Alumínio is one of the most versatile engineering materials thanks to its lightweight strength, resistência à corrosão, and high conductivity. It is widely used in aerospace, automotivo, eletrônicos de consumo, dispositivos médicos, e arquitetura. No entanto, raw or machined aluminum surfaces often require acabamento da superfície to enhance performance, durabilidade, e apelo visual.
Surface finishing is not just about aesthetics. It can dramatically improve aluminum’s resistance to corrosion, abrasão, and chemical attack, while also ensuring components meet tight tolerances and functional requirements. Whether you need a mirror-polished aluminum panel, a corrosion-proof aerospace part, or a durable consumer product casing, the right finishing method is critical.
Este guia explora why aluminum surface finishing matters, o 10 most common finishing methods, different surface effects and styles, and how to choose the right one for your application.
Why Do Aluminum Products Need Surface Finishing?
Surface finishing for aluminum serves both funcional e estética purposes. Below are the main reasons it is essential:
Resistência à corrosão: Aluminum naturally forms a thin oxide film, but in harsh environments, additional finishing (por exemplo., anodizing or chem film) ensures long-term protection.
Resistência ao desgaste: Many aluminum parts are exposed to friction or mechanical stress. Hard coatings improve scratch resistance and durability.
Electrical and Thermal Properties: Some finishes enhance conductivity (por exemplo., chem film), while others improve insulation (por exemplo., anodização).
Fricção Reduzida & Contamination: Smooth finishes lower friction and prevent dirt or moisture from accumulating in crevices.
Apelo Estético: Finishes such as polishing, escovar, and powder coating provide diverse styles, from mirror-like gloss to satin or matte textures.
Resumidamente, aluminum finishing directly influences a product’s lifespan, desempenho, and brand value.
10 Common Types of Aluminum Finishes
1. Acabamento amado
Processo: Part is left in its raw, machined state.
Surface Roughness: Typically Ra 0.2 – 3.2 μm, depending on machining parameters.
Prós: Baixo custo, accurate tolerances maintained.
Contras: Visible tool marks, limited corrosion protection.
Formulários: Internal components, protótipos, non-decorative parts.
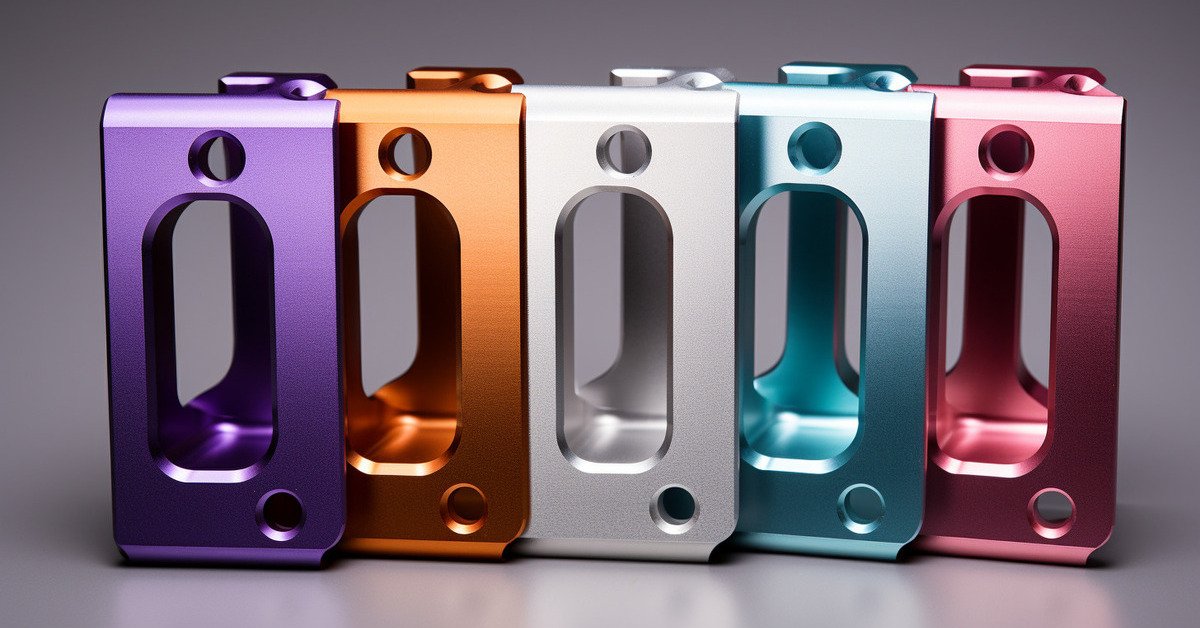
2. Anodização
Processo: Electrochemical treatment that forms a controlled oxide layer.
Grossura: 5–25 μm for decorative, até 50 μm for hard anodizing.
Benefícios:
Excellent corrosion and wear resistance.
Wide range of color options.
Non-conductive surface for electrical insulation.
Formulários: Painéis aeroespaciais, eletrônicos de consumo, dispositivos médicos.
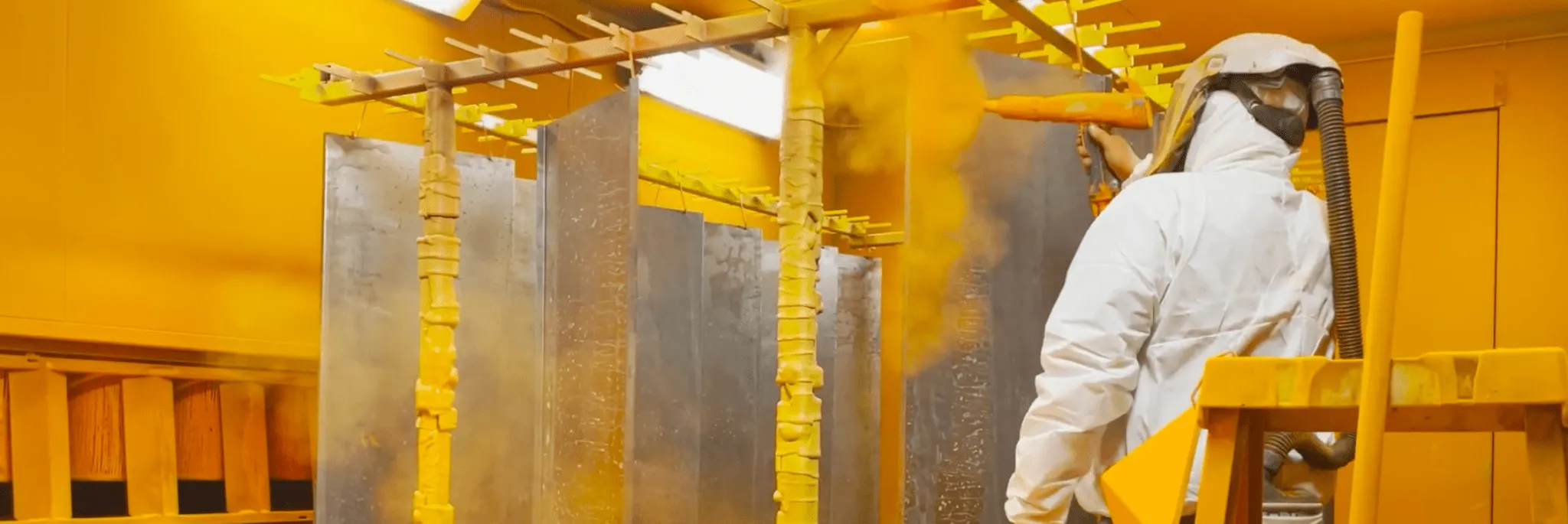
3. Revestimento em pó
Processo: Electrostatic spraying of powder particles, cured under heat.
Superfície: Protective, decorativo, slightly textured finish.
Benefícios:
No solvents → eco-friendly.
Excellent color variety.
Strong adhesion and durability.
Formulários: Automotive wheels, mobília, outdoor enclosures.
4. Alodine (Chem Film)
Processo: Immersion in a chemical bath that forms a conversion coating.
Benefícios:
Cost-effective corrosion resistance.
Maintains condutividade elétrica (unlike anodizing).
Ideal for parts that require painting afterward.
Formulários: Aerospace structures, Capinhas eletrônicas.
5. Jateamento de contas
Processo: Abrasive glass or steel beads blasted under pressure.
Superfície: Suave, Textura semelhante a cetim.
Benefícios:
Cleans impurities.
Creates uniform matte look.
Formulários: Consumer goods, hardware decorativo, automotive interiors.
6. Galvanoplastia
Processo: Deposition of metals like nickel, ouro, prata, or chromium on aluminum via electrolysis.
Benefícios:
Improved conductivity, resistência ao desgaste, and reflectivity.
Adds luxury aesthetics (gold/silver plating).
Formulários: Eletrônicos, conectores aeroespaciais, luxury consumer products.
7. Polimento
Processo: Mechanical or chemical polishing for a reflective surface.
Benefícios:
Enhances brightness and aesthetics.
Reduces oxidation by smoothing pores.
Formulários: Painéis decorativos, equipamento médico, display parts.
8. Escovação
Processo: Abrasive brushes create fine, Textura linear.
Superfície: Satin or metallic look, reduces visible scratches.
Formulários: Aparelhos de cozinha, automotive trims, architectural panels.
9. Laser Etching
Processo: Focused laser beam engraves permanent marks or text.
Benefícios:
Alta precisão e repetibilidade.
Permanent identification or branding.
Formulários: Componentes aeroespaciais, dispositivos médicos, Ferramentas industriais.
10. Bright Dipping
Processo: Chemical immersion in acid for mirror-like shine.
Benefícios:
Creates highly reflective, glossy surface.
Ideal for decorative parts.
Limitações: Not compatible with all alloys (best with 6463).
Formulários: Comida & beverage equipment, decorative profiles.
Different Surface Effects & Styles for Aluminum Finishes
Finishing isn’t just about protection—it also defines how aluminum looks and feels.
High Gloss (Brilhante, Reflexivo): Achieved via polishing, bright dipping, or anodizing with gloss. Common in electronics, automotive trims, and luxury items.
Cetim (Soft Glow, 72 GU gloss): Achieved via brushing or bead blasting. Balances aesthetics and durability, hides imperfections.
Fosco (Non-reflective, 30 GU gloss): Achieved via anodizing or powder coating. Resistant to fingerprints and low-maintenance.
Metálico (Luxury Appearance): Achieved via anodizing, escovar, or electroplating. Can mimic brass, cobre, ouro, or stainless steel finishes.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Aluminum Surface Finish
When selecting the right finish, engineers and designers must consider:
Application Environment: Indoor vs. outdoor use, UV exposure, corrosive chemicals, or abrasion.
Requisitos estéticos: Cor, lustro, textura, branding consistency.
Custo: Initial processing cost + long-term maintenance or replacement expenses.
Durabilidade: Expected lifespan of finish, resistance to wear and weathering.
Funcionalidade: Conductivity vs. isolamento, weight considerations, surface friction.
Industrial Applications of Aluminum Finishes
Aluminum finishes aren’t just about making metal look good—they also make parts stronger, longer-lasting, and more reliable in tough environments. Depending on the finish, aluminum can be used almost anywhere, from airplanes to smartphones.
Aeroespacial
Aircraft parts need to handle high stress, mudanças de temperatura, and exposure to moisture. Finishes like anodização e chem film (alodine) are widely used because they improve corrosion resistance without adding too much weight. Laser etching is also common for permanent part marking, which is important for safety and traceability.
Automotivo
Carros, caminhões, and motorcycles rely on aluminum finishes for both protection and style. Powder coating and anodizing are used on wheels, trims, and engine parts to protect against road salt, aquecer, e desgaste. Polished and brushed finishes are also popular for giving vehicles a sleek, modern look.
Eletrônicos de consumo
The smooth, shiny casing on your smartphone or laptop often comes from anodizing or bead blasting. These finishes make the device look premium while also protecting it from scratches and fingerprints.
Dispositivos médicos
Em assistência médica, materials must be seguro, fácil de limpar, e resistente à corrosão. Anodized and polished aluminum parts are often used in surgical tools, hospital equipment, and even implant components. These finishes keep surfaces smooth, sterile, e durável.
Arquitetura e construção
De window frames to building facades, aluminum is everywhere in modern architecture. Powder coating is especially popular here because it can provide durable protection and a wide range of colors to match design needs. Brushed or metallic finishes also add an upscale look to interior elements like furniture and lighting fixtures.
Maquinaria industrial
Heavy-duty machines often use anodized or electroplated aluminum components for added wear resistance and better electrical performance. This ensures that the parts can handle tough environments without breaking down quickly.
Conclusão
Aluminum finishing is a crucial step in ensuring that parts meet both functional and aesthetic requirements. With options ranging from cost-effective chem film to decorative bright dipping and high-performance anodizing, each finish offers unique benefits for different applications.
Considerando cuidadosamente application environment, durability needs, custo, and desired appearance, manufacturers can select the right aluminum surface finish to improve both the performance and lifespan of their products.
Perguntas frequentes
- What is the most durable aluminum finish?
Anodizing—especially hard anodizing—offers superior wear and corrosion resistance, making it one of the most durable finishes. - Which finish best prevents corrosion?
Anodizing and alodine are both effective, with anodizing offering better long-term resistance. - What is the most cost-effective aluminum surface treatment?
Chem film (alodine) is relatively inexpensive while still providing strong corrosion resistance and paint adhesion.