La prototipos rápidos ha revolucionado la forma en que se desarrollan los productos, Ayudar a las empresas e innovadores a moverse rápidamente del concepto a los modelos listos para la producción.. Sirve como un paso invaluable en el desarrollo de productos, habilitando una evaluación rápida de diseños, facilitando mejoras, y minimizar el riesgo antes de que comience la fabricación a gran escala.
Los beneficios clave de la prototipos rápidos incluyen líneas de tiempo de desarrollo acelerado, costos reducidos, y precisión mejorada del producto. Seleccionar el método de prototipos rápidos correctos puede influir directamente en el éxito y la eficiencia de su proyecto.
¿Qué es un prototipo??
Un prototipo es un modelo preliminar o muestra de un producto construido con el fin de probar un diseño, concepto, o funcionalidad. Los prototipos sirven varias funciones esenciales:
Prueba de concepto: Los prototipos verifican si una idea de diseño es factible, práctico, y cumple con los objetivos previstos.
Validación de diseño: Permite a los diseñadores e ingenieros identificar fallas, Refinar la estética, y mejorar la funcionalidad al principio del proceso.
Recopilación de comentarios: Facilita la obtención de la retroalimentación del usuario y el mercado antes de cometer recursos sustanciales para la producción en masa.
Evaluación de producción: Habilita una evaluación de los procesos de fabricación, materiales, y consideraciones de costos involucradas en la producción en masa.
Prototipos de innovación de expedición, reduce la incertidumbre, y a menudo resulta invaluable para garantizar el éxito del producto.
Opciones de fabricación de prototipos rápidos
Varios métodos se han vuelto frecuentes debido a su velocidad, exactitud, e idoneidad para diversas necesidades de proyectos. Los tres métodos prominentes de prototipos rápidos incluyen mecanizado CNC, 3impresión D, y fundición al vacío.
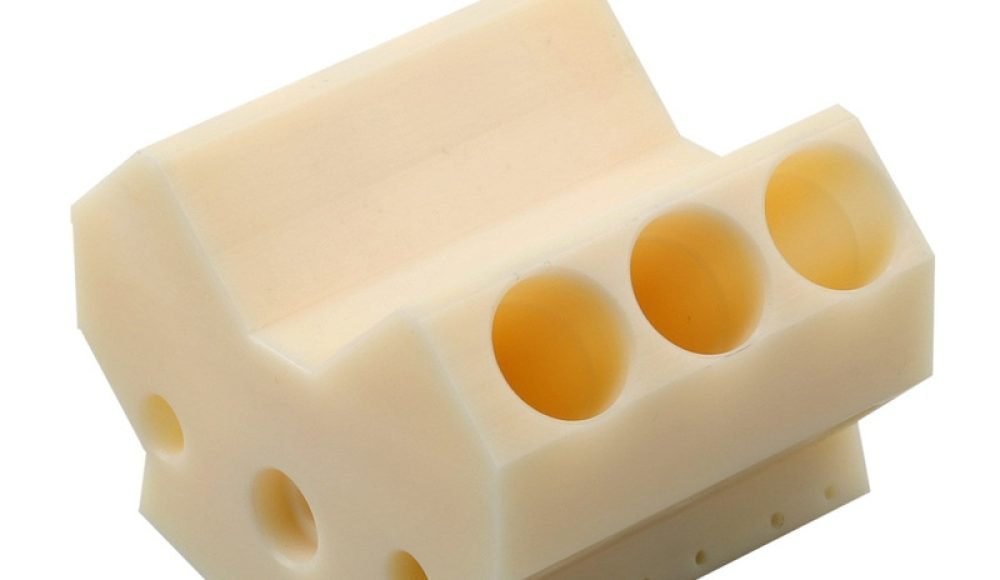
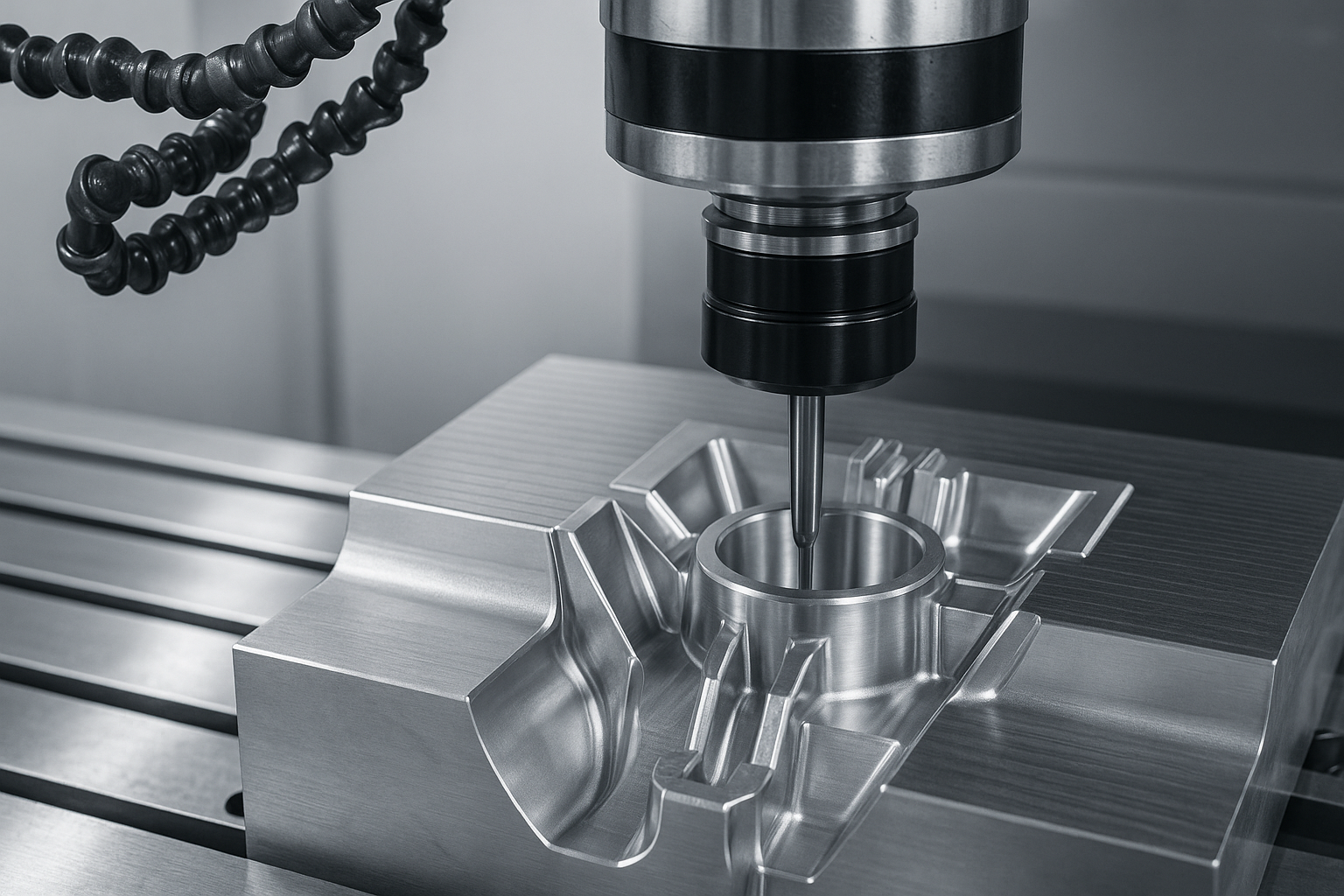
Mecanizado CNC
CNC (Control numérico de computadora) El mecanizado implica el uso de máquinas de corte y conformación controladas por computadora para tallar prototipos de bloques sólidos de material, típicamente metal o plástico.
Ventajas del mecanizado CNC:
Precisión y precisión excepcionales: Capaz de cumplir con tolerancias extremadamente ajustadas, haciéndolo ideal para diseños altamente detallados y exigentes.
Manejo de geometría compleja: El equipo CNC puede crear con precisión formas y características intrincadas que el mecanizado manual no puede.
Durabilidad y versatilidad del material: Los prototipos CNC son robustos y se parecen mucho a los productos finales en términos de resistencia y propiedades del material.
Excelente acabado superficial: Capaz de proporcionar acabados de alta calidad que requieren un postprocesamiento mínimo.
Aplicaciones típicas de prototipos CNC:
Componentes mecánicos
Piezas aeroespaciales y automotrices
Modelos de ingeniería complejos
Durable, Prototipos funcionales adecuados para pruebas rigurosas
3Impresión D
3impresión D, También conocido como fabricación aditiva, crea prototipos capa por capa utilizando un diseño asistido por computadora (CANALLA) archivos. Este método ha visto un rápido avance debido a su asequibilidad y velocidad.
Ventajas de la impresión 3D:
Velocidad y eficiencia: Tiempos de respuesta de producción rápida, Permitir procesos de diseño iterativos en un corto plazo de tiempo.
Rentabilidad: Relativamente económico, especialmente cuando se usa materiales plásticos estándar.
Alta precisión: Permite geometrías complejas y estructuras internas intrincadas difíciles de lograr mediante métodos de fabricación tradicionales.
Limitaciones de la impresión 3D:
Resistencia del material: Generalmente menor durabilidad en comparación con los prototipos mecanizados por CNC.
Acabado de la superficie: Generalmente requiere un postprocesamiento adicional para mejorar la suavidad de la superficie.
Aplicaciones típicas de impresión 3D:
Modelos conceptuales y diseños de etapas tempranas
Prostes Médicos y modelos dentales
Modelos arquitectónicos
Componentes funcionales de bajo estrés
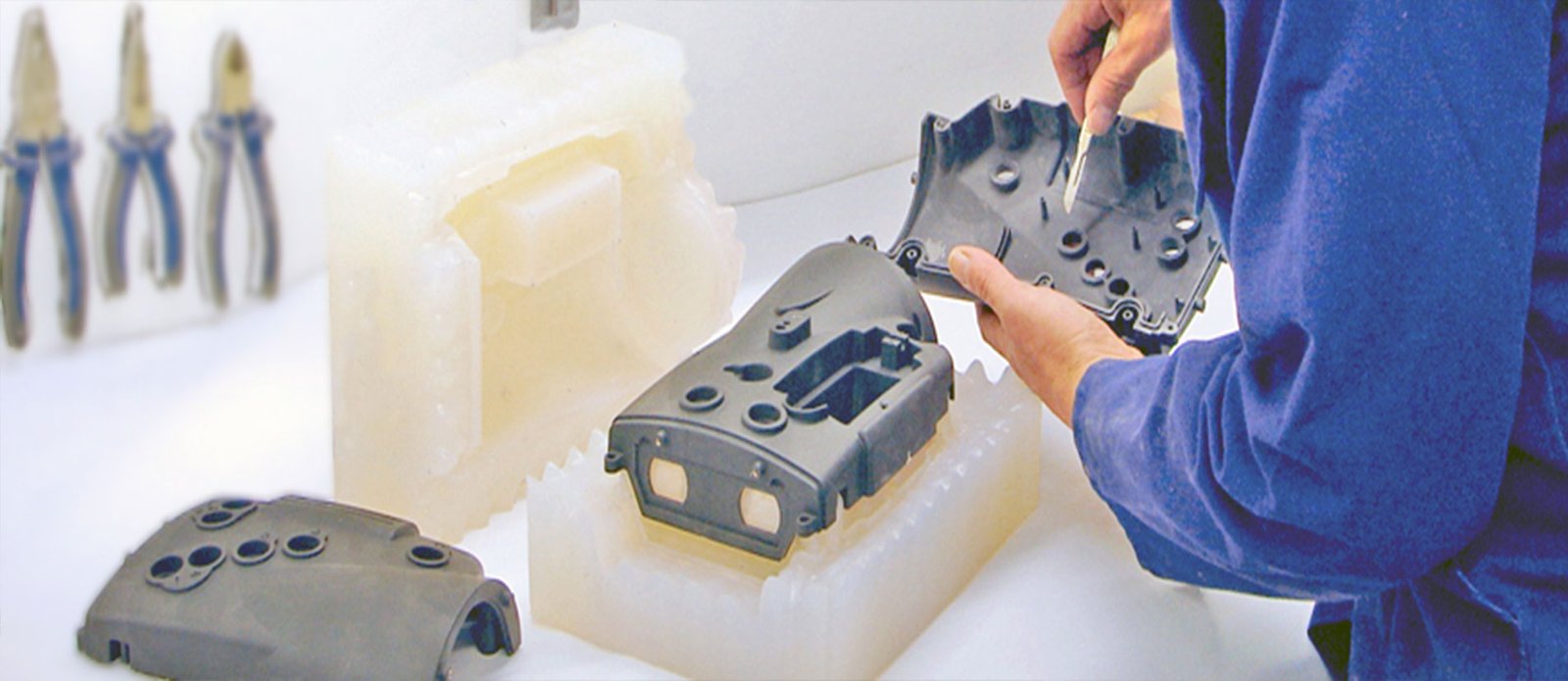
Colocación de aspiradoras
Colocación de aspiradoras, También conocido como fundición de uretano, implica crear un molde de silicona a partir de un patrón original (a menudo creado a través de mecanizado CNC o impresión 3D). La resina líquida o el metal se verta en el molde dentro de una cámara de vacío para eliminar las burbujas de aire, resultando en preciso, Castings sin defectos.
Ventajas de la fundición al vacío:
Precisión y detalle: Moldes replicar detalles de prototipos originales, Garantizar la alta fidelidad.
Versatilidad de materiales: Capaz de producir prototipos en varios materiales plásticos y elastoméricos que se parecen estrechamente a los materiales de producción finales.
Adecuado para carreras cortas: Ideal para lotes pequeños o carreras de producción limitadas debido a la reutilización de moho.
Limitaciones de la fundición al vacío:
Consideraciones de costos: Más caro por pieza en comparación con la impresión 3D, particularmente para pequeñas cantidades, Debido a la intensidad del material y al trabajo.
Vida limitada de moho: Los moldes de silicona generalmente se degradan después de un cierto número de moldes, limitando su reutilización.
Aplicaciones típicas de fundición al vacío:
Runs de lotes pequeños de preproducción
Modelos visuales de alta calidad
Prototipos de pruebas funcionales
Componentes que necesitan una estrecha semejanza con los productos finales
Elegir la técnica de creación de prototipos correcta
Seleccionar la técnica óptima de prototipos depende de varios factores como:
Objetivo prototipo: ¿Es principalmente funcional?, visual, o ambos?
Requisitos de materiales: Propiedades específicas del material (p.ej., fortaleza, flexibilidad, resistencia química).
Restricciones presupuestarias: Equilibrar la rentabilidad contra las necesidades de creación de prototipos.
Limitaciones de tiempo: Qué tan rápido se requiere el prototipo.
Necesidades de durabilidad: Si el prototipo se someterá a pruebas extensas o será puramente demostrativo.
Aprovechar la experiencia profesional asegura que estos factores sean evaluados con precisión. Los especialistas en prototipos experimentados pueden recomendar el mejor proceso basado en sus necesidades de diseño específicas, Línea de tiempo del proyecto, presupuesto, y consideraciones de producción.
Conclusión y llamado a la acción
La prototipos rápidos es una fase crítica del desarrollo de productos, Mejorar significativamente la viabilidad del producto y reducir los riesgos de producción potenciales. Mecanizado CNC, 3impresión D, y el lanzamiento de vacío cada una ofrece ventajas únicas adaptadas a diferentes escenarios de prototipos.
Al asociarse con un proveedor de prototipos confiable con una amplia experiencia en la industria, como la nuestra, con 15 Años de experiencia especializada: puede garantizar los resultados de la más alta calidad. Nuestro conocimiento integral, equipo avanzado, y diversas capacidades materiales nos colocan de manera única para recomendar y ejecutar el mejor enfoque de prototipos para sus requisitos específicos.
Cuando estás listo para avanzar, Lo invitamos a consultar a nuestros expertos para obtener orientación personalizada y una estimación precisa.. Permítanos ayudarle a hacer realidad sus ideas rápidamente, precisamente, y rentable.
Aquí hay cinco secciones de preguntas frecuentes que puede agregar al artículo para mejorar el SEO y abordar las consultas comunes de los lectores.:
Preguntas frecuentes
1. ¿Cuánto tiempo lleva la prototipos rápidos??
Los plazos de creación rápida de prototipos dependen de la técnica elegida y de la complejidad del diseño.. El mecanizado CNC y la impresión 3D pueden entregar prototipos en cuestión de días, mientras que la fundición al vacío suele tardar un poco más debido a la preparación del molde, generalmente entre una y dos semanas.
2. ¿Qué técnica rápida de prototipos es la más rentable??
Para prototipos iniciales, especialmente aquellos que requieren iteraciones frecuentes, 3impresión D A menudo proporciona la solución más rentable debido a su menor coste de instalación.. Mecanizado CNC y colocación de aspiradoras Son económicos para prototipos más robustos o cuando la durabilidad y la precisión justifican inversiones iniciales ligeramente mayores..
3. ¿Se pueden usar prototipos para pruebas funcionales??
Sí, Los prototipos realizados a través del mecanizado CNC y la fundición al vacío son particularmente adecuados para pruebas funcionales rigurosas debido a su resistencia y precisión del material. 3D Los prototipos impresos son adecuados para el encendedor, Escenarios de prueba menos rigurosos.
4. ¿Hay limitaciones en los materiales prototipo??
La elección del material varía con el método de prototipos. CNC Machining ofrece la variedad más amplia, incluyendo metales e ingeniería de plásticos. 3D La impresión generalmente utiliza plásticos y resinas específicos, Mientras que los materiales de fundición al vacío imitan de cerca a plásticos y elastómeros de grado de producción, ofreciendo una buena flexibilidad de material.
5. ¿Qué tan precisos son prototipos rápidos en comparación con el producto final??
Todos los métodos de prototipos rápidos discutidos: mecanizado de CNC, 3impresión D, y fundición al vacío: producir prototipos altamente precisos. El mecanizado CNC generalmente ofrece la más alta precisión, seguido de cerca por la fundición al vacío y la impresión 3D. La elección depende de los requisitos de precisión de su proyecto y la aplicación prevista.
Meta título: Técnicas de fabricación de prototipos rápidos: CNC, 3Impresión D & Colocación de aspiradoras
Meta descripción: Aprenda sobre técnicas rápidas de prototipos como el mecanizado CNC, 3impresión D, y fundición al vacío. Descubre sus ventajas, limitaciones, aplicaciones, y cómo elegir el mejor método para el diseño de su producto.
Leer más:






1 pensamiento en “Técnicas de fabricación de prototipos rápidos: Mecanizado CNC, 3Impresión D, y fundición al vacío”