Casting de zinco é um processo de pedra angular na fabricação de precisão, oferecendo precisão dimensional excepcional, força, e custo-efetividade. De componentes automotivos a dispositivos médicos, ligas de zinco são usadas para criar peças duráveis e complexas com excelentes acabamentos superficiais e tolerâncias restritas.
Este guia abrangente explora os principais aspectos da fundição sob pressão de zinco - desde os princípios e métodos de trabalho até as máquinas líderes, propriedades da liga, aplicações comuns, e as inúmeras vantagens que tornam o zinco a melhor escolha para componentes de alto desempenho.
O que é fundição sob pressão de zinco?
A fundição sob pressão de zinco é um processo de fabricação no qual o zinco fundido é injetado sob alta pressão em moldes de aço. (morre) para formar preciso, peças repetíveis. Devido ao ponto de fusão relativamente baixo do zinco (~420–450°C) e moldabilidade superior, o processo permite paredes finas, complexo, e peças de alta resistência.
As ligas de zinco usadas na fundição sob pressão - como as séries Zamak e ZA - são projetadas para propriedades mecânicas aprimoradas, incluindo resistência ao desgaste, estabilidade dimensional, e resistência. Estas ligas permitem a criação de peças com características finas, tolerâncias apertadas (± 0,001 in / 0.0254 milímetros), e excelentes acabamentos superficiais adequados para revestimento ou pintura.
Métodos de fundição sob pressão de zinco
Visão geral
As técnicas de fundição sob pressão dependem de injeção de alta pressão para obter o preenchimento completo do molde e a replicação precisa da geometria do molde. A fluidez superior e o baixo ponto de fusão do zinco o tornam ideal para este processo, permitindo designs complexos e alta repetibilidade.
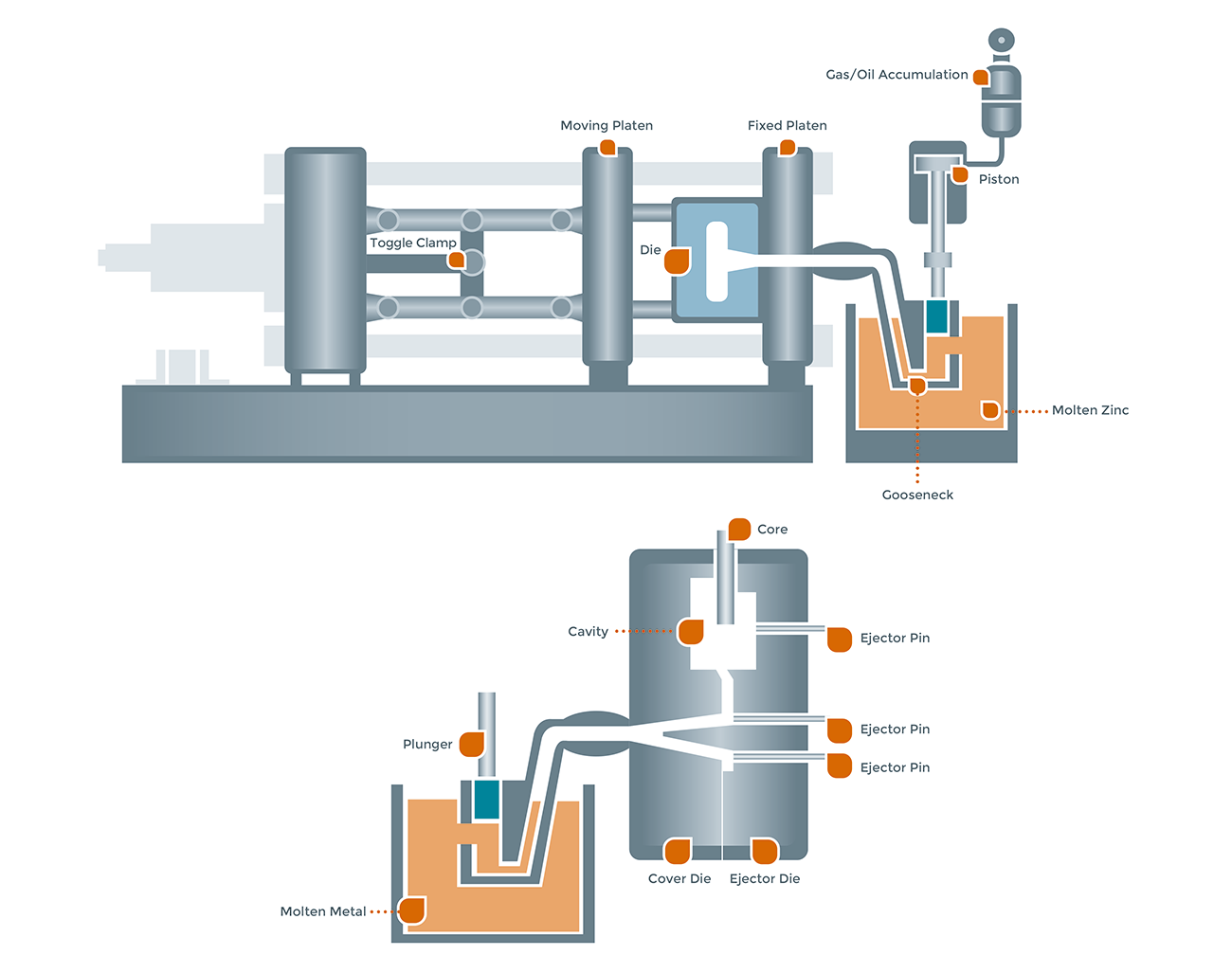
Fundição sob pressão de zinco em câmara quente
Componentes do Processo:
Forno: Integrado com a máquina, derretendo e alimentando continuamente liga de zinco.
Pescoço de ganso: Transfere zinco fundido do forno para a matriz.
Bocal: Canaliza o zinco para a cavidade da matriz.
Êmbolo: Fornece força de injeção até 5000 psi.
Tipos de matrizes:
Dado Único: Para protótipos ou pequenas tiragens.
Dados Múltiplos: Para produção em massa, reduz o custo por peça.
Matriz de Combinação: Funde peças diferentes em um único ciclo.
Dado da Unidade: Insertos modulares para trocas rápidas.
Etapas do processo:
Enchimento: O êmbolo puxa o zinco fundido para a câmara de injeção.
Injeção: De alta velocidade, injeção de alta pressão na matriz.
Retenção de pressão: Mantém a pressão durante a solidificação.
Resfriamento: Dissipação rápida de calor para tempos de ciclo rápidos.
Ejeção e Acabamento: A peça é ejetada e acabada por meio de corte, polimento, ou revestimento.
A fundição em câmara quente é preferida para peças pequenas e médias que exigem alto volume e tolerâncias restritas.
Fundição sob pressão de zinco em câmara fria
Usado quando são necessárias ligas de zinco com pontos de fusão mais elevados ou composições especiais.
Componentes:
Forno Separado: Externo, fornece melhor controle de liga.
Câmara de tiro: Câmara pré-aquecida minimiza defeitos.
Êmbolo Hidráulico: Força o zinco fundido no molde.
Etapas do processo:
Concha: A liga de zinco é derramada na câmara.
Injeção: O êmbolo hidráulico injeta zinco na matriz.
Resfriamento & Ejeção: O molde esfria e a peça é ejetada.
Acabamento: Tratamentos de superfície conforme necessário.
A fundição em câmara fria é ideal para, componentes mais densos e proporciona mais flexibilidade no uso da liga.
Principais máquinas de fundição sob pressão de zinco
A fundição sob pressão de alto desempenho requer equipamentos de precisão. Abaixo estão máquinas notáveis usadas globalmente:
Urpé CC25
Forno integrado, 42 força kN
Ideal para produção contínua e peças de médio porte
Modos manuais para totalmente automáticos
Francês ZL60
Sistema modular de câmara quente
Adapta-se a uma ampla variedade de tamanhos de peças
Monitoramento em tempo real, eficiente de energia
BühlerPrince HMT1600
Máquina resistente para fundições industriais de zinco
Placa grande, controles de circuito fechado
Sistema de injeção multiestágio
Techmire ZDC-2000
Compactar, máquina multi-slide
Adequado para alta mixagem, corridas de baixo volume
Velocidade e precisão excepcionais
ZP francês 8
Máquina de câmara quente de alta capacidade
Pulverização de matriz integrada e controle de processo
Sistema de servo injeção
Cada máquina oferece recursos exclusivos em termos de força de fixação, velocidade de tiro, automação, e compatibilidade de liga.
Ligas de zinco usadas em fundição sob pressão
As ligas de fundição sob pressão de zinco são projetadas para oferecer desempenho em diversas aplicações industriais. Eles incluem:
Série de cargas
os fardos 2: Alta dureza e resistência à fluência.
os fardos 3: Mais comum, Excelente estabilidade dimensional.
os fardos 5: Mais forte, melhor resistência à corrosão do que Zamak 3.
PARA 8: Alumínio mais alto, usado em processos de câmara quente.
Ligas Especiais
ACuZinc5: Alto teor de cobre para resistência ao desgaste.
EZAC: Desenvolvido para resistência à fluência e estabilidade térmica.
ZA-12: Gravidade ou câmara fria adequada, para peças de alta resistência.
GDSL: Fundição ultrafina, espessura da parede tão baixa quanto 0.3 milímetros.
A seleção depende da força, ductilidade, resistência à corrosão, desempenho de fluência, e requisitos específicos da aplicação.
Aplicações de fundição sob pressão de zinco
A fundibilidade e a resistência do zinco permitem seu uso em diversas indústrias:
Automotivo
Engrenagens do cinto de segurança, fechaduras de portas, caixas de airbag
Molduras de espelho retrovisor, limpadores de pára-brisa
Suportes estruturais e peças de transmissão
Instrumentos médicos
Alojamento para ferramentas de diagnóstico
Engrenagens e juntas para mesas cirúrgicas
Blindagem EMI em equipamentos de monitoramento
Fechaduras e ferragens
Acabamentos lisos e alta durabilidade para fechaduras tubulares
Usado em sistemas de segurança comerciais e residenciais
Eletrônicos
Gabinetes com blindagem EMI/RFI
Dissipadores de calor com aletas integradas detalhadas
Componentes personalizados
Projetos totalmente personalizados com geometrias complexas
Peças de precisão de paredes finas para montagens
Vantagens da fundição sob pressão de zinco
Eficiência de custos de ferramentas
Aço P20 usado para matrizes de zinco (contra. H13 para alumínio), reduzindo custos
Morrer vida útil: 1,000,000+ tiros - 10x mais do que o alumínio
Desempenho Mecânico
Força elevada, rigidez, e resistência à fluência
Forte resistência ao impacto mesmo em baixas temperaturas
Precisão Dimensional
Tolerâncias: ± 0,001 in
Espessura da parede tão baixa quanto 0.006 em (0.15 milímetros)
Nega a necessidade de usinagem na maioria dos casos
Condutividade
Excelente desempenho térmico e elétrico
Adequado para aplicações de blindagem (EMI, RFI, ESD)
Geometrias Complexas
Bordas afiadas, paredes finas, recursos integrados
Perfeito para montagens mecânico-funcionais
Acabamento de superfície superior
Superfícies prontas para uso com trabalho secundário mínimo
Compatível com cromatização, pintura, e chapeamento
Alta taxa de produção
150–Tempos de ciclo 200% mais rápidos que o alumínio
O processo de câmara quente combina fusão e injeção
Integração de montagem eficiente
Matrizes combinadas para fundição de múltiplas peças
Reduz etapas de mão de obra e montagem
Conclusão
A fundição sob pressão de zinco continua sendo uma das soluções de fabricação mais econômicas e versáteis do mundo industrial. Aproveitando o baixo ponto de fusão do material, excelente moldabilidade, força mecânica, e reprodução de detalhes finos, indústrias podem alcançar alto volume, produção de precisão a custos reduzidos.
Quer você esteja adquirindo componentes automotivos leves, intrincados gabinetes eletrônicos, ou elementos estruturais duradouros, a fundição sob pressão de zinco oferece uma combinação única de velocidade, precisão, e força que poucos outros processos podem igualar.
Para resultados ideais, os fabricantes devem selecionar o método de fundição correto (câmara quente ou fria), liga apropriada, e máquina adequada. A parceria com fornecedores experientes de fundição sob pressão garante a qualidade do produto, desempenho a longo prazo, e posicionamento competitivo no mercado.
Leia mais:
Fundição sob pressão vs.. Usinagem CNC: O que é certo para sua parte?
Câmara quente vs.. Comparação de fundição sob pressão em câmara fria
Guia completo para fundição de matrizes de alumínio
Materiais de fundição sob pressão