質の高いテストと検査は、重要な役割を果たします CNC加工, directly impacting product reliability, 機能性, and customer satisfaction. ツールを理解する, テクニック, and inspection stages involved ensures consistently high-quality output. This article offers a detailed guide to CNC machining quality testing and inspection practices.
In precision manufacturing, 特にCNC加工, maintaining exceptional quality is non-negotiable. Every part must meet strict specifications, ensuring reliability and performance. Comprehensive testing and inspection form the backbone of quality management, helping manufacturers produce flawless components consistently.
What is Quality Testing and Inspection in CNC Machining?
Quality testing and inspection involve examining machined components to verify their compliance with specified criteria—such as dimensions, 公差, 材料特性, および表面の品質. The objective is to detect and eliminate defects before the product reaches the end user, ensuring optimum functionality and reliability.
Quality Control vs. Quality Inspection vs. 品質保証
品質管理 (QC): Making Sure Everything Goes Right
Quality Control means the activities you do during production to keep quality consistent. It’s about checking the process, finding issues early, and fixing them quickly—so you don’t have defects later. Think of QC like following a recipe carefully every time you cook, making sure each dish tastes just as good as the last.
品質検査: Checking the Finished Product
Quality Inspection involves carefully examining finished parts or materials to make sure they match the required specifications. This step focuses on measuring dimensions, checking surfaces, and visually looking for any flaws or defects. Imagine inspecting fruit at a market—you pick each piece up and make sure it’s ripe, unbruised, and good enough to buy.
品質保証 (Qa): Planning to Prevent Problems
Quality Assurance is about planning and improving processes so that problems don’t happen in the first place. It includes creating guidelines, setting standards, and training employees. QA helps everyone know exactly how to do their jobs properly, ensuring the final products meet quality standards consistently. It’s like practicing good hygiene to stay healthy instead of just treating illnesses after they happen.
Key Quality Control Parameters in CNC Machining
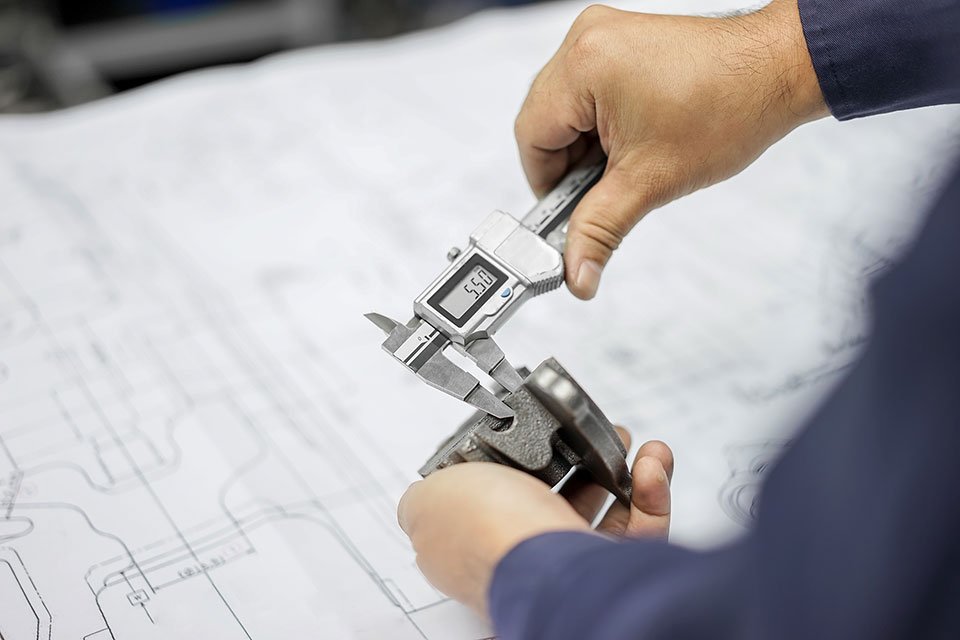
Engineering inspection check dimension automotive parts reference drawing by vernier caliper in industrial factory
Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerance
Dimensional precision is crucial for part performance and fit. High-quality machining demands exact adherence to specified tolerances.
Surface Finish and Roughness
A quality surface finish influences the part’s aesthetic appeal and functional performance, 摩擦と摩耗を軽減する.
Material Hardness and Strength
Proper material hardness and strength ensure components withstand their intended operational stresses.
Geometric Tolerancing (GD&T)
Ensures accurate shape, position, and orientation of machined features, critical for assembly and performance.
Machining Process Control
Real-time adjustments and statistical methods maintain consistent machining parameters (スピード, 餌, とツーリング).
ツールの摩耗と寿命
Monitoring tool condition prevents degradation in dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Assembly and Fit
Precise part dimensions ensure seamless assembly without further modifications.
環境要因
Controlled temperature and humidity are essential to maintaining dimensional stability.
Compliance with Standards and Regulations
Meeting quality benchmarks such as ISO 9001 (一般的な製造) and AS9100 (aerospace-specific) ensures consistent quality assurance.
Essential Quality Control Techniques and Tools
Dimensional Measurement Tools
Calipers and Micrometers: Accurate measurements for length, 直径, and thickness.
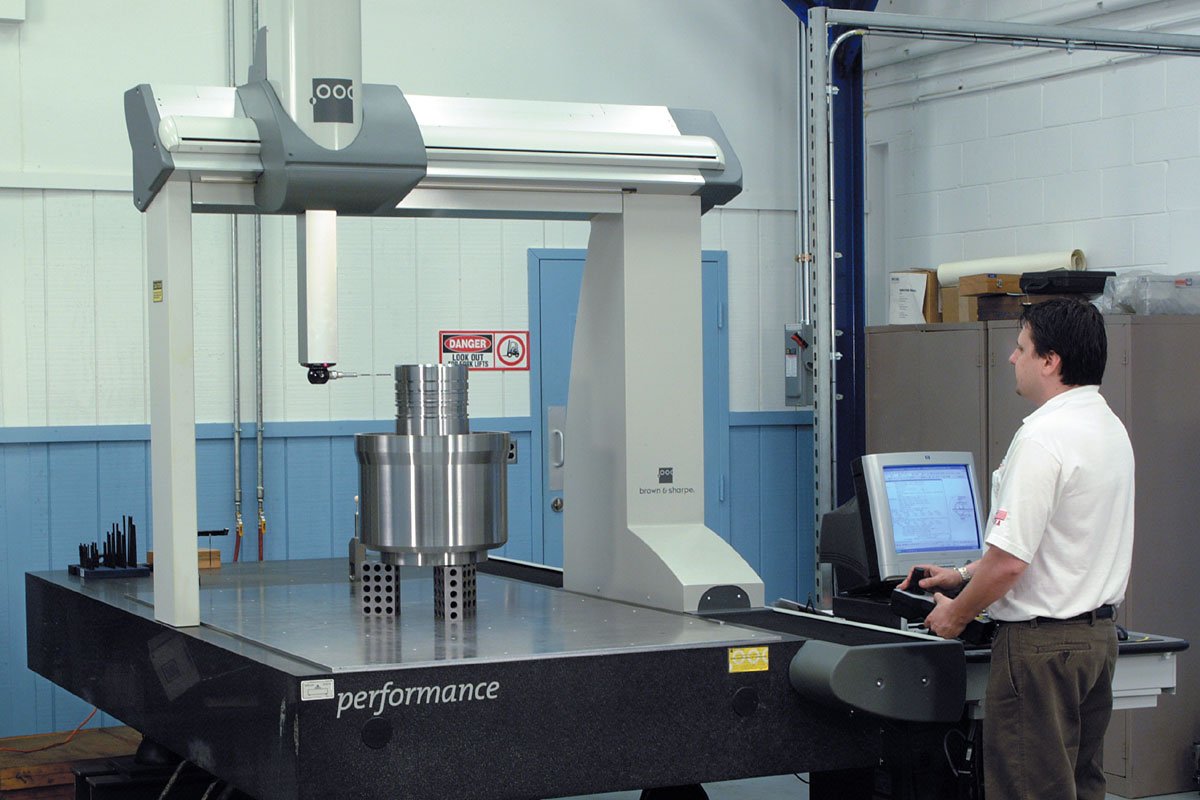
測定機を調整します (三次元測定機): Complex dimensional inspection for intricate geometries.
Gauge Blocks and Thread Gauges: Standardization and thread accuracy verification.
Surface Roughness Testers
Profilometers: Detailed surface roughness measurement.
光学コンパレータ: Visual inspection of detailed surface characteristics.
Hardness Testing Equipment
Rockwell Hardness Testers: Common method for metals.
Brinell Hardness Testers: Suitable for softer metals and alloys.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Ultrasonic Testing: Detects internal flaws with sound waves.
X-ray Inspection: Identifies internal defects and material inconsistencies.
Magnetic Particle Inspection: Surface and sub-surface defect detection in ferrous materials.
Statistical Process Control (SPC) ソフトウェア
Real-time monitoring and statistical analysis ensure consistency and reliability.
Tool Condition Monitoring
Devices and automated systems track tool wear, preventing unexpected failures.
Environmental Monitoring Equipment
Temperature and humidity sensors maintain machining conditions for precision stability.
幾何学的な寸法と公差 (GD&T) ツール
Gauges and fixtures verify form, 向き, and positional accuracy.
Visual Inspection Tools
Magnifying devices, 顕微鏡, and borescopes facilitate detailed visual analysis.
Material Analysis Equipment
Spectrometers: Verify elemental composition.
Microstructure Analysis: Assesses grain structures and material integrity.
Assembly and Fit Testing Tools
Go/No-Go Gauges: Quick dimensional checks.
Functional Testing Rigs: Validate performance under realistic operating conditions.
Documentation and Traceability Systems
Software tracks inspection data, ensuring transparency and compliance.
Stages of Machining Quality Testing and Inspection
Raw Material Inspection
Verifying material properties before production to ensure compliance.
最初の記事の検査 (ファイ)
Detailed inspection of the first component produced to confirm initial quality adherence.
インプロセス検査
Regular checks during machining to identify defects immediately and prevent costly rework.
寸法検査
Careful verification of part dimensions using calibrated measuring instruments.
Surface Finish Inspection
Analyzing surface quality to ensure compliance with functional and aesthetic requirements.
Visual Inspection
Identifying visible imperfections, 傷, and defects that can affect part usability.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Inspecting for internal flaws without harming parts, essential for high-risk applications.
硬度テスト
Ensuring material hardness meets specified mechanical property requirements.
機能テスト
Confirming that parts perform as intended in realistic operating scenarios.
Assembly and Fit-Up Inspection
Validating correct assembly and proper fit of components.
最終検査
A comprehensive review of finished parts to ensure complete adherence to quality specifications.
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Ongoing monitoring of production processes using statistical methods.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Comprehensive record management ensures accountability and facilitates quality improvements.
マシン後の治療
Inspecting results of secondary processes like heat treatment or plating.
Packaging and Shipping Inspection
Ensuring finished parts remain damage-free during transportation and delivery.
Importance of Personnel Training
Skilled personnel are critical to machining quality. Regular training ensures operators understand and effectively apply the latest quality control methods and standards. Training covers:
Proper use of measurement tools.
Interpretation of specifications and tolerances.
Implementation of quality assurance practices.
Quality Inspection and Assurance at Tops Precision
最高の精度, quality assurance is integral to our operations. We deploy state-of-the-art inspection equipment including:
X-ray Material Tester: Rapid material identification ensures accuracy in prototype and production.
On-Machine Inspection Systems: Real-time adjustment to machining parameters.
Optical Projectors: Precision geometric measurements.
測定機を調整します (CMMS): Advanced geometric and dimensional verification.
Our process integrates thorough inspections from material reception through final product validation, guaranteeing excellence at every step.
結論
Achieving and maintaining high-quality CNC machined parts requires diligent application of robust inspection techniques, skilled personnel, and advanced equipment. By understanding these practices and continually improving upon them, manufacturers can reliably produce precision components, fostering customer trust and industry reputation.
よくある質問
Q1: Why is dimensional accuracy critical in CNC machining?
Dimensional accuracy ensures parts fit and function correctly, avoiding assembly problems and functional failures.
第2四半期: How does surface finish affect component performance?
Surface finish impacts aesthetics, 摩擦, 耐摩耗性, そして疲労寿命.
Q3: What is non-destructive testing (NDT)?
NDT methods detect internal or external defects without damaging the component, essential in safety-critical industries.
Q4: Why is compliance with ISO and aerospace standards important?
Meeting these standards ensures parts meet universally recognized quality and safety criteria.
Q5: How frequently should inspection occur during machining?
Regular inspections should occur at critical stages including initial material check, 最初の商品検査, in-process monitoring, and final validation.
続きを読む:






