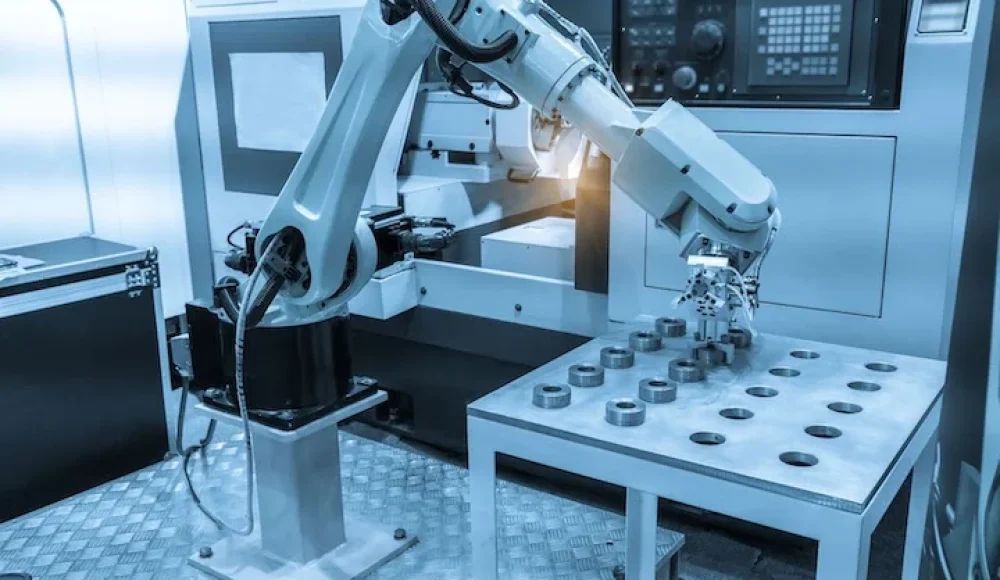
CNC robotics and automated machining have witnessed unprecedented growth in recent years, becoming integral components in advanced manufacturing environments. CNC robotics combines the precision of CNC machines with the flexibility and automation capabilities of industrial robots. This integration significantly enhances productivity, 精度, and operational efficiency. This detailed guide explores CNC robotics in-depth, highlighting its benefits, common applications, and comparisons with conventional CNC machining processes.
Introduction to CNC Robotics and Automated Machining
The manufacturing industry’s continuous evolution has led to the widespread adoption of robotic automation in CNC machining processes. While CNC machines historically represented precision manufacturing, robotics integration offers superior automation, 多用途性, と効率. 一緒に, CNC machining and robotics blur the traditional boundaries, driving industrial automation forward.
What Is CNC Robotics?
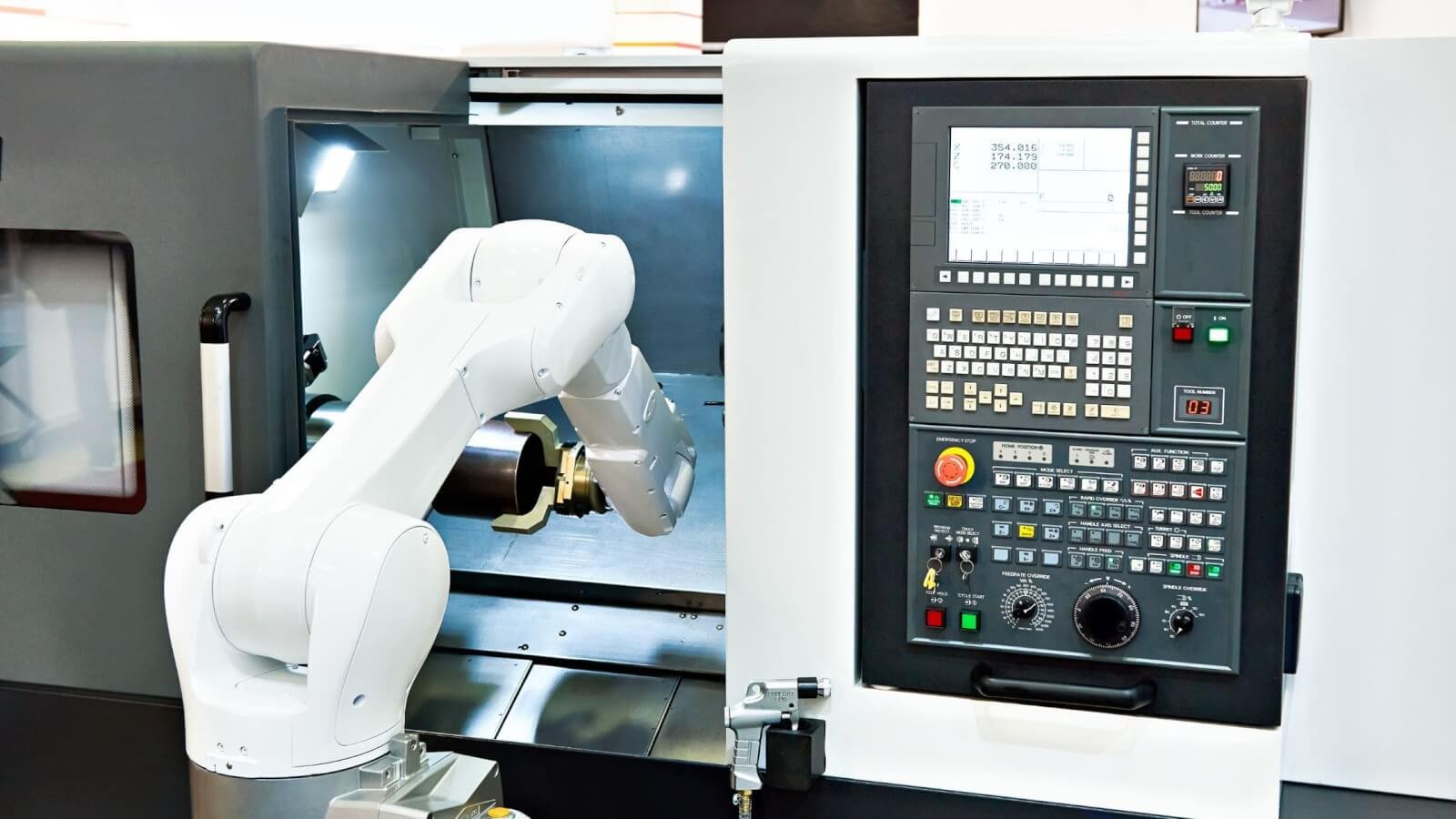
CNC robotics refers to robotic systems specifically designed to complement or enhance CNC machining processes. These robotic systems are equipped with advanced sensors, actuators, controllers, and software enabling automated handling, manipulation, and processing of components. CNC robotics reduce reliance on manual operators, enhancing repeatability, 効率, そして精度.
Unlike traditional CNC machines—which require operator interaction to load and unload workpieces—CNC robotics operate autonomously following programmed instructions, greatly minimizing human intervention.
Advantages of CNC Machining for Producing Robotic Parts
CNC加工 remains the most favored method for producing high-quality robotic components. Several critical advantages justify its widespread adoption in manufacturing robotics:
Increased Speed and Efficiency
CNC machining offers rapid turnaround times and exceptional production speed. Custom robotic parts, 複雑さに応じて, can be manufactured within just 1–3 days, facilitating faster prototyping and iteration cycles.
Exceptional Dimensional Accuracy
Precision is paramount in robotics. CNC machining consistently achieves tight tolerances (up to ±0.0002 inches or ±0.005 mm), ensuring robotic components operate smoothly, predictably, and with high repeatability.
Broad Material Compatibility
Robotic components often require robust materials like aluminum alloys, 鋼, チタン, and engineering plastics. CNC machining effectively handles these diverse materials, allowing engineers to optimize performance, 重さ, 強さ, そしてコスト.
優れた表面仕上げ
CNC machining delivers excellent surface finishes, typically Ra 0.8 μm or lower, essential for minimizing friction and enhancing durability. Additional finishing processes like polishing, コーティング, and anodizing further enhance component performance.
CNC Machining and Robotics Industry Integration
CNC machining and robotics are interconnected in modern manufacturing. CNC machining produces critical robotic components, while robots increasingly automate CNC machining operations.
Common Robotic Parts Made with CNC Machining
CNC Robotic Arms
Robotic arms replicate human-like motion to handle tasks requiring precise movement and strength. Common materials include aluminum, 鋼鉄, 補強されたプラスチック, machined precisely for mechanical stability.
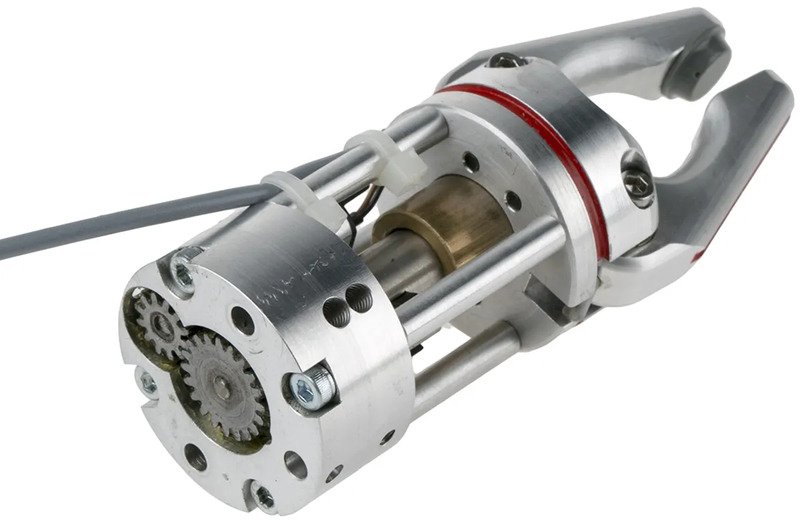
End Effectors
End effectors, including grippers, vacuum attachments, and specialized tools, directly interact with products or materials. CNC machining precisely crafts these critical attachments for exacting applications.
Custom Jigs and Fixtures
Jigs and fixtures securely hold workpieces during robotic operations, ensuring repeatable positioning. CNC machining customizes these devices economically and efficiently.
Sensors and Controllers
Sensors and controllers rely heavily on precision-machined printed circuit boards (PCB). CNC machining overcomes traditional chemical etching limitations, 精度を確保します, environmental safety, そして信頼性.
Common Robots Used in CNC Machining
Articulated Robots
With rotary joints allowing multiple axes of movement, articulated robots handle complex machining, 組み立て, 溶接, and material handling operations. Their flexibility and versatility make them prevalent across industries.
SCARA Robots (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm)
SCARA robots provide precise, high-speed performance for repetitive assembly tasks, component inspection, およびパッケージング操作, ideal for compact workspace integration.
Delta Robots
Known for rapid pick-and-place tasks, delta robots offer superior speed and precision, ideal for sorting, 梱包, and assembly operations on conveyor lines.
Gantry (Cartesian) Robots
Operating along linear axes (バツ, Y, Z), gantry robots manage heavier payloads and larger workspaces, making them ideal for material handling, 梱包, loading/unloading, and precision cutting tasks (laser or waterjet cutting).
Benefits of Robotics in CNC Machining Operations
Integrating robotics into CNC machining processes offers significant operational advantages, 含む:
Enhanced Production Speed
Robotic automation ensures continuous, uninterrupted operations, significantly reducing production cycle times. Robots maintain consistent output even during prolonged, repetitive tasks.
Improved Manufacturing Precision
Robotic systems achieve exceptional positional accuracy during loading, unloading, and component handling operations, typically maintaining precision within ±1 mm, greatly enhancing manufacturing consistency.
Optimal Surface Finishes
Robotic handling ensures precise alignment and minimizes surface imperfections, improving the quality and consistency of finished products.
Multitasking Capabilities
Robots efficiently handle simultaneous operations like loading/unloading, 検査, と包装, maximizing productivity while CNC machines perform primary machining tasks.
Differences Between CNC Machines and CNC Robotics
Despite overlapping functions, CNC machines and CNC robots exhibit key performance differences:
正確さ
CNC Machines: Achieve ultra-high precision (±0.02–0.05 mm), with specialized Swiss lathe systems offering even finer tolerances.
CNCロボット: Generally achieve ±0.1–0.2 mm precision, focusing more on repeatability than absolute accuracy.
多用途性
CNC Machines: Specialized for precise machining tasks like milling, 旋回, 掘削, with limited degrees of freedom.
CNCロボット: Offer significantly higher versatility, easily adapting to multiple tasks simultaneously with greater degrees of freedom.
Rigidity
CNC Machines: High rigidity (>50 N/µm), ensuring accuracy during heavy cutting and machining of hard materials.
CNCロボット: Lower rigidity (<1 N/µm), suitable primarily for softer materials like plastics, 複合材, or lightweight metals.
Workspace Size
CNC Machines: Typically offer limited workspace based on their enclosed design.
CNCロボット: Feature larger, flexible workspace configurations that can be expanded with additional axes.
Affordability
CNC Machines: Cost-effective for repetitive, high-volume precision machining tasks.
CNCロボット: Offer broader operational flexibility, making them cost-effective for multitasking and complex workflows.
Will CNC Robotics Replace CNC Machines?
While CNC robotics continues to evolve, CNC machines retain superior precision, 剛性, and specialization capabilities. CNC robotics complement rather than replace CNC machines, effectively handling automation tasks and complex motions, while CNC machines remain best suited for ultra-precision machining tasks.
Integration of CNC robotics and CNC machining achieves optimal productivity, 正確さ, and operational efficiency.
精度の高いトップ CNC Machining Services for Robotic Components
Manufacturing precision robotic parts demands a reliable CNC machining partner. Tops Precision provides professional CNC machining services, featuring:
Highly skilled engineering teams and expert CNC operators.
Rigorous quality control and inspection processes.
速いターンアラウンド, competitive pricing, and superior quality assurance.
Customers can send CAD designs to Tops Precision, receive instant quotations, and obtain automated Design for Manufacturing (DFM) 報告.
試す 精度の高いトップ today for efficient and accurate CNC machining services.
結論
CNC robotics represents an exciting advancement in automated manufacturing, seamlessly merging robotic flexibility with CNC precision. As CNC machines remain essential for specialized machining, robotics augment automation, 柔軟性, そして生産性.
Choosing a qualified manufacturing partner ensures optimized outcomes. For professional CNC machining of robotic components, contact Tops Precision and experience unmatched precision, スピード, and service quality.
よくある質問
1. What is the main difference between CNC Machines and CNC Robotics?
The core difference lies in Accuracy vs. 多用途性. CNC machines are built with extreme 剛性 (high stiffness) to achieve ultra-high precision (例えば, ± 0.02 んん) during heavy, specialized cutting tasks. CNC robots have lower rigidity, resulting in slightly less accuracy (例えば, ± 0.1 んん), but offer much greater 柔軟性, a larger workspace, and better multitasking capabilities (取り扱い, loading, 検査, 等).
2. Why is CNC Machining the preferred method for making robotic components?
CNC machining is preferred because robotic systems demand parts with exceptional 寸法精度 and specific material properties. CNC delivers:
-
厳しい公差: Ensuring smooth, repeatable operation of joints and actuators.
-
材質の適合性: Effectively processing high-strength materials like specialized aluminum alloys and titanium is required for lightweight, strong robotic arms.
-
優れた表面仕上げ: Reducing friction and wear on moving parts.
3. Can I use a CNC robot for heavy-duty metal cutting?
It is generally not recommended for heavy cutting (high material removal rates) on hard metals like stainless steel or tool steel. Due to their inherently lower 剛性 (compared to a heavy CNC mill), robots are prone to おしゃべり and vibration under heavy load, leading to poor surface finish and reduced accuracy. They are better suited for light materials, finishing tasks (研削, 研磨), or handling/loading operations.
4. Can existing CNC machines be retrofitted with robotic automation?
はい, most existing CNC machines can be retrofitted to integrate robotics. This typically involves adding an external articulated robot or gantry system dedicated to machine tending (loading and unloading workpieces) or performing secondary operations like part cleaning or inspection. This integration significantly boosts spindle uptime and efficiency without replacing the primary machining asset.
5. What is “creep resistance,” and why is it important in robotic parts made with CNC?
クリープ is the slow, permanent deformation of a material under continuous stress, especially at elevated temperatures. In robotics, components like motor mounts and structural joints must maintain their shape precisely over thousands of cycles. CNC machining allows the use of specific, high-performance alloys (例えば, specialized aluminum) that have been engineered for excellent 耐クリープ性, ensuring the robot’s long-term positional accuracy and reliability.
6. What types of robots are most commonly used to automate CNC machining operations?
The most common types include:
-
Articulated Robots: Highly flexible, used for complex material handling and machine tending, often reaching multiple machines.
-
Gantry (Cartesian) Robots: Operate along linear axes (バツ, Y, Z), ideal for handling heavy payloads and servicing very large workspaces, often used for loading/unloading large workpieces or pallets.
7. Will CNC Robotics eventually replace traditional CNC machines?
いいえ, they are generally seen as complementary technologies. Traditional CNC machines will continue to dominate the niche requiring ultra-high absolute accuracy, maximum rigidity, and the ability to perform heavy, demanding material removal. CNC robotics specializes in オートメーション, 柔軟性, そして multitasking. Optimal manufacturing utilizes both: the CNC machine cuts the part with precision, and the robot handles it efficiently.
続きを読む:
Guide to CNC Milling and Turning
Understanding Surface Finishes in CNC Machining
CNC Machining Quality Control Procedures