Le broyage CNC peut sembler complexe, Mais à la base, c'est un moyen précis et automatisé de retirer le matériau d'une pièce à l'aide d'une roue de broyage en rotation. Dans ce guide complet, Nous explorerons le broyage CNC en profondeur, y compris son histoire, principes de travail, Types de processus de broyage, matériaux, industries qui comptent sur elle, Et les avantages qu'il offre.
Introduction au broyage CNC
Qu'est-ce que le broyage CNC?
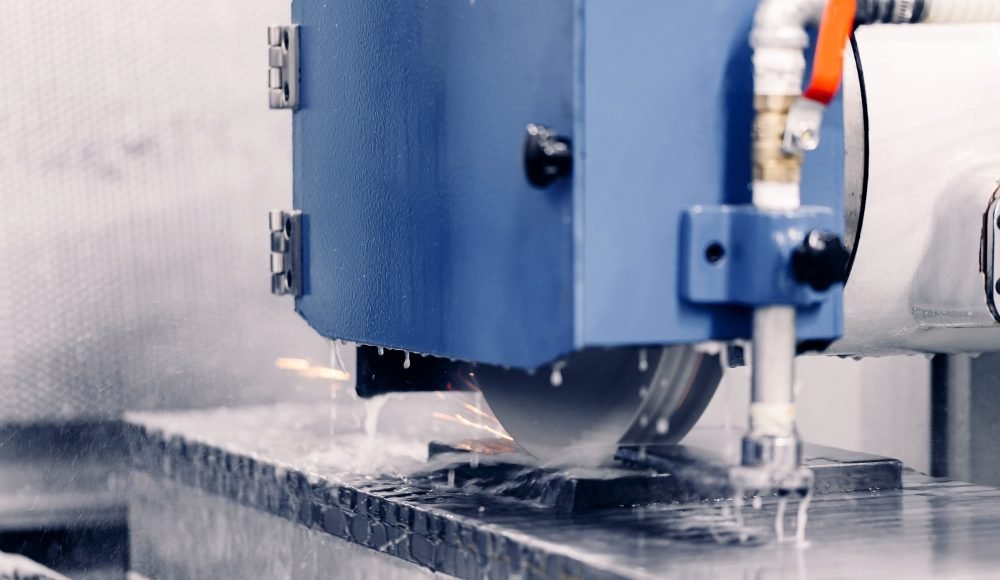
CNC (Commande numérique par ordinateur) Le broyage est un processus d'usinage qui utilise une roue de broyage rotative à grande vitesse pour éliminer le matériau d'une pièce. Contrairement au broyage manuel conventionnel, Le broyage CNC est automatisé, ce qui signifie chaque aspect du processus, comme la profondeur de coupe, vitesse d'avance, et la vitesse des roues - est précisément contrôlée par la programmation informatique.
Pourquoi le broyage CNC est-il important?
- Assure l'extrême précision et répétabilité en usinage.
- Produit finitions de surface supérieures pour les composants hautes performances.
- Capable de manipuler Matériaux difficiles à marins, comme le titane et la céramique.
- Réduit erreur humaine, Augmentation de l'efficacité et de la productivité.
Le broyage CNC est utilisé dans les industries où tolérances étroites et finitions de surface fines sont critiques, En faire un élément essentiel de la fabrication moderne.
Histoire du broyage CNC
Techniques de broyage précoce
Avant la technologie CNC, affûtage a été terminé manuellement en utilisant des pierres abrasives et des machines de broyage précoce. Ces méthodes étaient lentes, à forte intensité de main-d'œuvre, et manquait de précision.
Innovation de l'après-Seconde Guerre mondiale
Après la Seconde Guerre mondiale, Des industries telles que l'aérospatiale et l'automobile ont besoin Usinage de haute précision Pour les technologies avancées. L'introduction d'un contrôle numérique précoce (Caroline du Nord) Les machines ont ouvert la voie à un broyage automatisé.
Pionniers de l'usinage CNC
John T.. Parsons et Frank L. Sulen a joué un rôle déterminant dans le développement de la technologie CNC dans les années 40 et 1950, Poser les bases des machines de broyage CNC d'aujourd'hui.
Avancées dans le broyage CNC
- 1970S-1980: Introduction de microprocesseurs et de commandes numériques.
- 1990S-2000: Intégration CAD / CAM pour la programmation automatisée.
- Aujourd'hui: Les machines de broyage CNC axées et compatibles avec l'IOT améliorent la précision et l'efficacité.
Comment fonctionne le broyage CNC
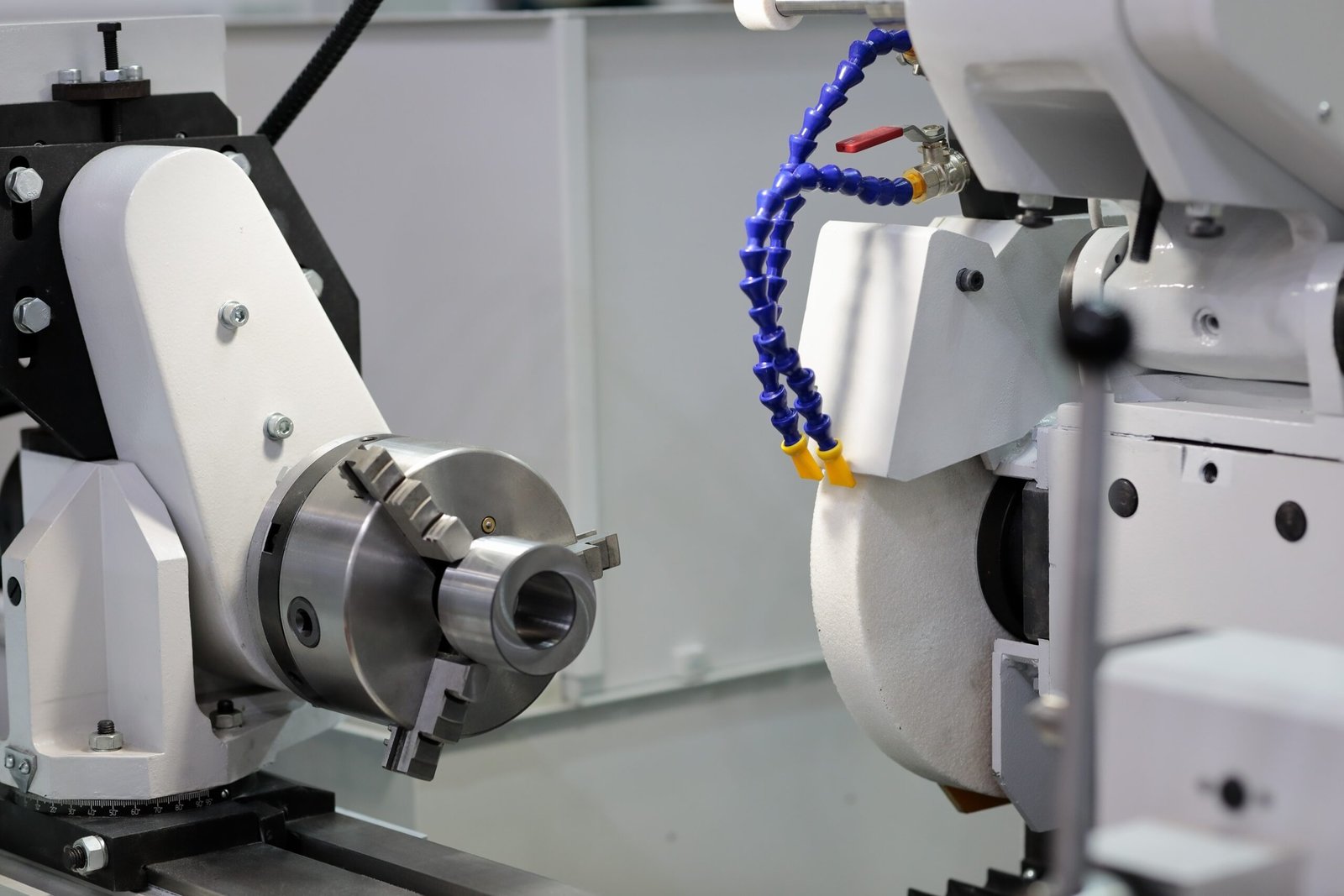
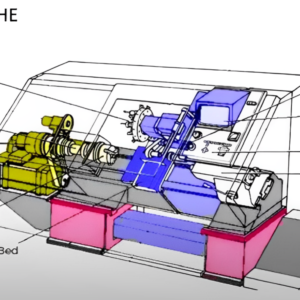
Les parties clés d'une machine de broyage CNC
Avant de plonger dans le processus, Il est important de comprendre les principaux composants qui rendent le broyage CNC possible:
🔹 Roue de broyage - c'est l'outil de coupe qui élimine le matériau de la pièce. Il tourne à grande vitesse et se présente sous différentes formes et matériaux, Selon le travail.
🔹 Système de contrôle CNC - c'est le cerveau de la machine, contrôler chaque mouvement avec une extrême précision. Il suit une conception préprogrammée pour guider le processus de broyage.
🔹 Aménagement de la pièce - Le mécanisme de rétention qui maintient le matériau en place pendant le broyage. Il assure la stabilité et empêche les erreurs de mouvement.
🔹 Système de liquide de refroidissement - Empêche la surchauffe et réduit les frictions en gardant la zone de broyage au frais. Cela aide également à prolonger la durée de vie de l'outil.
🔹 Servomoteur & Drives d'axe - Ces déplacer la roue de broyage et la pièce dans différentes directions pour obtenir la forme et la finition parfaites.
Processus de broyage CNC étape par étape
Étape 1: Programmation de la machine CNC
Tout commence par un plan numérique. A Cad (Conception assistée par ordinateur) Le modèle de la pièce est créé, et le logiciel CNC le convertit en un ensemble d'instructions (Code G) Pour que la machine puisse suivre.
✔ Définit le chemin de roue de broyage.
✔ Définit les vitesses de coupe et la profondeur.
✔ assure la précision en automatisant les mouvements.
💡 Pensez-y comme cuire un gâteau: La recette (Code G) dit à la machine exactement quoi faire, pas à pas!
Étape 2: Sécuriser la pièce
Le matériel qui a besoin de broyage est serré en place Pour empêcher le mouvement. UN Aménagement fort et stable assure la précision, Ainsi, la roue de broyage peut éliminer précisément le matériau.
✔ Empêche les vibrations et les erreurs.
✔ tient la pièce étroite en place.
💡 Imaginez essayer de trancher une tomate sur une planche à découper tremblante - vous avez besoin de stabilité pour des coupes parfaites!
Étape 3: Le broyage commence
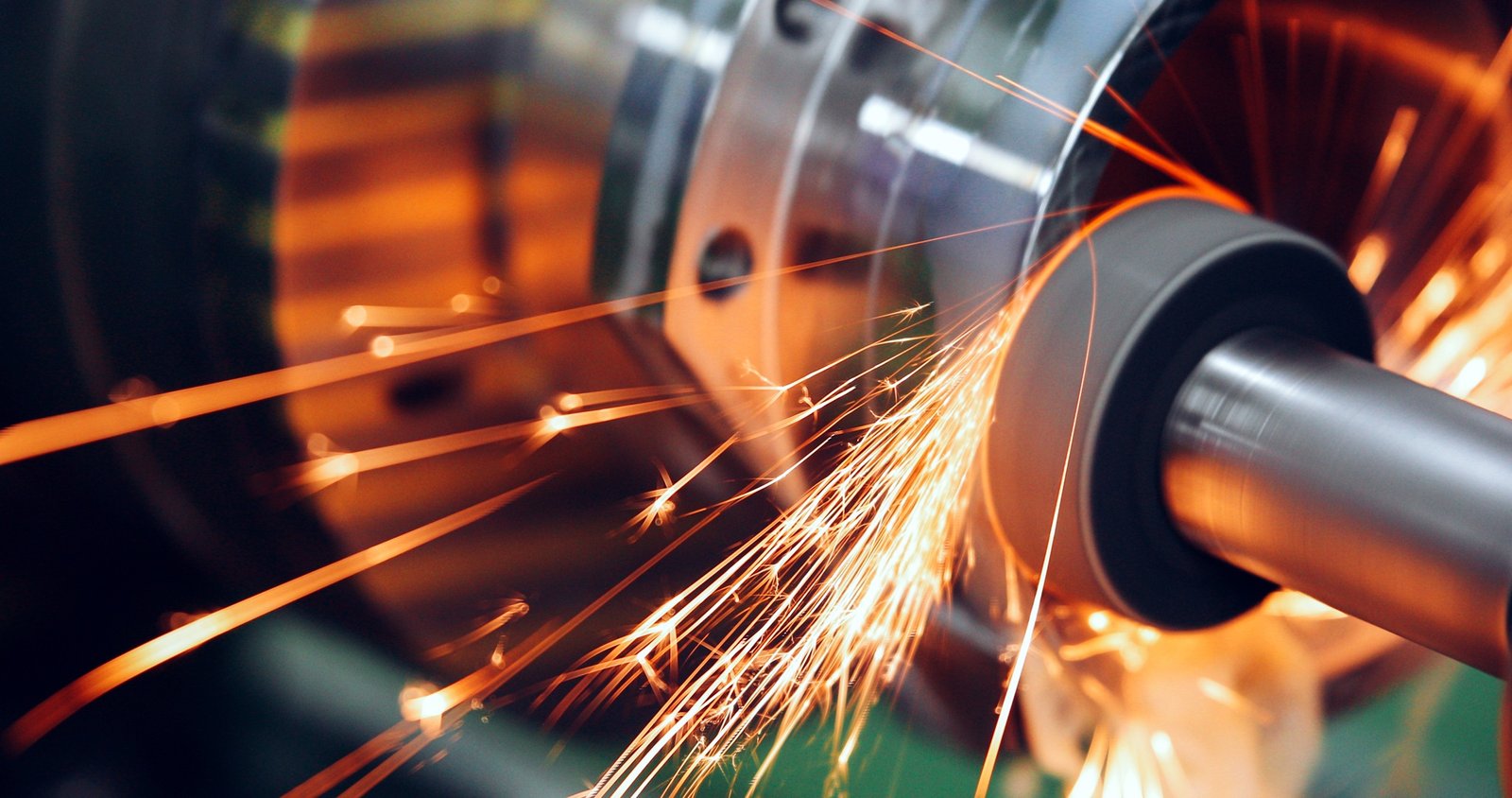
Le système CNC déplace maintenant la roue de broyage vers la pièce à la bonne vitesse et à l'angle. Comme la roue tourne à grande vitesse, il élimine de minuscules morceaux de matériau, Façon de pièce selon le design programmé.
✔ La roue de broyage peut se déplacer côté à côté, de haut en bas, Et en avant / en arrière.
✔ Certains moules CNC peuvent même faire pivoter la pièce pour 360-broyage de degré.
✔ Le matériau est enlevé la couche par couche, assurer un finition lisse et précise.
💡 Pensez-y comme du bois de ponçage - mais beaucoup plus précis et contrôlé!
Étape 4: Refroidissement et lubrification
Le broyage génère beaucoup de chaleur en raison de la friction. À protéger la pièce et la roue de broyage, Les liquides de refroidissement et les lubrifiants sont pulvérisés sur la zone de broyage.
✔ réduit la surchauffe et empêche la distorsion des matériaux.
✔ maintient la roue de broyage tranchante et efficace.
✔ Améliore la finition de surface finale.
💡 Tout comme un moteur de voiture a besoin de liquide de refroidissement pour éviter la surchauffe, Les broyeurs CNC utilisent des liquides de refroidissement pour rester en forme supérieure!
Étape 5: Inspection finale et finition
Une fois le broyage terminé, la pièce est mesuré et inspecté Pour s'assurer qu'il répond aux spécifications requises.
✔ Si la pièce correspond au plan, c'est bon d'y aller! 🎉
✔ Si ajustements sont nécessaires, La machine CNC peut apporter des corrections mineures.
✔ Certaines pièces subissent supplémentaire polissage ou traitement thermique pour une durabilité supplémentaire.
💡 Pensez-y comme un contrôle de qualité dans une usine - chaque produit doit passer le contrôle final avant l'expédition!
Principaux types de processus de broyage CNC
Broyage de surface - pour des surfaces parfaitement plates
🔹 Mieux pour: Création lisse, surfaces planes sur le métal, céramique, et matériaux composites.
🔹 Comment ça marche:
✔ Une rotation La roue de broyage se déplace sur la surface de la pièce à usiner, raser de minuscules couches pour la rendre parfaitement lisse.
✔ La pièce est maintenu en place sur une table ou un luminaire magnétique pendant que la roue se déplace d'avant en arrière.
✔ La machine assure haute précision, fabrication de pièces Exactement niveau et Libéré de points rugueux.
🔹 Où il est utilisé:
✅ Automobile - blocs moteurs, composants de frein.
✅ outil & Making Die - Dies de précision, outils de coupe.
✅ Machines industrielles - pièces de machine plate, plaques métalliques.
💡 Pensez-y comme un ponçage d'une table en bois mais avec une extrême précision!
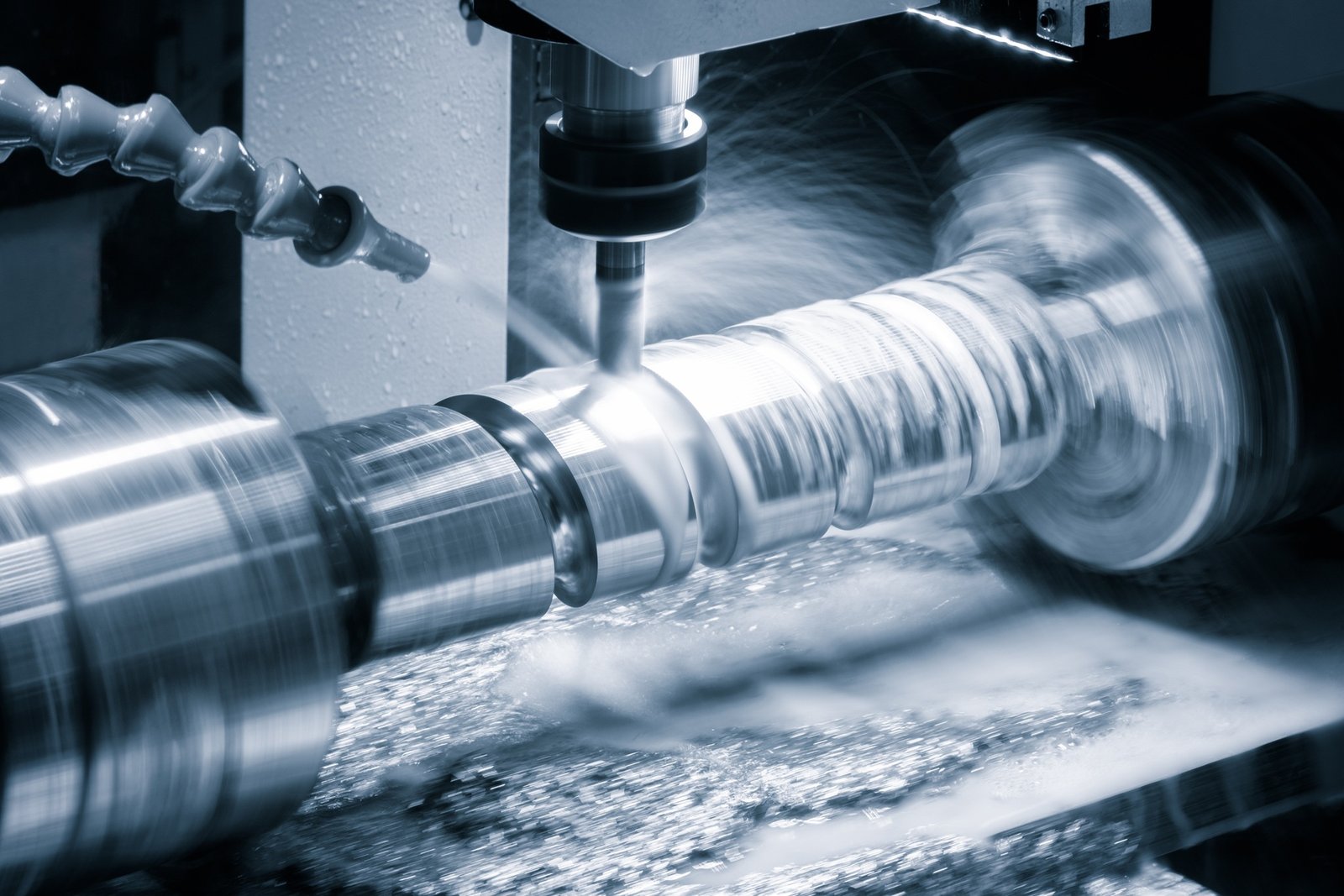
Broyage cylindrique - pour des pièces parfaitement rondes
🔹 Mieux pour: Mise en forme objets cylindriques comme les arbres, tiges, et roulements.
🔹 Comment ça marche:
✔ La pièce faire tourner tandis que la roue de broyage se déplace sur sa surface.
✔ Cela garantit un uniforme, forme circulaire avec une finition incroyablement lisse.
✔ Les commandes CNC permettent Réglages de diamètre précis jusqu'à la plus petite fraction d'un millimètre.
🔹 Où il est utilisé:
✅ Aerospace - arbres de moteur d'avion.
✅ Automobile - arbres de transmission, pistons.
✅ Cylindres hydrauliques industriels, roulements de roulements.
💡 Imaginez aiguiser un crayon uniformément de tous les côtés - c'est ainsi que fonctionne le broyage cylindrique!
Broyage sans centre - plus rapide et plus efficace
🔹 Mieux pour: Production à grande vitesse de petit, parties rondes comme des épingles, boulons, et des bagues.
🔹 Comment ça marche:
✔ Contrairement au broyage cylindrique, la pièce n'est pas maintenu en place par une pince ou un luminaire.
✔ Au lieu de cela, il est soutenu par un Blade de repos de travail et guidé entre un roue de broyage et un réglementation.
✔ La roue de régulation contrôle la vitesse et l'alimentation, garantissant taille et forme cohérentes.
🔹 Où il est utilisé:
✅ Production de masse - petites pièces métalliques, broches de précision.
✅ Automobile - injecteurs de carburant, composants de vanne.
✅ Medical - épingles chirurgicales, petites pièces d'implantation.
💡 Pensez à un hot-dog roulant sur un gril - c'est comment le broyage sans centre maintient les pièces en mouvement tout en les broyant uniformément!
Broyage interne - pour des trous précis et des surfaces intérieures
🔹 Mieux pour: Affûtage à l'intérieur Une partie creuse, comme des tubes, roulements, et cylindres de moteur.
🔹 Comment ça marche:
✔ un petit roue de broyage est inséré dans le diamètre intérieur de la pièce à usiner.
✔ La roue emménage, façonner la surface intérieure à précision parfaite.
✔ Idéal pour les pièces qui doit s'adapter de manière transparente, comme des boîtiers de roulements ou des cylindres hydrauliques.
🔹 Où il est utilisé:
✅ Aerospace - pièces de moteur à réaction.
✅ Automobile - alésages de cylindre, Gear Hubs.
✅ Medical - Tubes médicaux de précision.
💡 Pensez-y comme utiliser un mini tambour de ponçage à l'intérieur d'un tuyau pour lisser les murs!
Broyage du matériel - création de dents de vitesse de précision
🔹 Mieux pour: Fabrication engrenages de haute précision pour les moteurs, transmissions, et machines.
🔹 Comment ça marche:
✔ Une roue de broyage spécialisée façonne chaque dent de l'équipement.
✔ Le processus garantit Taille dentaire exacte, espacement, et les angles, Prévenir le bruit et les vibrations.
✔ produit des engrenages qui durer plus longtemps et courir plus facilement.
🔹 Où il est utilisé:
✅ Automobile - Transmissions de voitures et de camions.
✅ Industrial - Machines lourdes, robotique.
✅ Aerospace - Gears d'atterrissage des avions, éoliennes.
💡 Pensez-y comme aiguisant une lame de scie, mais beaucoup plus précis et durable!
Broyage des aliments pour fluage - pour profondément, Coupures
🔹 Mieux pour: Enlèvement de grandes quantités de matériaux en une seule passe.
🔹 Comment ça marche:
✔ utilise un taux d'alimentation très lent Mais un profondeur de broyage profonde Pour couper les matériaux difficiles.
✔ Idéal pour Matériaux difficiles à marins comme le titane, Inconel, et acier à outils.
✔ produit Moins de chaleur et de stress, Empêcher les matériaux de la déformation ou de la fissuration.
🔹 Où il est utilisé:
✅ Aerospace - lames de turbine, composants d'avion.
✅ Medical - prothèses, implants orthopédiques.
✅ Énergie - Pièces de centrales électriques, composants d'éoliennes.
💡 Pensez-y comme utiliser un burin pour se tailler de grandes sections au lieu de raser de minuscules couches!
Broyage du gabarit - pour des trous et des contours super précis
🔹 Mieux pour: Façon de trou ultra-précis et finitions de surface affinées.
🔹 Comment ça marche:
✔ utilise un grande vitesse, petite roue de broyage pour faire minuscules ajustements à la forme d'une partie.
✔ Souvent utilisé pour moules, meurt, et composants aérospatiaux.
✔ peut réaliser Tolérances extrêmement serrées (jusqu'à ± 0,001 mm!).
🔹 Où il est utilisé:
✅ outil & Making Day - Moules d'injection, dies à l'estampage.
✅ Aerospace - Composants du moteur de précision.
✅ Électronique - pièces micro-mécaniques, composants semi-conducteurs.
💡 Imaginez la sculpture avec un crayon tranchant laser - tout est sur les détails et la précision extrêmes!
Quel processus de broyage CNC vous convient?
Voici une comparaison rapide pour vous aider à décider:
| Type de broyage | Mieux pour | Avantage clé |
| Broyage de surface | Surfaces plates | Lisse, finition précise |
| Broyage cylindrique | Parties rondes (arbres, rouleaux) | Haute précision, Même forme |
| Broyage sans centre | Petites pièces rondes (épingles, boulons) | Rapide, production en grand volume |
| Broyage interne | Trous et tubes intérieurs | Précis, surfaces intérieures lisses |
| Broyage | Gears pour moteurs / machines | Coupez parfaitement les dents de l'équipement |
| Broyage des aliments pour fluage | Métaux durs, coupes profondes | Supprime les grandes quantités de matériaux |
| Broyage du gabarit | Minuscule, ajustements détaillés | Précision ultra-élevée (± 0,001 mm) |
Matériaux utilisés dans le broyage CNC
Que ce soit du métal, plastique, céramique, ou même matériaux composites, Le broyage CNC peut les façonner avec une haute précision et des finitions de surface parfaites.
Mais tous les matériaux ne sont pas tout aussi faciles à broyer - certains sont doux et faciles à façonner, tandis que d'autres sont super durs et nécessitent des roues de broyage spéciales.
Métaux - Les matériaux les plus courants pour le broyage CNC 🏗️
Les métaux sont de loin les matériaux les plus utilisés dans le broyage CNC. Ils sont forts, durable, et utilisé dans Presque toutes les industries, de l'aérospatiale aux dispositifs médicaux.
Voici une ventilation des métaux les plus courants:
🔹 Steel - Strong et fiable
✔ Utilisé dans: Automobile, aérospatial, machinerie industrielle
✔ Types: Acier au carbone, acier inoxydable, acier à outils
✔ Pourquoi il est utilisé:
✅ Super fort et durable.
✅ peut être à la chaleur pour une ténacité supplémentaire.
✅ Polyvalent - Utilisé dans tout, des engrenages aux outils chirurgicaux.
⚠️ Challenge: Aciers plus durs Portez rapidement des roues de broyage.
💡 Considérez l'acier comme le «cheval de bataille» de la fabrication - c'est partout!
🔹 Acier inoxydable - résistant à la corrosion
✔ Utilisé dans: Dispositifs médicaux, transformation des aliments, pièces marines
✔ Pourquoi il est utilisé:
✅ ne rouille pas ou ne corrode pas.
✅ Idéal pour hygiénique candidatures (Comme des outils médicaux).
✅ peut être polie à un finition miroir.
⚠️ Challenge: Acier inoxydable travail-harde, le rendre difficile à grincer.
💡 Imaginez essayer de poncer un super encore, Surface brillante - c'est en acier inoxydable!
🔹 Aluminium - léger et facile à moudre
✔ Utilisé dans: Aérospatial, automobile, électronique
✔ Pourquoi il est utilisé:
✅ Doux et facile à machine.
✅ ne rouille pas.
✅ peut être polie à un finition lisse.
⚠️ Challenge: La douceur peut entraîner un colmatage des roues de broyage.
💡 Si l'acier est le champion des poids lourds, L'aluminium est l'athlète agile - léger et rapide!
🔹 Titane - Super fort mais difficile à moudre
✔ Utilisé dans: Aérospatial, implants médicaux, véhicules hautes performances
✔ Pourquoi il est utilisé:
✅ Incroyablement fort mais léger.
✅ hautement résistant à la chaleur.
✅ Utilisé dans applications critiques où l'échec n'est pas une option.
⚠️ Challenge: Le titane a faible conductivité thermique, pour que se réchauffe rapidement, Rendre le broyage difficile.
💡 Considérez le titane comme un métal de super-héros - fort mais a besoin d'une manipulation spéciale!
🔹 cuivre & Laiton - doux et lisse
✔ Utilisé dans: Composants électriques, plomberie, pièces décoratives
✔ Pourquoi il est utilisé:
✅ Excellente conductivité (Utilisé en pièces électriques).
✅ Facile à moudre et façonner.
✅ peut être polie à un brillant.
⚠️ Challenge: Les matériaux mous comme le laiton peuvent gommer les roues de broyage.
💡 Grincer en laiton, c'est comme affûter un crayon doux - c'est facile mais nécessite une touche prudente!
Céramique - dure mais cassant 🏺
Les céramiques sont incroyablement dur, les rendre super pour résistant à l'usure parties, Mais ils sont aussi fragile et peut se fissurer s'il n'est pas manipulé soigneusement. Le broyage CNC est l'un des seulement façons de les façonner précisément.
🔹 Céramiques communes utilisées dans le broyage CNC:
✔ Alumine (Oxyde d'aluminium) - Utilisé dans l'électronique et les outils de coupe.
✔ Carbure de silicium - trouvé dans les applications et abrasifs à haute température.
✔ Zircone - Utilisé dans les implants médicaux et les couronnes dentaires.
💡 Pensez à la céramique comme le verre - duper, mais peut casser si vous ne faites pas attention!
Plastiques - Facile à moudre mais sensible à la chaleur 🔬
Les plastiques sont couramment utilisés dans médical, automobile, et électronique grand public, Mais ils doivent être terre à la bonne vitesse à Évitez de fondre.
🔹 plastiques communs pour le broyage CNC:
✔ Polycarbonate - fort, Résistant aux impacts, Utilisé dans l'équipement de protection.
✔ Acrylique - utilisé dans les lentilles et affichages optiques.
✔ PTFE (Téflon) - Friction basse, Utilisé dans les applications médicales et industrielles.
💡 Les plastiques broyés, c'est comme couper du beurre avec un couteau chaud - trop de chaleur, Et ça fond!
Matériaux composites - Le meilleur des deux mondes 🔗
Les composites se combinent Deux matériaux ou plus Pour créer quelque chose encore mieux. Ils sont fort, léger, et résistant à la chaleur, Mais ils Portez rapidement des outils de broyage.
🔹 Exemples de matériaux composites:
✔ Fibre de carbone - super fort, utilisé dans les équipements aérospatiaux et sportifs.
✔ Fibre de verre - utilisé dans les bateaux, voitures, et les matériaux de construction.
💡 Les composites de broyage sont délicats - comme essayer de poncer à la fois en métal et en plastique en même temps!
Métaux exotiques et précieux - valeur élevée, Haute précision 💎
Certaines industries, comme bijoux, électronique, et aérospatiale, nécessitent du broyage de rare, métaux coûteux.
🔹 Métaux précieux communs:
✔ Or - utilisé en électronique et détails fins.
✔ Argent - idéal pour la conductivité électrique.
✔ Platine - trouvé dans les implants médicaux et les bijoux.
💡 Ces matériaux sont chers, Donc, chaque petit morceau de déchets est important!
Quel matériel vous convient?
Voici un rapide comparaison de différents matériaux de broyage CNC:
| Matériel | Force | Facilité de broyage | Utilisation courante |
| Acier | 🟢 Super fort | 🔴 Difficile à moudre | Engrenages, outils, aérospatial |
| Aluminium | 🟡 Léger | 🟢 Facile à moudre | Automobile, électronique |
| Titane | 🔴 Ultra-fort | 🔴 Difficile à moudre | Implants médicaux, aérospatial |
| Laiton & Cuivre | 🟢 Soft & lisse | 🟢 Très facile | Électrique, plomberie |
| Céramique | 🔴 Extrêmement dur | 🟡 a besoin d'un broyage spécial | Médical, électronique |
| Plastiques | 🟡 Flexible & sensible à la chaleur | 🟢 Facile (Mais regardez la chaleur!) | Médical, automobile |
| Matériaux composites | 🟢 Strong & léger | 🔴 DUR DES OUTILS DE GRINDING | Aérospatial, équipement de sport |
| Métaux précieux | 🟢 Précieux & résistant à la corrosion | 🟡 Grincement délicat nécessaire | Bijoux, électronique haut de gamme |
Les industries qui utilisent le broyage CNC
🏭 Aérospatial - Blades de turbine, composants du train d'atterrissage.
🚗 Automobile - pièces de moteur, engrenages, composants de frein.
⚕️ Équipement médical - Outils chirurgicaux, implants, prothèses.
🔬 Électronique - Affinages semi-conducteurs, micro-composants.
🔧 Outil & Mourir - Moules, outils de coupe, meurt.
Avantages du broyage CNC
Précision folle et précision 🎯
L'un des plus grand Les avantages du broyage CNC sont son précision super-élevée. Contrairement au broyage manuel, qui dépend de la compétence de l'opérateur, Le broyage CNC est sous-contrôlé, garantissant précision parfaite à chaque fois.
✅ peut tenir des tolérances aussi serrées que ± 0,001 mm - c'est plus mince qu'un cheveux humains!
✅ crée impeccable, finitions lisses Sans bords ou imperfections rugueuses.
✅ Idéal pour industries de haute précision Comme l'aérospatiale, médical, et automobile.
💡 Si vous avez besoin de pièces qui s'adaptent parfaitement, Le broyage CNC est votre meilleur pari!
Super cohérent et reproductible 🔄
J'ai déjà essayé de couper quelque chose à la main et d'obtenir deux pièces qui ne correspondent pas tout à fait? Que Jamais arrive Avec le broyage CNC!
✅ Chaque partie sort exactement le même, Que ce soit le premier ou le 10 000e pièce.
✅ Non erreurs humaines - La machine suit parfaitement les instructions programmées.
✅ Idéal pour production de masse où la cohérence est la clé.
💡 Imaginez la fabrication 1,000 engrenages, Tout identique au micromètre - le broyage CNC le rend possible!
Gire les matériaux durs et durs 💪
Quelques matériaux, comme titane et céramique, sont super dur et peut détruire des outils de coupe réguliers. Mais le broyage CNC? Aucun problème!
✅ peut moudre acier durci, carbure, titane, Et même le verre.
✅ fonctionne sur Matériaux résistants à la chaleur et résistants à l'usure que d'autres outils ont du mal.
✅ Utilise roues de broyage spécial Pour couper les matériaux les plus durs avec facilité.
💡 Si d'autres méthodes d'usinage luttent, Le broyage CNC peut relever le défi!
Fonctionne pour des formes complexes et de minuscules détails 🛠️
Le broyage CNC n'est pas seulement pour surfaces planes ou parties simples- il peut créer complexe, Formes détaillées que les autres machines ne peuvent pas.
✅ peut moudre trous internes, surfaces courbes, et minuscules rainures avec une extrême précision.
✅ parfait pour outils personnalisés, implants médicaux, et parties aérospatiales complexes.
✅ Utilise Techniques de broyage spécialisées comme le broyage sans centre pour les formes uniques.
💡 Si votre partie a des angles étranges, tolérances étroites, ou courbes complexes, Le broyage CNC peut y arriver!
À grande vitesse et efficace ⚡
CNC Grinceing automatise le processus, ce qui signifie que les pièces sont faites plus rapide et avec moins de déchets.
✅ Pas besoin d'ajustements constants - Définissez simplement le programme et laissez-le fonctionner.
✅ réduit Temps d'installation et travail humain, Réduction des coûts de production.
✅ peut gérer plusieurs opérations de broyage en une seule configuration, gagner du temps.
💡 Plus de vitesse + plus d'efficacité = des coûts inférieurs et des délais de livraison plus rapides!
Moins d'usure sur les outils = coûts inférieurs 💰
Outils de coupe traditionnels user rapidement, surtout sur métaux durs. Mais la broyage des roues dans le broyage CNC dure beaucoup plus longtemps Parce qu'ils sont faits pour un travail à haute endurance.
✅ Les roues de broyage sont Conçu pour la durabilité, signification moins de remplacements.
✅ Non accumulation de chaleur excessive, réduire les dommages à l'outil et à la pièce.
✅ Moins de déchets = Plus d'économies de coûts à long terme.
💡 Les roues de broyage sont comme des coureurs de marathon - ils durent beaucoup plus longtemps que les outils de coupe réguliers!
Fonctionne sur une large gamme de matériaux 🌍
Le broyage CNC ne se limite pas à les métaux- il peut gérer plastiques, céramique, matériaux composites, Et même le verre.
✅ fonctionne sur doux, fragile, ou matériaux ultra-durs.
✅ peut moudre alliages résistants à la chaleur utilisés dans les applications aérospatiales et médicales.
✅ Idéal pour Matériaux délicats qui nécessitent des lisses, coupes précises.
💡 Si c'est l'aluminium, fibre de carbone, ou en acier trempé, Le broyage CNC fait le travail!
Meilleure finition de surface = aucun travail supplémentaire nécessaire ✨
Un grand prime du broyage CNC est le finition super lisse il crée. De nombreuses pièces sortent prêt à l'emploi, sans polissage ou finition supplémentaire.
✅ Feuilles miroir surfaces avec rugosité zéro.
✅ réduit le besoin de étapes de finition secondaire, Économiser du temps et de l'argent.
✅ parfait pour parties esthétiques ou composants hautes performances qui ont besoin d'une surface impeccable.
💡 Si vos pièces ont besoin de chercher et de fonctionner parfaitement, Le broyage CNC est la voie à suivre!
Peut être entièrement automatisé = moins de main-d'œuvre nécessaire 🤖
Les machines de broyage CNC peuvent être entièrement automatisé, ce qui signifie qu'ils courir 24/7 avec une supervision minimale.
✅ peut être intégré à la robotique Pour les lignes de production entièrement automatisées.
✅ réduit la dépendance à opérateurs qualifiés, réduire les coûts de main-d'œuvre.
✅ peut fonctionner pendant la nuit ou pendant le week-end Pour maximiser la productivité.
💡 Laissez les machines faire le travail pendant que vous vous concentrez sur l'innovation!
CNC Gringing vs. Broyage traditionnel - une comparaison rapide
| Fonctionnalité | Rectification CNC ✅ | Broyage traditionnel ❌ |
| Précision 🎯 | ± 0,001 mm (super précis) | Dépend de la compétence de l'opérateur |
| Cohérence 🔄 | 100% reproductible | Petites variations possibles |
| Vitesse ⚡ | Rapide et automatisé | Ralentissez, Ajustements manuels nécessaires |
| Options de matériel 🔩 | Fonctionne sur les métaux durs, céramique, matériaux composites | Meilleur pour les matériaux plus doux |
| Usure d'outil 🛠️ | Les roues de broyage durent plus longtemps | Les outils de coupe s'usent plus rapidement |
| Finition de surface ✨ | Finition en forme de miroir | Peut avoir besoin de polissage supplémentaire |
| Complexité 🏗️ | Peut créer du complexe, formes complexes | Mieux pour des formes plus simples |
| Coûts de main-d'œuvre 💰 | Entièrement automatisé, faibles coûts de main-d'œuvre | Nécessite des opérateurs qualifiés |
Facteurs de coût dans le broyage CNC
💰 Coût de la machine:
- Machines d'entrée de gamme: $10,000+
- Machines de milieu de gamme: $50,000- 200 000 $
- Machines de précision haut de gamme: $500,000+
⏳ Facteurs de temps:
- Parties simples: Quelques minutes par morceau.
- Parties complexes: Plusieurs heures pour le broyage complexe.
Conception & Conseils opérationnels pour le broyage CNC
🔹 Choisissez la bonne roue de broyage - Sélectionner en fonction de la dureté des matériaux.
🔹 Optimiser le taux d'alimentation & Vitesse - Empêcher l'usure des outils et la surchauffe.
🔹 Utiliser le liquide de refroidissement & Lubrifiants - Améliorer la vie de l'outil et la qualité de la surface.
🔹 Entretien régulier des machines - Assurer une précision et des performances à long terme.
🔹 Évitez les conceptions trop complexes - Simplifier les géométries pour un usinage efficace.
Conclusion
Le broyage CNC est un processus essentiel dans la fabrication moderne, fournir une précision inégalée, efficacité, et répétabilité. Que ce soit pour l'aérospatiale, automobile, ou applications médicales, Le broyage CNC assure la production de composants de haute qualité qui répondent à des tolérances strictes.
En comprenant le processus, matériaux, et les facteurs de coût impliqués, Les fabricants peuvent optimiser leurs opérations de broyage pour une efficacité et une productivité maximales.
FAQ
1️⃣ Comment pouvez-vous améliorer l'efficacité du broyage CNC?
Maintenez régulièrement la machine, Utilisez des techniques appropriées, Choisissez la bonne roue de broyage, et optimiser les paramètres de coupe pour les meilleurs résultats.
2️⃣ Combien de temps dure le processus de broyage CNC?
La vitesse de broyage dépend de la dureté des matériaux, vitesse de broche (12,000-24,000 RPM), et la profondeur de coupe, avec des tâches simples prenant des minutes et des pièces complexes prenant des heures.
3️⃣ Combien coûte une machine de broyage CNC?
Les modèles de base commencent à $10,000, tandis que les machines de précision haut de gamme peuvent dépasser $500,000, avec des coûts supplémentaires pour la maintenance, outillage, et logiciel.
4️⃣ Quelles sont les spécifications clés d'une machine de broyage CNC?
Les spécifications typiques incluent la taille du tableau (200mm × 500 mm +), vitesse de broche (1400-24,000 RPM), Taille de la roue de broyage (355 × 40 × 127 mm), et puissance du moteur (750W-5000W).
5️⃣ Quels sont les différents types de broyage CNC?
Les principaux types incluent le broyage de surface (pièces plates), broyage cylindrique (arbres), broyage sans centre (production de masse), broyage interne (trous de précision), et broyage des outils (outils de reharpelage). 🚀
Liens externes recommandés (Backlinks pour un apprentissage plus approfondi)
Présentation du broyage CNC - https://www.mmsonline.com/articles/the-volution-of-cnc-grinding
Types de roues de broyage - https://www.nortonabrasives.com/en-us/grinding-weels
Analyse des coûts de broyage CNC - https://www.thefabricator.com/the-ins-and-stots-f-cnc-griding
Matériaux utilisés dans le broyage de précision - https://www.ingineeringclicks.com/materials-in-griding
Broyage de surface vs. Broyage cylindrique - https://www.machinemfg.com/grinding-machine-ypes-and-uses






9 réflexions sur "Rectification CNC: Le guide ultime de l'usinage de précision”