gama de materiais (metais, plásticos, compósitos).
- Pode ser usado para protótipo e produção de alto volume.
- Limitações:
- Relativamente mais lento do que girar ao usinar peças cilíndricas.
- Pode exigir configurações mais complexas para determinadas geometrias.
2. Torneamento CNC
- Processo: A virada da CNC envolve girar uma peça de trabalho enquanto uma ferramenta de corte estacionária remove o material. A peça de trabalho é mantida em um mandril ou acessório e girada ao longo de seu eixo, com a ferramenta de corte se movendo ao longo dos eixos X e Z para moldar a parte. A torneamento do CNC é comumente usada para produzir cilíndricos, cônico, ou peças esféricas com simetria rotacional.
- Formulários: A torneamento da CNC é ideal para criar uma rodada, cilíndrico, ou partes simétricas, como eixos, buchas, e componentes roscados. É normalmente usado para peças com um alto grau de simetria rotacional ou geometrias simples, frequentemente visto em indústrias como automotivo, usinagem, e eletrônica.
- Vantagens:
- Altamente eficiente para criar peças cilíndricas.
- Remoção de material mais rápida para peças redondas em comparação com a moagem.
- Pode produzir peças com alta precisão e acabamentos suaves.
- Limitações:
- Limitado a peças com simetria rotacional.
- Menos flexibilidade na criação de formas 3D complexas ou recursos irregulares.
Resumo das diferenças
| Recurso | Fresagem CNC | Torneamento CNC |
| Movimento | Cutter rotativo se move em vários eixos (X, S, Z, A, B) | A peça de trabalho gira; Cutter se move ao longo dos eixos X e Z |
| Formulários | Formas complexas, 3D Recursos, superfícies planas ou contornadas | Redondo, cilíndrico, ou partes simétricas |
| Velocidade | Mais lento para peças cilíndricas | Mais rápido para peças redondas |
| Flexibilidade | Alto; pode criar peças 3D complexas | Limitado a peças rotacionalmente simétricas |
| Materiais comuns | Metais, plásticos, compósitos | Metais, plásticos |
Quanto custa a fresagem CNC?
Diferentes indústrias oferecem preços diferentes. Mas aqui estão alguns custos estimados que podem ajudá-lo a entender as opções de orçamento disponíveis no mercado.
| Fator de custo | Descrição | Faixa Típica |
| Tempo da Máquina | Taxa horária para uso da máquina CNC | $50 – $200 por hora |
| Custos de configuração | Configuração inicial e calibração da máquina | $100 – $500 por configuração |
| Custos de ferramentas | Custo de ferramentas e acessórios de corte | $20 – $100+ por ferramenta |
| Custos de materiais | Custo das matérias-primas | Varia amplamente com base no material |
| Custos de programação | Custo para criação de programas CNC (Código G) | $50 – $100 por hora |
| Custos de acabamento | Processos adicionais como rebarbação, revestimento | $10 – $50 por parte |
O futuro da moagem do CNC
1. Automação e robótica
A automação no moinho de CNC está se expandindo além da operação tradicional da máquina. Braços robóticos e trocadores de ferramentas automatizados estão sendo integrados aos sistemas CNC, permitindo linhas de produção totalmente automatizadas que operam 24/7. Isso reduz os custos de mão -de -obra, acelera a produção, e aumenta a precisão, especialmente na fabricação de alto volume. Os robôs também estão sendo usados para manuseio de peças e inspeção de qualidade, Aumentar ainda mais a eficiência do fluxo de trabalho.
2. 3D Impressão e fabricação híbrida
A combinação de Moagem CNC e impressão 3D está emergindo como uma solução de fabricação híbrida. Este processo híbrido permite que os fabricantes usem a impressão 3D para recursos aditivos (como estruturas internas complexas) e moagem CNC para usinagem subtrativa de recursos externos precisos. Essa abordagem não apenas reduz o desperdício de material, mas também melhora a flexibilidade e a complexidade das partes que podem ser produzidas.
3. Moagem CNC baseada em nuvem
Moagem CNC baseada em nuvem está revolucionando a indústria, permitindo que os fabricantes controlem as máquinas CNC remotamente via software conectado à nuvem. Isso permite o monitoramento em tempo real, Diagnóstico, e atualizações de software de qualquer local. As plataformas em nuvem também facilitam colaboração entre engenheiros e designers, Melhorando o fluxo de trabalho de design para produção. Além disso, Os sistemas baseados em nuvem permitem melhor armazenamento e análise de dados, Melhorando a otimização do processo e a tomada de decisão.
4. Sustentabilidade e eficiência energética
Como as indústrias se concentram mais em sustentabilidade, futuras máquinas de moagem CNC estão sendo projetadas para serem mais eficiente de energia e ecologicamente correto. As inovações incluem Sistemas de refrigeração aprimorados, Materiais recicláveis, e recursos de economia de energia que minimizam o consumo de energia. Adicionalmente, Reduzir o desperdício de materiais por meio de usinagem de precisão e melhor gerenciamento de vida útil da ferramenta ajudará as empresas a cumprir as metas de sustentabilidade.
5. Aumento da precisão e micro-fabricação
Como as indústrias exigem maior precisão e micro-manufatura recursos, O moinho de CNC está evoluindo para atender a essas necessidades. O uso de micro-usinagem As tecnologias permitirão a produção de componentes extremamente pequenos e detalhados, como os usados em eletrônicos, dispositivos médicos, e aplicações aeroespaciais. Essas inovações permitirão a criação de peças com tolerâncias medidas em microns, alcançar níveis sem precedentes de precisão.
O que Sdeve ser COnsidered Cgalinha CDosagem CNC Mdoença Manufator?
Ao selecionar a Fabricante de moagem CNC, Vários fatores importantes devem ser levados em consideração para garantir que o fabricante atenda às suas necessidades e requisitos específicos. Abaixo estão as principais considerações para ajudar a guiar sua decisão:
-
Experiência e experiência
O fabricante experiência e especialização na moagem do CNC são críticos. É importante escolher um fabricante com um histórico comprovado na produção dos tipos de peças que você precisa. Garanta que eles tenham experiência nas indústrias ou materiais específicos relevantes para o seu projeto, Seja aeroespacial, automotivo, médico, ou outro setor. Sua compreensão das propriedades do material e das técnicas de usinagem afetará a qualidade e a precisão das peças que eles produzem.
-
Tecnologia e equipamento
Um dos principais fabricantes de moagem CNC deve ter acesso ao último Máquinas CNC e tecnologia de ponta. As capacidades das máquinas, como o número de eixos (3-eixo, 4-eixo, ou 5 eixos), e o tipo de ferramenta que eles usam influenciarão a complexidade e a precisão das peças produzidas. Verifique se o fabricante usa máquinas avançadas que podem lidar com os requisitos específicos do seu projeto, especialmente se você precisar de alta precisão ou trabalhar com geometrias complexas.
-
Controle de qualidade e precisão
Controle de qualidade é essencial na moagem do CNC. O fabricante deve ter processos rígidos de garantia de qualidade para garantir que todas as partes produzidas atendam às suas especificações. Isso inclui o uso de instrumentos de medição calibrada, Inspeção em vários estágios de produção, e aderir aos padrões da indústria. Certifique -se de perguntar sobre o fabricante níveis de tolerância e a capacidade deles de atender à sua precisão desejada.
-
Tempo de resposta
A pontualidade é um fator crítico em muitas indústrias. Discutir com o fabricante o seu Tempos de entrega Para projetos de moagem CNC, e verifique se eles podem cumprir seus prazos de produção. Um fabricante confiável deve fornecer horários de entrega precisos e ser transparentes sobre sua capacidade de lidar com ordens urgentes, se necessário.
-
Personalização e Flexibilidade
Seu projeto pode exigir soluções personalizadas, Portanto, é essencial escolher um fabricante que ofereça flexibilidade em seus serviços. Isso pode incluir a capacidade de trabalhar com uma variedade de materiais, Ofereça o desenvolvimento de protótipos, ou acomodar mudanças nos desenhos. Um bom fabricante de moagem CNC deve ser capaz de se adaptar às suas necessidades específicas e ajudar a otimizar os projetos para fabricação.
-
Estrutura de custos e preços
O custo da moagem do CNC varia dependendo de fatores como material, complexidade, e quantidade. É importante conseguir um compreensão clara da estrutura de preços do fabricante. Peça cotações detalhadas e considere se o preço é justificado pela qualidade e serviço oferecidos. Compare preços de vários fabricantes, Mas não faça custar o único fator decisivo. Às vezes, Custos antecipados mais altos podem levar a melhores resultados e economias a longo prazo devido à melhoria da qualidade e aos tempos de produção mais rápidos.
-
Suporte ao Cliente e Comunicação
Eficaz comunicação e Suporte ao cliente são vitais em todo o processo de moagem do CNC. O fabricante deve fornecer comunicação clara e oportuna, mantendo você atualizado sobre o progresso do seu projeto. Eles também devem responder às suas perguntas e oferecer suporte se surgirem algum problema durante o processo de produção.
Por que escolher TOPS para fresamento CNC?
TOPOS é uma indústria principal, oferecendo diferentes tipos de operações de fresagem. Nossas instalações estão equipadas com diferentes fresadoras CNC. Podemos realizar várias operações de moagem em menos tempo. além disso, temos uma equipe especializada e engenheiros que nos ajudam a fabricar peças precisas e de alta precisão em grandes quantidades. Então, se você está procurando serviços especializados de fresagem CNC. Estamos aqui para atendê-lo de todas as maneiras possíveis. Obtenha sua cotação hoje.
Conclusão
Para concluir, A fresagem CNC é uma maneira única e precisa de fazer diferentes peças de trabalho. Ajuda a remover o excesso de material preso à peça metálica e proporciona um acabamento liso. além disso, é um processo importante para diversas indústrias, ou seja. automotivo, aeroespacial, construção, e eletrônica. Então, A fresagem CNC é capaz e benéfica para fazer protótipos e produções de grande volume.
perguntas frequentes
1º trimestre. Como você diferenciaria entre fresamento CNC e Torneamento CNC?
Embora ambos os processos ajudem a cortar o excesso de material. Mas eles têm configurações diferentes. A fresagem CNC possui ferramentas de corte rotativas que cortam o material. Torneamento CNC possui ferramentas de corte estacionárias e cortam a peça rotativa usando um torno.
2º trimestre. Quais materiais suportam as máquinas de moagem CNC?
Estas máquinas podem trabalhar com diferentes materiais, ou seja. metais, plásticos, compósitos, e madeira.
3º trimestre. Quão precisas são as fresadoras CNC?
Essas máquinas são bastante precisas e precisas. Eles podem alcançar precisão dentro de micrômetros. Então, depende das capacidades da máquina e do material que você usa.
4º trimestre. Qual é a diferença entre guias e slideways?
As principais diferenças entre guias e slideways estão em precisão, complexidade estrutural, Áreas de aplicação, e capacidade de suporte de carga. Os guias são mais adequados para alta precisão, aplicações de alta carga e são comumente encontradas em máquinas CNC avançadas, enquanto slideways são usados em mais simples, Aplicações mais leves, onde o custo é um fator-chave.
Q5. Há muita matemática na usinagem do CNC?
Sim, Há uma quantidade razoável de matemática envolvida no CNC (Controle Numérico Computadorizado) usinagem. Enquanto a própria máquina CNC é controlada por software que automatiza muitos aspectos do processo de usinagem, Entender e aplicar a matemática é essencial para vários estágios da usinagem CNC, como design, programação, configurar, e solução de problemas.
Q6. Quão difícil é aprender o moinho de CNC?
Aprender a moagem do CNC pode variar em dificuldade, dependendo do seu conhecimento prévio e da profundidade da experiência que você deseja alcançar. No entanto, Como muitas habilidades técnicas, com os recursos e prática certos, O moinho de CNC pode ser aprendido passo a passo.










16 pensamentos "O que é fresagem CNC | O guia definitivo de fresamento CNC”