Mold Making is an interesting and precise process that is a key way to produce high-quality products in many industries. If you are making plastic toys or metal automotive parts, the mold-making process establishes consistency and accuracy during mass production. So, let’s get into the complete mold-making process and dissect it step-by-step.
What is Mold Making?
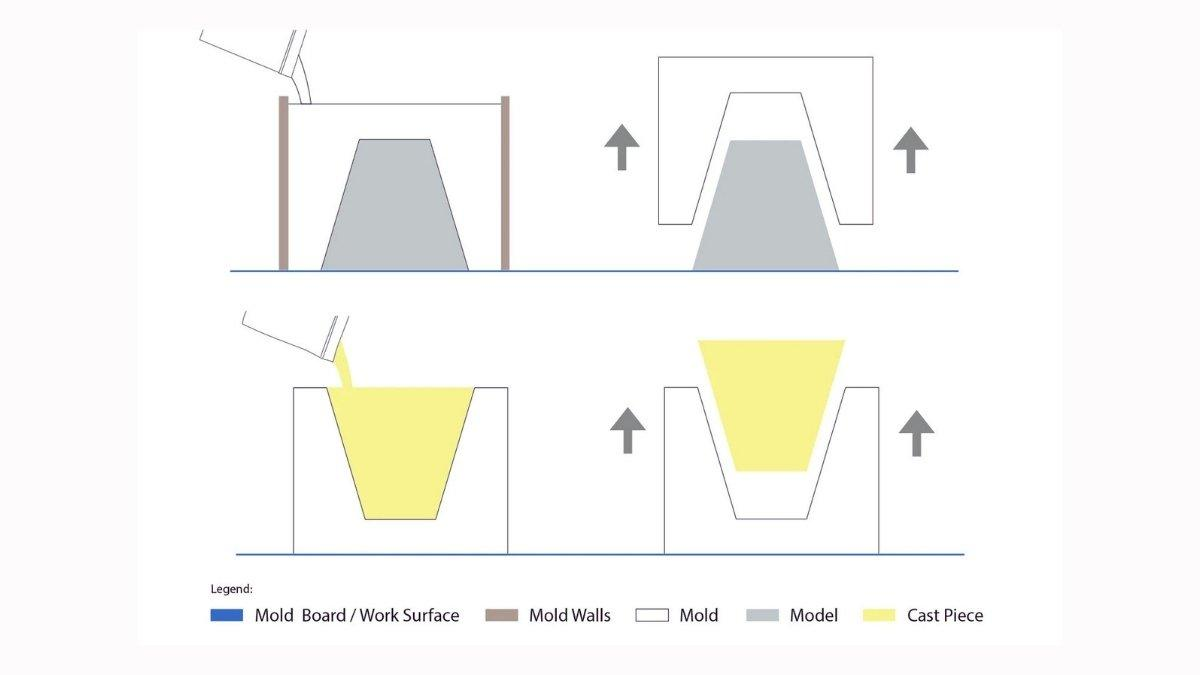
Mold making, at the most basic level, is the process of creating a mold — a hollow cavity or form — that material is then poured, injected, or otherwise placed into. As the material cools or hardens, it takes the shape of the mold and creates a replica of the original part. It is essentially a blueprint for mass production. From tools to medical devices, molds are used across industries, from automotive to plastic containers and engine components.
Types of Molds
Each type of mold serves a specific substance and fabrication procedure. We’ll look at the most prevalent types:
Injection Molds
Injection molds — where molten material (usually plastic) is injected into a mold cavity. The material solidifies and takes on the form of a mold. This mold is the mold we use for large-scale production.
Compression Molds
These molds are also ideal for rubber and thermoset plastics. In this process, the material is introduced into the heated mold cavity, after which pressure is applied to shape the part.
Die-Casting Molds
Molds used for die-casting are mostly for metal components. High-pressure injected molten metal into the mold cavity, where it solidified into the exact part. Their application is that of manufacturing parts such as engine blocks or various components.
Blow Molds
Blow molds form hollow plastic products, such as bottles. An air is blown into a heated plastic tube, which forms the shape of the mold cavity.
Steps Involved in Mold Making
Now that we have some basics let’s go step-by-step through the most important steps of how to make a mold.
Design and Prototyping
Design is the foundation of everything. Engineers design a molded part, creating a 3D model using CAD software. They also define the mold in and of itself, ensuring it’s able to accommodate the material and provide the precisions needed. A prototype is developed, and sometimes a 3d model is created to verify fit and function if the design is complex.
Material Selection
Choosing the best material for your mold is a key factor. Steel is typically selected for high-volume production runs due to its strength and durability, and aluminum is used for lower-volume production runs, for instance. Silicone molds are a good choice for prototypes or more flexible materials.
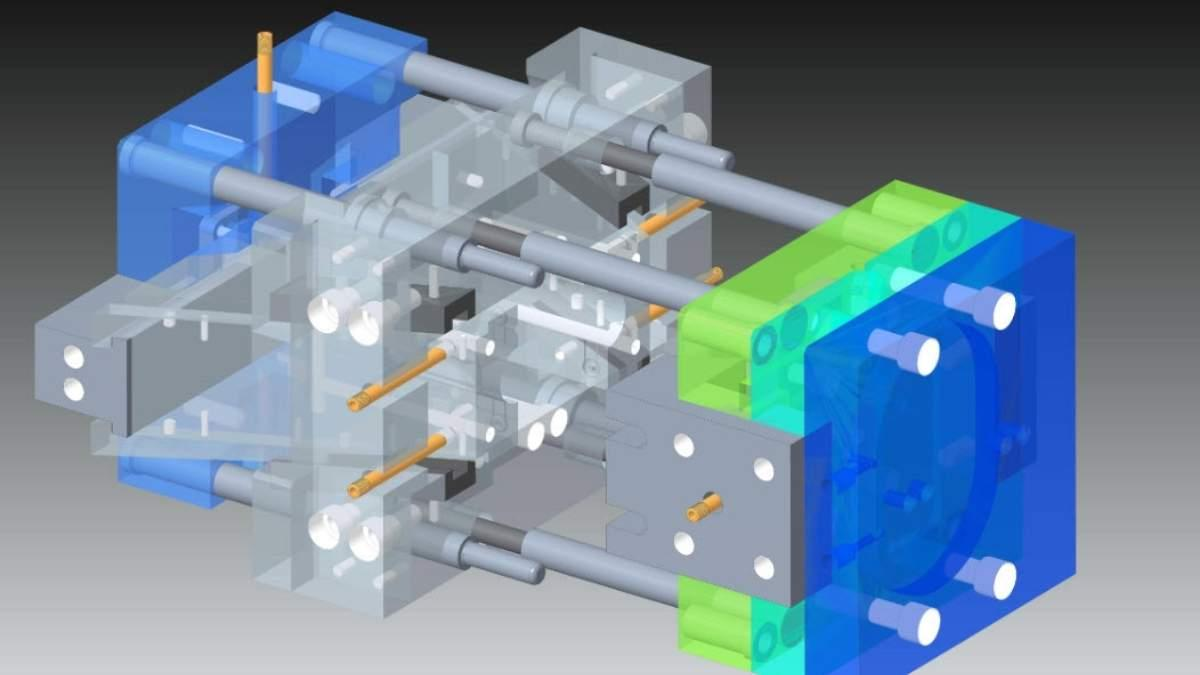
Mold Fabrication
This is where the magic takes place. After the material is chosen, the mold is created. Based on the 3D design, CNC machines, EDM, for example (Electrical Discharge Machining), etc. Making sure the mold is accurate is critical since the better quality of the mold, the better quality parts you can fabricate.
Mold Assembly
After all the components are fabricated, the mold is ready for assembly. That can include the addition of ejector pins, cooling channels, and other features to facilitate part removal and cooling. At this point, the mold is being tweaked for maximum efficiency.
Testing the Mold
The mold must be tested before going into full production. A few sample parts are made to confirm that the mold operates as it should and that parts conform to the necessary specifications. If changes are necessary, they will be applied here.
Full-Scale Production
Once tested, the mold is ready for mass production. The mold is now being used to make parts in high volume. In all stages of the production, if needed, more adjustments are completed to keep the quality stable!
Important Factors in Mold Making
The process of making a mold can seem simple, but there are a few nuances that should be taken into consideration to gain the greatest results.
Tolerances and Accuracy
Dead-on tolerances are vital if parts must fit together or operate under specific circumstances. Even small nicks in the mold can cause defects or improper performance in the finished part.
Material Selection
The mold is another crucial factor to consider when preparing to begin the production process. The mold material should endure wide pressure and temperature range while maintaining its shape across thousands of cycles.
Cooling System Design
Air conditioning is an essential part to ensure that the injected parts are being desired. These cooling channels lead through the mold to allow the material to shrink evenly and can lead to greatly reduced cycle times and fewer defects.
Mold Maintenance
A mold is an investment in itself, and with proper care, its life can be extended. This material can soften or be worn down after extensive use; thus, molds might take on repair or modification. Keeping molds in tip-top shape during long production runs requires regular cleaning and checking.
Common Applications of Mold Making
Mold making is not only for one type of industry. It is used across myriad fields to produce several different products. Most commonly, you will see the following applications:
Automotive Industry: Bumpers, dashboards, engine components, etc.
Consumer: Toys, home products, and packaging.
Medical Devices: Precision components such as syringes, implants, and diagnostic apparatuses.
Electronics: Bubbles for computers, phones, and others.
Challenges in Mold Making
Mold making is a precise and reliable way to make parts, but there are some difficulties to consider.
Option to Use Different Types of Molds: If there is an error in material selection for the tube mold, it will result in the defects of the molded parts.
Complexity: Components that have complex geometries or features may lead to more complex tooling, requiring more manufacturing steps.
Cost: The cost of manufacturing high-quality molds, such as steel molds, can be significant. This is especially crucial for smaller production runs.
Wear and Tear: Molds can break down with time, particularly if class in and out of molds is a constant occurrence. So regular maintenance is important to make sure they last as long as possible.
Conclusion
Mold making - ensuring parts are manufactured with high repeatability and precision. Ensuring the mold is working properly is critical, and that is why every step, including but not limited to design, materials, and fabrication, is included in this process. Despite the challenges involved in the process, the advantages of creating molds for mass production outweigh them greatly.
Learn how to approach mold-making with confidence — from plastic parts and metal components to anything that falls in the middle by contacting us!