Metal is generally linked with properties, i.e. strength, durability, and rigidity. However, not all metals can be thought of as hard. Some metals are incredibly soft, meaning they are quite special in their applications. Of these, the most interesting one is special for its low hardness, malleability, and ductility. So, in this article, we shall disclose the facts and explain what is the softest metal on earth. Besides this, we will discuss its numerous applications in different areas of life.
What is the Softest Metal on Earth?
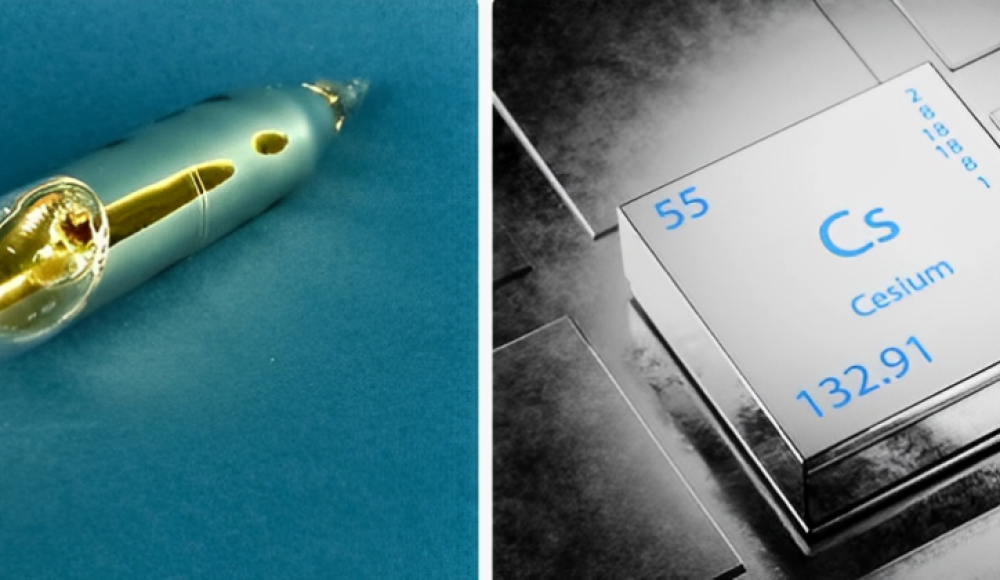
Cesium is the softest metal on the planet and a part of the alkali metal group. So, it is more reactive than other metals. Besides this, we can shave it off with a knife. If we talk about its melting point, it is 83.3°F (28.5°C). So, it can mold easily in different shapes.
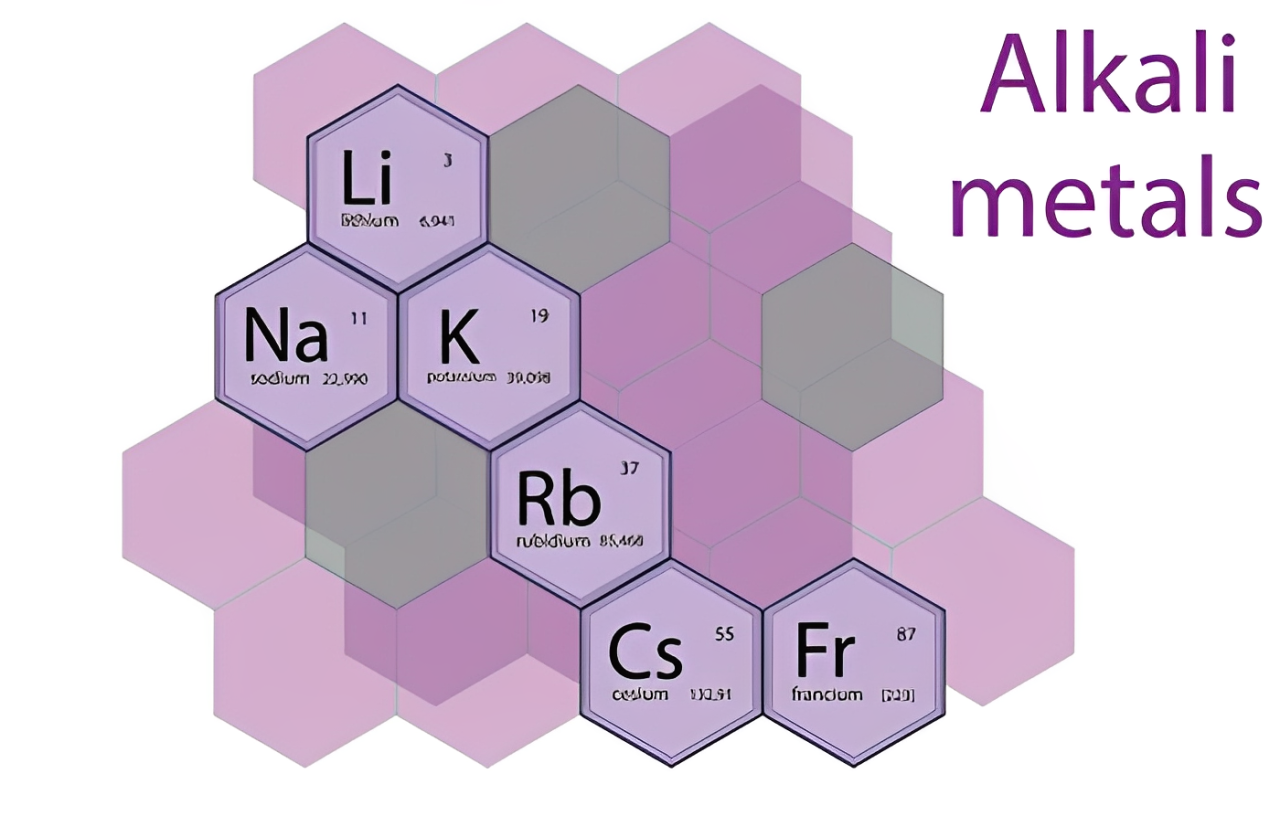
Cesium is the softest metal on the list, along with lithium, sodium, and potassium. Alkali metals are very reactive and relatively lightweight, and all these elements have many common properties. However, cesium can be described as the softest element, demonstrating some other ways besides the periodic table.
Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Cesium
So, here are some of the features of cesium – the softest metal on earth:
1. Physical Properties
Let’s talk about its physical properties:
- Appearance: Cesium, at standard conditions, is shiny and silver like most metals having a golden hue.
- Density: Still, its density, 1.93 g/cm³, puts cesium among relatively low-density metals.
- Melting Point: It is easily melted under slightly warm conditions; it is solid at temperatures below 28.5°C (83.3°F) and melts when the temperature is raised to this level and a little higher.
- Softness: Cesium is malleable, like the common lead, which can easily be hand-shaped, though it cannot be handled due to its extreme reactivity.
2. Chemical Properties
Here are its chemical properties:
- Reactivity: The element is very reactive – especially with water, combining with it to form an explosive reaction.
- Alkali Metal Group: It is in Group 1 of the periodic table and has characteristics such as low ionization energy and high electropositive character.
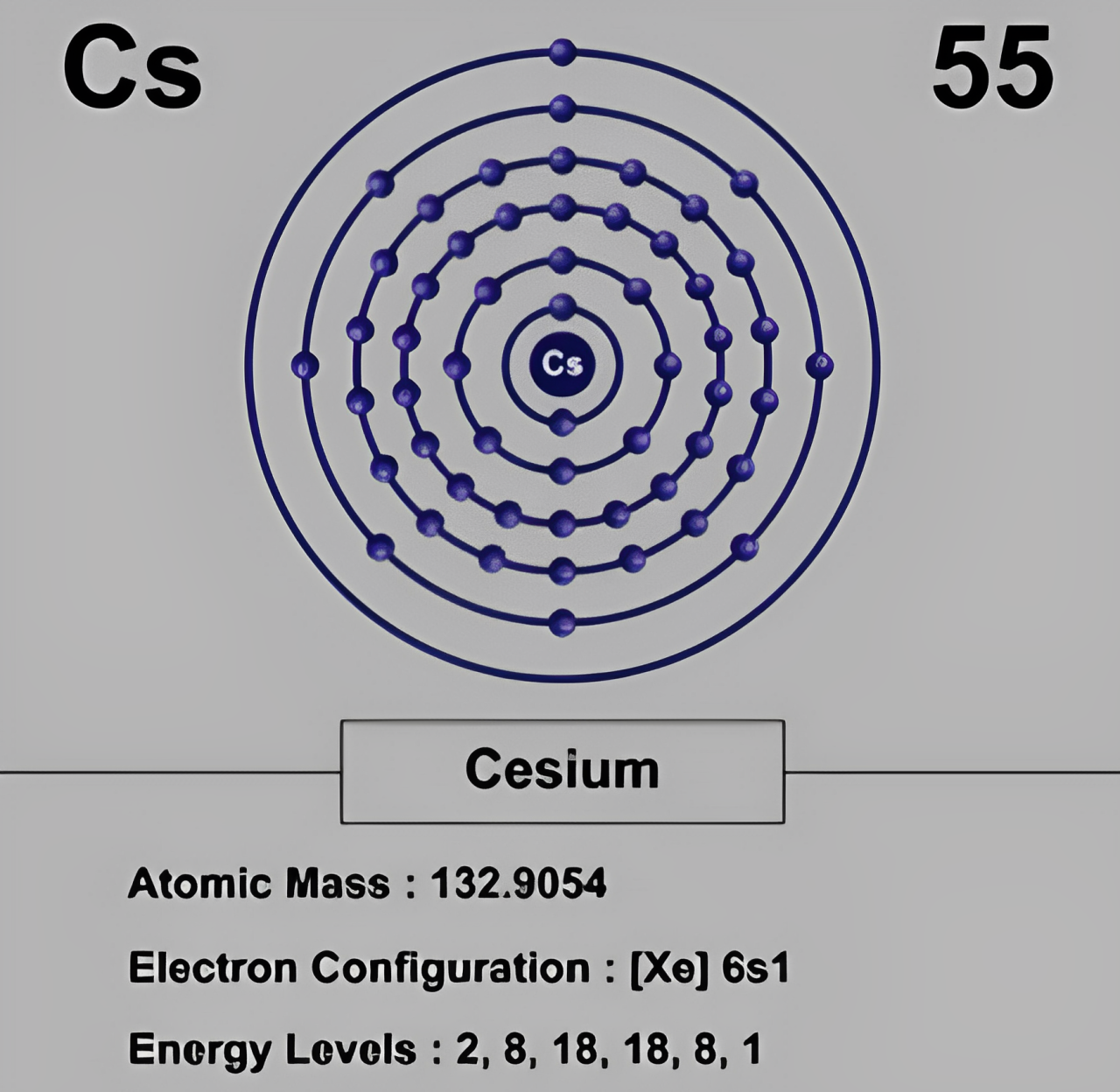
- Electron Configuration: Cesium only has one valence electron. So, Cesium has a great tendency to form ionic bonds.
These features are summarized in the following table:
| Feature | Value/Description |
| Physical Properties | |
| Appearance | Silvery-gold metallic luster |
| Density | 1.93 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 28.5°C (83.3°F) |
| Softness | Extremely soft; can be molded by hand (requires careful handling due to reactivity) |
| Chemical Properties | |
| Reactivity | Highly reactive; explosive reaction with water |
| Alkali Metal Group | It belongs to Group 1 of the periodic table |
| Electron Configuration | [Xe] 6s¹ (one valence electron, highly reactive and forms ionic bonds) |
Softness of Metals – Why Cesium is the Softest Metal
The atomic nature of cesium makes it the softest of all the elements. The atom’s effective atomic number located the outermost electron in cesium very far from the nucleus because of its large atomic size. So, this reduces the metallic bond between the atoms making the material. This makes it very soft.
A Comparison with Other Soft Metals
So, let’s compare Cesium and other soft alkali elements:
1. Lithium (Li)
- Softness: It may be sliced with a knife but is more rigid than cesium.
- Reactivity: More reactive than the majority of metals, yet not as reactive as cesium.
- Uses: Batteries and alloys.
2. Sodium (Na)
- Softness: More malleable than lithium but less so than cesium.
- Reactivity: Reacts violently with water.
- Uses: Sodium vapor lamps, chemical synthesis Sodium vapor lamps Chemical synthesis
3. Potassium (K)
- Softness: It can be rubbed on its surface with a file, but it is harder than lead and less soft than cesium.
- Reactivity: A violent reaction with water accompanied by heat and the evolution of hydrogen gas.
- Uses: Arable land and chemical amendments.
So, cesium is different from these metals it is extremely soft and has a distinct golden color.
Here is the table to summarize the comparison of the different softest metals on Earth:
| Metal | Softness | Reactivity | Uses |
| Lithium (Li) | Harder than cesium, cuttable with a knife | Extremely reactive but less than cesium | Batteries, alloys |
| Sodium (Na) | Softer than lithium, harder than cesium | Reacts violently with water | Sodium vapor lamps, chemical synthesis |
| Potassium (K) | Softer than sodium, harder than cesium | Highly reactive, produces heat and hydrogen with water | Fertilizers, chemical reactions |
| Cesium (Cs) | Softest metal, easily moldable | Extremely reactive, especially with water | Atomic clocks, space tech, medical uses |
Industrial and Scientific Uses of Cesium
However, cesium is an extremely soft metal; It is not used for general purposes because it is highly reactive and not very abundant. It is very crucial in technical sectors.
1. Atomic Clocks
Cesium is a foundational component of the most accurate time-keeping devices known to man, atomic clocks. These clocks work as the frequency of the cesium atoms oscillates regularly, and nothing can match this level of precision. It is so necessary for GPS and telecoms.
2. Oil and Gas Exploration
High density and low viscosity make this fluid give better support to boreholes. At the same time lowers the effects on the environment as compared to normal fluids.
3. Medical Applications
Cesium isotopes but especially Cesium-137 are applied in cancer treatment with the help of radiotherapy. They assist in the selective elimination of cancerous tissue and minimize harm to surrounding tissues.
4. Space Technology
The metal ions cesium are used in ion thrusters to propel a spacecraft. Due to its ability to react easily and ionize, cesium is the most suitable fuel for producing thrust in space travel.
5. Optical Glass
The non-radioactive element of cesium is used to adjust the quality of certain types of glass. It makes them clearer and more resilient. Cesium-based glass is employed in enhanced lenses and machines that demand improved reflective surface optics.
6. Research and Development
Cesium is used in laboratories in chemistry, and physics experiments due to its property being a soft and reactive metal. For this reason, it is useful in ionization and metallic bonding qualities examination.
Pros and Cons of Using Cesium – the Softest Metal on Earth
Nevertheless, as can be seen, cesium has faster and much better properties than other alkali metalloids; however, this element has drawbacks that impede the increased application of such material.
1. Reactivity
Cesium reactivity is very high and thus hazardous. It is incombustible, reacts violently with water, and should be preserved under an inert atmosphere. These may include mineral oil or sealed glass ampoules.
2. Rarity and Cost
Cesium is a silver-yellow alkali metal that is relatively rarely used and mostly obtained from pollucite. It is rare, and therefore, is costly, thereby being useful only in particular fields.
3. Toxicity
Acute toxicity of cesium can result in oral or inhalation exposure. During handling, appropriate measures have to be taken. So, we can ensure that there are no adverse health consequences.
4. Environmental Concerns
The mining of cesium and the removal of radioactive isotopes including cesium-137 are considered environmentally sensitive operations. For these reasons, there are very tight rules and controls on application.
The Significance of Softness in Metals
The metal’s softness is an advantageous characteristic. It is quite likely that one would consider confounding what metals are conventionally used for. They are relatively easy to manipulate, or form and fuse with other materials, and are thus suitable when high formability is needed.
1. Benefits of Soft Metals
- It is easier to process and manipulate than other databases and data storage instruments.
- Appropriate for complex patterns and differential cutting instruments.
- Usually added in alloys, to give certain characteristics to the stronger metals.
2. Trade-offs
Soft metals are fragile and require to be handled carefully. They are frequently used with other harder materials for greater functions.
Interesting Facts About Cesium
Below are some lesser-known facts about cesium – the softest metal on the Earth:
- Discovery: Cesium is a chemical element that was found in 1860 by two German scientists, Robert Bunse,n and Gustav Kirchhoff by flame spectroscopy.
- Name Origin: The detail gets its name after the Latin word – which means sky blue because cesium gives blue lines in the emission spectrum.
- Melting in Hand: You might find it interesting that cesium if handled on a warm day, will melt in your hand – a feat that should not be done given the vitality of the chemical element.
Other Soft Metals in Everyday Life
While cesium is the softest metal, we have several other metals for their softness and numerous applications:
- Gold: Relatively soft and easy to shape or mold, especially where we make jewelry and electronics.
- Lead: Soft, with low density, and utilized in batteries and Radiation shielding.
- Tin: Light and tough material that exhibits good resistance to corrosion. Moreover, it has common applications in coatings and alloys.
Conclusion
In conclusion – cesium is the softest metal globally and its features make it an interesting element with specific applications. Its high chemical reactivity, low density, malleability, and scarcity make it suitable for applications like atomic clocks, space exploration, and medicine. Nevertheless, its disadvantages, i.e. high drawbacks and environmental constraints limit its usage. Besides this, it has a few applications as a specialty material rather than usually metal.
Cesium and other soft metals will be able to value their role in supporting science, and technology. They have prominent significance in industrial growth demonstrating that even soft materials can have a global influence. Compared with soft metals, in extremely high temperature, wear or corrosion environments, zirconia ceramics or alumina ceramics can be used as substitutes when hardness, wear resistance and corrosion resistance are key requirements. Contact us for more information.
FAQ
1. Is it possible for cesium to melt at normal temperature?
Of course, cesium can melt at slightly above room temperature, 28.5 °C (83.3 °F). It can turn into a liquid in warmer climates.
2. What do you know about the element, cesium?
Cesium helps generate atomic clocks as a drilling fluid in the oil and natural gas industries. So, it can power space booster rockets, cancer therapy, and fine optical glass manufacturing.
3. Is cesium safe to handle?
Since cesium is highly reactive, it should be used only in its inert environment for various applications. It is very sensitive to water and reacts violently when in contact with it.
4. Where does cesium stand with other soft metals such as gold or lead?
Compared with gold and lead as softer elements, cesium is relatively softer because of the atomic layout. Nevertheless, gold and lead are steadier metals and have a wide scope of applications in everyday life.