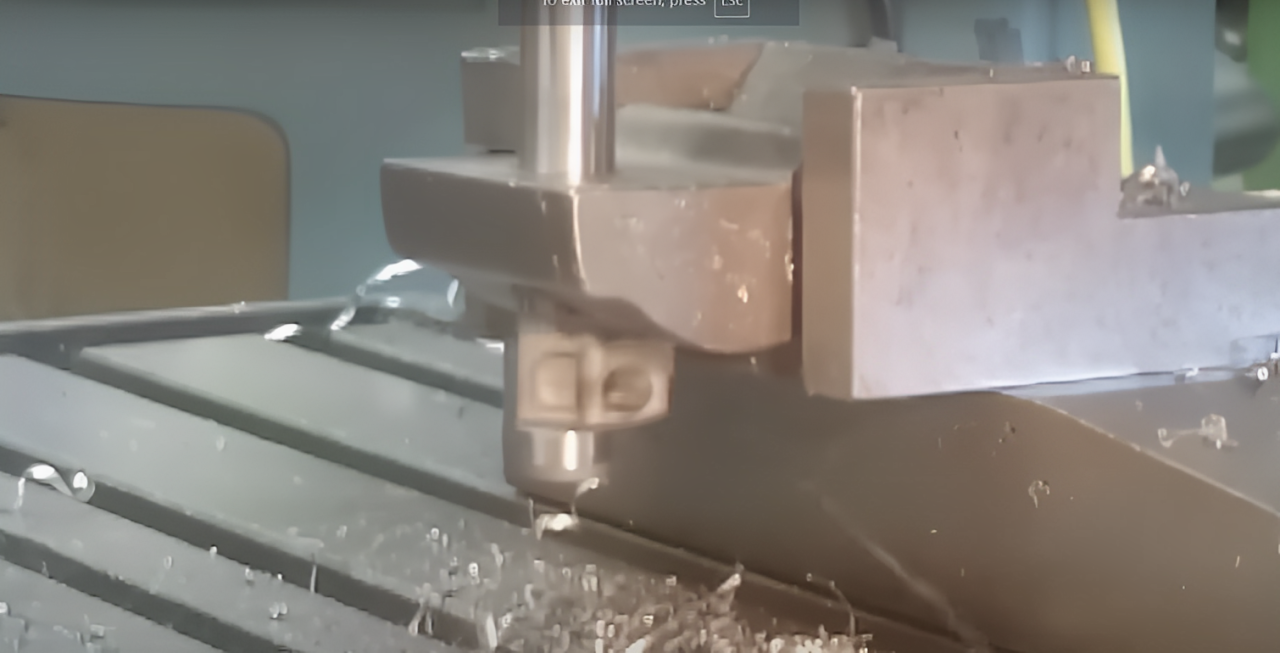
En mecanizado de precisión, Especificar la geometría adecuada del agujero es crucial. Los componentes mecánicos obtienen el ajuste y la función adecuados utilizando estos parámetros. Los agujeros de los contramanos y Spotface se encuentran entre los tipos más populares de modificación de agujeros y cada uno tiene usos comunes pero superpuestos. De este modo, Los agujeros de los contrtes permiten que los sujetadores casi se alineen con la superficie. Por otro lado, Los agujeros de Spotface crearán un área de asiento plano para los cabezales y las arandelas de los pernos.
En este articulo, Discutiremos el significado de esas definiciones, aplicaciones, métodos de mecanizado, y símbolos en dibujos de ingeniería y los compararán.
¿Qué es un agujero en el contrario??
Un orificio de contrarrebo es una cavidad cilíndrica de fondo plano que amplía los agujeros existentes. Entonces, Pueden ajustar sujetadores planos solo en las superficies de material o debajo de. La agenda principal de Counterbores es crear bolsillos para cabezas de perno., lavadoras, y nueces. Les ayuda a no sobresalir por encima de la superficie de trabajo.
Counterbores ayuda a lograr los tamaños requeridos. Los agujeros de contrarrestar precisos requieren ampliaciones cilíndricas con paredes paralelas que tengan cargas uniformemente, cubriendo ambos sujetadores y piezas de trabajo. Es útil para equipos especializados, tales como brocas con pilotos guiados.
Contenedores en dibujos de ingeniería
Los dibujos de ingeniería representan contadoras utilizando el símbolo "⌴", que parece un cuadrado u. Las especificaciones son un grupo de dimensiones que describen las dimensiones del contrario, es decir., diámetro, profundidad, y tamaño del diámetro del agujero.
El documento de dibujo dirige a los técnicos a hacer "⌀25 x 10 profundo para el perno m12 "contrarrestar, que requiere un 25 mm diámetro de diámetro cortado a una profundidad de 10 mm para acomodar un perno m12. El sistema de notación es específico y demuestra al personal de mecanizado qué especificaciones se requieren para proporcionar un ajuste adecuado.
¿Qué es un agujero de Spotface??
La característica de la superficie llamada Spotface Forms incluso superficies alrededor de los agujeros. Permite las tuercas y las cabezas de perno de lavado para descansar en posiciones pares. Spotface proporciona un corte poco profundo a través de menos material. Puede crear una superficie uniforme sin ir a tamaños de contratornos de profundidad completa. Los agujeros de Spotface le dan a los sujetadores un ajuste al ras en las superficies extrañas y curvas. Borre las herramientas Crear agujeros de Spotface que realicen cortes poco profundos para guardar materia prima pero aún tienen áreas de contacto adecuadas.
Agujeros de Spotface en dibujos de ingeniería
A Spotface utiliza el mismo símbolo que Counterbores ("⌴") Sin embargo, requiere notas adicionales de "SF" o "Spotface" para diferenciarlo. Los agujeros de dimensionamiento de Spotface comienzan especificando el diámetro al mismo valor que la cabeza del sujetador o la lavadora y luego se mueven para dimensionar la profundidad del orificio a menos que sea necesario para la funcionalidad. Los spotfaces aparecen en piñones y superficies ásperas. Desempeñan un papel vital cuando los diseñadores necesitan un área de asiento de uniforme plano.
Una comparación detallada de Counterbour Vs. Spotface:
La diferencia entre los agujeros de contraído y Spotface se traslada a sus aplicaciones de tamaños de usos, y procesos de mecanizado con sus estándares de ingeniería relacionados.
1. Usar
Counterbores juega su papel principal al dar espacio a los sujetadores bajo superficies exteriores para soportar y prevenir la interferencia de hardware. Los orificios de Spotface crean un área de unión suave para sujetadores en materiales irregulares o curvos sin alterar la verdadera densidad del material.
2. Profundidad
Los dibujos de ingeniería especifican valores de profundidad para contraportados que son lo suficientemente profundos como para acomodar cabezas o arandelas de pernos. Las profundidades de los agujeros de Spotface siguen siendo bajas ya que solo requieren unos pocos milímetros de profundidad para cumplir con la nivel de la superficie.
3. Solicitud
La aplicación funcional de contadores se encuentra durante el montaje de sujetadores debajo de las superficies de los materiales en conjuntos mecánicos junto con estructuras aeroespaciales y componentes de motores automotrices. Las spotfaces ofrecen superficies de rodamiento estándar en piezas rudas y fundidas en maquinaria y equipos industriales pesados.
4. Proceso de mecanizado
Las operaciones de fabricación de agujeros para el mostrador y el agujero de la superficie incluyen operaciones de perforación y luego fresado. Los contadores requieren herramientas guiadas por el piloto, mientras que las facios de manchas toman herramientas similares cuando los operadores usan el control de profundidad para evitar la exhaustación.
5. Especificaciones de ingeniería
Los dibujos de ingeniería indican estas características utilizando el mismo símbolo "⌴", pero las spotfaces también tienen una anotación SF adicional. El diámetro y las dimensiones de profundidad denotan los contrarrillos en los dibujos, pero las facios de mancha generalmente necesitan dimensiones de diámetro ya que la profundidad es muy poco.
6. Impacto estructural
Contrarrestar afecta negativamente la integridad estructural de las piezas. Dado que este proceso de producción elimina cantidades significativas de material. Aquí, La pieza de trabajo se mide antes de comenzar la operación de mecanizado. Estas piezas usan spotfaces para mantener muy bien su integridad estructural, ya que eliminan un material mínimo para el aplanamiento.
Podemos diferenciarlos brevemente en la siguiente tabla:
| Característica | Contramanario | Spotface |
| Objetivo | CONSEJOS DE CONSEJOS PARA FIJA | Creando una superficie plana para cabezas de sujetador |
| Profundidad | Puede ser profundo dependiendo del sujetador | Muy superficial, eliminación mínima de material |
| Uso común | Usado en ensamblajes que requieren pernos montados en descarga | Usado en áspero, elenco, o superficies curvas para garantizar la estabilidad del sujetador |
| Símbolo en dibujos | ⌴ con especificaciones de diámetro y profundidad | ( ⌴ )con las letras "SF" dentro de él, con un diámetro (profundidad a menudo omitida) |
| Eliminación de materiales | Elimina material significativo | Elimina el material mínimo |
Mecanizado de contramanario y spotface
Los procedimientos de mecanizado de contraman y Spotface implican herramientas de corte de precisión que producen limpios, agujeros de fondo plano. Las prensas de perforación y las fresadoras CNC generalmente producen dimensiones precisas y acabados superficiales.
1. Mecanizado
- Utiliza un cortador piloto de contraído.
- Proporciona un receso de tamaño preciso para cabezas de sujetador.
- Generalmente hecho después de perforar el orificio inicial.
2. Mecanizado de Spotface
- Utiliza una herramienta guiada de fatigaciones piloto.
- Solo elimine el material suficiente para proporcionar un suave, superficie plana.
- Típicamente utilizado en piezas de fundición o superficies desiguales.
Herramientas de contramanario y Spotface
Se utilizan varias herramientas de corte en la producción de características de contraído y spotface, como:
- Cortadores: Pilotado para la alineación de precisión.
- Herramientas de SpotFace: Son los mismos que los cortadores de los contrtesistas, pero están diseñados para la eliminación de materiales poco profundos.
- Fábricas finales: Utilizado en Mecanizado CNC para producir superficies precisas de contraído o superficie de Spotface.
- Taladros especializados: Ciertos bits de perforación tienen capacidades de contraído o Spotface incorporados.
Consideraciones generales de fabricación para contraypers y spotface
Los fabricantes consideran lo siguiente al diseñar piezas con contadores o facios de manchas:
- tipo de material: Los materiales más duros se pueden acomodar con herramientas especializadas.
- Requisitos de tolerancia: Precisión precisa para el ensamblaje adecuado.
- Especificaciones de sujetador: Compatibilidad con tornillos y pernos.
- Acabado de la superficie: Un piso, Se requiere una superficie lisa para los mejores asientos de sujetador.
Identificación de símbolos de Spotface y Contrankor
Los símbolos en ingeniería son vitales para la fabricación precisa. El símbolo para el contraído/spotface está generalizado, como:
- Anotación de diámetro (Ø).
- Notación de profundidad del contrario.
- La profundidad de Spotface generalmente solo se usa si es esencial.
Cual es mejor? Controlante VS. Agujeros de Spotface?
El uso apropiado de los agujeros de la superficie de la superficie de los puntos de vista depende únicamente de sus funciones, Un diseñador necesita. Los contadores resultan efectivos para lograr la integridad estructural. Proporcionan agujeros más profundos para esconder o recesar sujetadores. Por otro lado, Spotfaces encuentre su mejor aplicación cuando los usuarios requieren asientos de sujetador incluso en superficies no descriptivas y irregulares o curvas.
Utilizamos contarbores al diseñar para carga de carga, Mientras que los spotfaces funcionan mejor para lograr una distribución de fuerza uniforme. El proceso de selección para una técnica de modificación de agujeros adecuados comienza con un conocimiento preciso de los requisitos de aplicación.
Conclusión
En conclusión, Las características de mecanizado necesarias necesitan una instalación adecuada de sujetador y distribución de carga, incluidos los contadores y las spotfaces.. Los contadoras dan asientos empotrados a pernos y tornillos. Mientras que los spotfaces crean caras planas en materiales no planos. Las diferencias del eje, aplicaciones, y el mecanizado permiten a los ingenieros y maquinistas tomar decisiones informadas.
Preguntas frecuentes
- ¿Cuál es la principal diferencia entre un contrario y un agujero de Spotface??
El contrario es más profundo y acomodará los sujetadores. Por otro lado, Una cara de spot tiene una profundidad extremadamente superficial con una superficie plana para asientos adecuados.
- Es una opción de Spotface en lugar de un contrario?
No siempre. Estos spotfaces son demasiado poco profundos para los sujetadores de recesación completamente. No se recesan lo suficientemente lejos como para que se adapten a los que se usan donde se necesita el montaje de descarga.
- Es el mecanizado de spotface una herramienta que requiere herramientas especiales?
Sin embargo, La profundidad de las herramientas de los contrtesistas se puede controlar para la creación de spotfaces.
- ¿Qué las industrias hacen los contratbores y las caras spotes vienen a jugar en?
Las principales industrias incluidas en él son; aeroespacial, automotor, carpintería de maquinaria pesada, e industrias médicas.