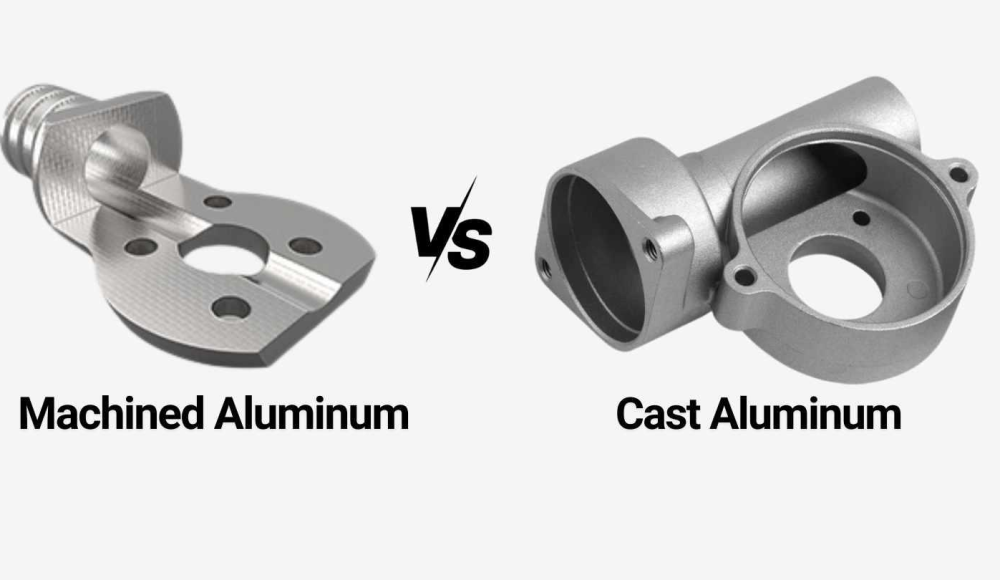
Aluminium est l'un des métaux les plus utilisés dans la fabrication moderne, valorisé pour son poids léger, résistance à la corrosion, et excellentes propriétés mécaniques. Lors de la production de pièces en aluminium, Deux méthodes principales sont couramment utilisées: la casting et l'usinage. Mais comment comparent-ils, Et lequel est le mieux pour vos besoins spécifiques?
Cet article explorera les différences entre l'aluminium coulé et Aluminium usiné, leurs avantages, inconvénients, et les facteurs à considérer lors du choix de la bonne méthode pour votre projet.
Introduction
L’industrie de l’aluminium dans des industries telles que l’aérospatiale, automobile, électronique, et la construction provient de ses propriétés uniques. Le choix entre les pièces en aluminium de coulée et d'usinage dépend de facteurs comme la complexité de conception, volume de production, exigences de précision, et des considérations de coûts.
Qu'est-ce que l'aluminium usiné?
Définition et processus
Les pièces en aluminium usinées sont créées en éliminant le matériau d'un bloc solide d'aluminium à l'aide d'outils de coupe contrôlés par un contrôle numérique d'ordinateur (CNC) machines. Ce processus de fabrication soustractif permet une haute précision et est idéal pour produire des géométries complexes avec des tolérances étroites.
Techniques d'usinage communes
- Fraisage CNC: Implique des outils de coupe rotatifs pour éliminer le matériau de la pièce, permettant la création de formes et de fonctionnalités complexes.
- Tournage CNC: La pièce est tournée tandis qu'un outil de coupe stationnaire le façonne, qui est couramment utilisé pour produire des pièces cylindriques.
- Forage: Utilise des bits de forage rotatifs pour créer des trous précis dans la pièce en aluminium.
- Affûtage: Emploie des roues abrasives pour obtenir des finitions de surface fines et des dimensions précises.
Industries qui utilisent l'aluminium usiné
- Aérospatial: Composants tels que les pièces et boîtiers structurels des avions.
- Automobile: Pièces de moteur, dissipateurs de chaleur, et composants de suspension.
- Médical: Instruments chirurgicaux et dispositifs prothétiques.
- Électronique: Enveloppes d'ordinateur et connecteurs de précision.
L'usinage est préféré dans les applications nécessitant une haute précision, force, et excellentes finitions de surface.
Qu'est-ce que l'aluminium coulé?
Définition et processus
Les parties en aluminium coulées sont produites en versant de l'aluminium fondu dans des moules, où il se solidifie dans la forme souhaitée. Ce processus est bien adapté pour créer des géométries complexes et est rentable pour les courses de production à haut volume.
Méthodes de coulée courantes
Coulée de moisissure permanente
- Moulage sous pression: L'aluminium fondu est injecté sous haute pression dans les moules en acier, permettant une production rapide de pièces précises.
- Coulée sous vide: Un vide aide à attirer l'aluminium fondu dans le moule, Réduire le piégeage de l'air et améliorer la qualité des pièces.
- Moulage d'investissement: Utilise des motifs de cire pour créer des moules pour produire des composants complexes et détaillés.
Coulée de moisissure consommable
- Coulée de sable: Emploie des moules à base de sable qui sont détruits après chaque utilisation, Le rendre adapté à de grandes pièces et à des volumes de production inférieurs.
- Casting de cire perdu: Implique la création d'un modèle de cire, l'enrober d'un matériau réfractaire pour former un moule, puis fondre la cire et verser en aluminium fondu.
Les industries qui utilisent l'aluminium coulé
Automobile: Blocs de moteur, cas de transmission, et des roues.
Construction: Composants architecturaux et supports structurels.
Appareils: Pièces pour les poêles, machines à laver, et équipement de cuisine.
La coulée est avantageuse pour produire des formes complexes et est rentable pour la production de masse.
Différences clés entre l'aluminium usiné et coulé
| Catégorie | Aluminium usiné | Couler en aluminium |
| Types de matériaux | Les alliages communs incluent 6061, 7075, et 2024, connu pour leur force et leur machinabilité. | Utilise généralement des alliages comme A356, A380, et A390, choisi pour leurs propriétés de coulée et leurs caractéristiques mécaniques. |
| Vitesse de production | Convient aux volumes de production faible à moyenne; La configuration est rapide, Mais le temps d'usinage augmente avec la complexité en partie. | Efficace pour la production à haut volume une fois les moules créés; La fabrication initiale des moisissures peut prendre du temps et coûteuse. |
| Finition de surface | Atteint des finitions lisses et personnalisables directement à partir du processus d'usinage; Le polissage supplémentaire peut améliorer l'apparence. | Peut présenter des imperfections de surface; nécessite souvent le post-traitement comme l'usinage ou le polissage pour atteindre la finition souhaitée. |
| Précision & Tolérances | Capable d'atteindre des tolérances étroites, Le rendre idéal pour les composants où la précision est critique. | Offre généralement une précision plus faible en raison de facteurs tels que l'usure des moisissures et le retrait du métal pendant le refroidissement; adapté aux pièces où les tolérances exactes sont moins critiques. |
| Force & Durabilité | Les pièces usinées maintiennent la résistance inhérente du matériau et sont exemptes de défauts internes, offrir une haute fiabilité. | Les pièces coulées peuvent contenir une porosité ou des inclusions, Potentiellement réduction de la résistance; cependant, Ils sont adéquats pour de nombreuses applications. |
| Considérations relatives aux coûts | Coût plus élevé par unité en raison du temps d'usinage et de l'usure des outils; Pas besoin de moules coûteux, le rendre rentable pour les petits lots ou les prototypes. | Coût inférieur par unité en production de masse, Mais l'investissement initial dans la création de moisissures est substantiel; RETENDANT pour les grandes quantités. |
| Meilleures applications | Idéal pour les composants aérospatiaux, Équipement médical, et les instruments de précision où une grande précision et une intégrité des matériaux sont primordiales. | Adapté aux pièces automobiles, biens de consommation, et des composants structurels où les formes complexes et la rentabilité sont prioritaires sur une précision extrême. |
Pour les avantages et les inconvénients de l'aluminium usiné
Avantages
- Haute précision: L'usinage CNC permet des dimensions exactes et des tolérances serrées, Essentiel pour les applications critiques.
- Finition de surface supérieure: Produit des pièces avec une excellente qualité de surface, Réduire le besoin de processus de finition supplémentaires.
- Intégrité des matériaux: Maintient les propriétés des matériaux uniformes sans défauts internes, Assurer des performances cohérentes.
- La flexibilité: Puisqu'aucun moule n'est nécessaire, L'usinage CNC peut facilement s'adapter aux modifications de conception et aux petites séries de production.
- Sélection de matériaux larges: Une variété d'alliages d'aluminium, y compris des notes à haute résistance comme 7075, peut être utilisé pour l'usinage.
Les inconvénients
- Coût plus élevé pour les cours de production importants: Bien que super pour les petits lots, L'usinage CNC devient coûteux lors de la mise à jour en raison des temps de production prolongés et de l'usure des outils.
- Déchets de matériaux: Puisque l'usinage CNC est un processus soustractif, Une quantité importante de matériau est supprimée, conduisant à des coûts de matériaux plus élevés par rapport à la coulée.
- Complexité de conception limitée: Alors que l'usinage CNC peut produire des formes complexes, quelques géométries extrêmement complexes (comme les cavités internes) sont mieux adaptés pour le casting.
Pour les avantages et les inconvénients de l'aluminium coulé
Avantages
Rentable pour la production de masse: Une fois le moule fabriqué, La coulée permet une production à haut volume à un coût à faible unité.
Excellent pour les formes complexes: L'aluminium coulé peut atteindre des géométries complexes qui seraient difficiles ou impossibles à machine.
Déchets de matériaux inférieurs: Le moulage utilise uniquement la quantité requise d'aluminium fondu, Minimiser les déchets de matériaux.
Bon rapport force / poids: Les composants en aluminium coulé sont suffisamment forts pour de nombreuses applications tout en restant léger.
Les inconvénients
Précision inférieure: Les pièces coulées nécessitent souvent une usinage supplémentaire pour répondre aux tolérances étroites.
Imperfections de surface: Porosité, rétrécissement, et des textures rugueuses peuvent se produire, nécessitant des processus de finition secondaire.
Coûts initiaux plus élevés: La création de moules pour la coulée coûte cher et prend du temps, Le rendre moins idéal pour les petits cycles de production ou le prototypage.
Quand choisir l'aluminium usiné vs. Couler en aluminium
| Exigence | Meilleur choix | Raison |
| Haute précision & Tolérances strictes | Aluminium usiné | L'usinage CNC atteint une précision supérieure, Le rendre idéal pour l'aérospatiale, médical, et mécanique de précision. |
| Géométrie complexe & Formes complexes | Couler en aluminium | La coulée permet des conceptions très complexes qui seraient difficiles à machine. |
| Petits cours de production | Aluminium usiné | Pas besoin de moules coûteux; L'usinage CNC est rentable pour les projets à faible volume. |
| Fabrication à grande échelle | Couler en aluminium | La coulée est plus rentable pour la production à haut volume. |
| Fort, Pièces haute performance | Aluminium usiné | L'usinage préserve l'intégrité du matériau, produire des composants plus forts et plus fiables. |
| Rentabilité pour les pièces simples | Couler en aluminium | La coulée est plus économique pour produire des composants de base avec un minimum d'usinage. |
Conclusion
L'aluminium et l'aluminium coulé usinés ont leur place dans la fabrication. L'usinage CNC excelle en précision, force, et qualité de surface, Le faire idéal pour les applications hautes performances. D'autre part, La coulée est le choix de référence pour produire de grandes quantités de pièces complexes à moindre coût.
Choisir la bonne méthode dépend des exigences de votre projet, budget, et volume de production. Si vous avez besoin d'une grande précision et force, L'usinage est la meilleure option. Si le coût et la complexité de conception sont plus importants, Le casting est la voie à suivre.
Si vous ne savez pas quel processus correspond le mieux à vos besoins, La consultation avec un fabricant expert peut vous aider à prendre la bonne décision.
Apprendre encore plus & Obtenez un devis
Pour plus d'informations sur Machinage CNC et moulage en aluminium, visite:
🔗 Xométrie - services d'usinage CNC
🔗 Phb Corp - Die Casting expliqué
🔗 Fabrication Leclaire - Coulage de sable VS. Moulage sous pression
Souhaitez-vous ajouter des détails supplémentaires ou modifier des sections spécifiques? 😊