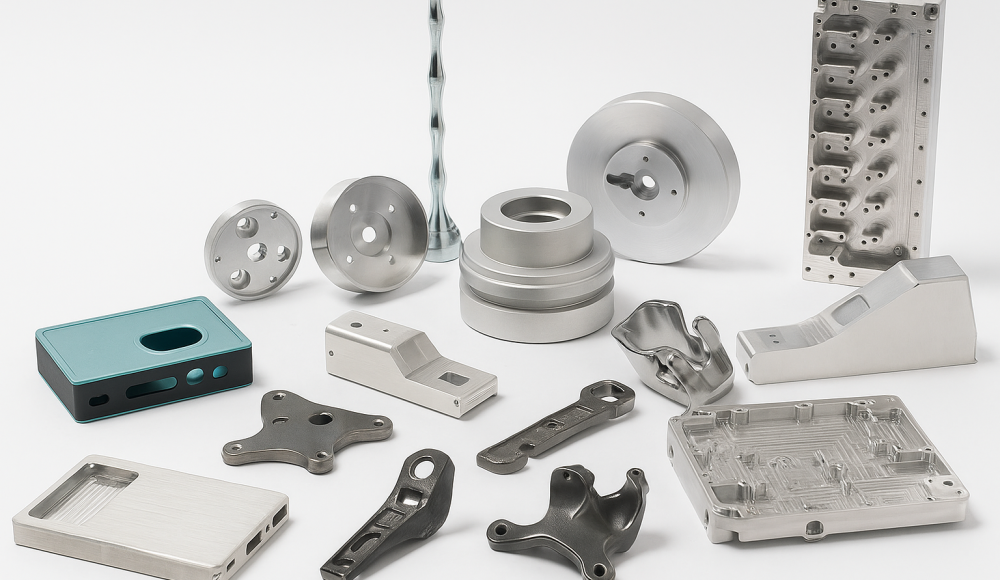
Moulage est un processus de fabrication métallique très efficace utilisé pour produire des pièces métalliques précises avec des géométries complexes. Cependant, Le processus de casting de dépérisation seul ne garantit pas toujours les pièces avec l'apparence ou les propriétés de surface souhaitée. Donc, L'application de la bonne finition de surface est essentielle pour atteindre, esthétique, et pièces fabriquées durables.
Dans cet article, Nous explorerons profondément 13 Types de finitions de surface couramment utilisé dans le moulage, mettre en évidence leurs définitions, avantages, Applications appropriées, et des considérations.
Importance de choisir la bonne finition de surface
Sélection de l'emploi approprié état de surface a un impact sur les propriétés critiques suivantes:
Durabilité: Améliore la résistance à la corrosion et prolonge la durée de vie des parties.
Apparence: Améliore l'attrait visuel et la valeur marchande des composants.
Fonctionnalité: Assure l'aptitude à des applications et conditions spécifiques.
Le choix d'une finition de surface incorrecte peut entraîner des défaillances de partie prématurées, Pauvre esthétique, entretien accru, et les coûts inutiles.
13 Types de finitions de surface de coulée de matrice
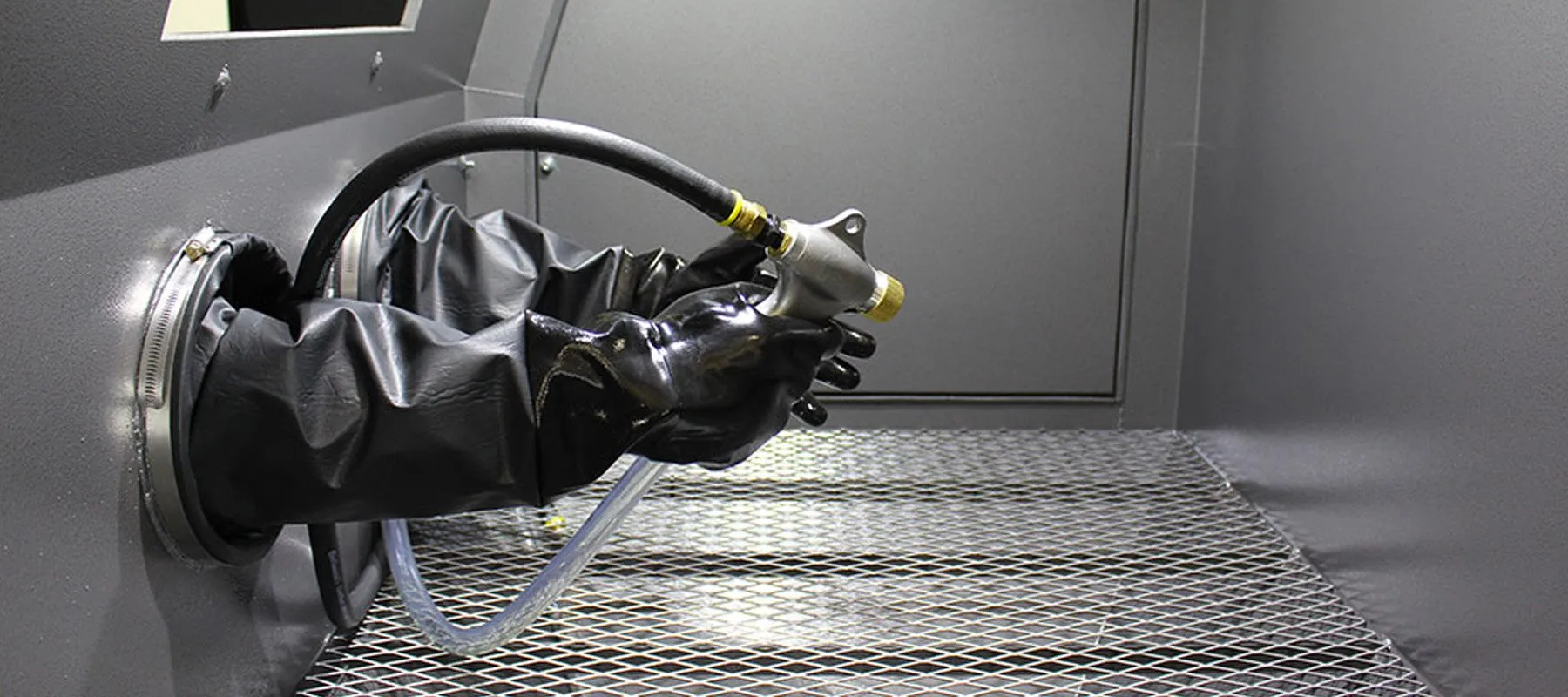
1. Sablage (Dynamitage abrasif)
Le sablage implique la propulsion de particules abrasives fines (par exemple., sable, perles de verre) sur la surface de la partie sous haute pression.
Avantages:
Finition mate uniforme
Adhésion améliorée pour les revêtements
Élimination efficace des impuretés et des contaminants
Applications:
Composants automobiles et industriels
Parties nécessitant une adhésion élevée pour la peinture ou le revêtement
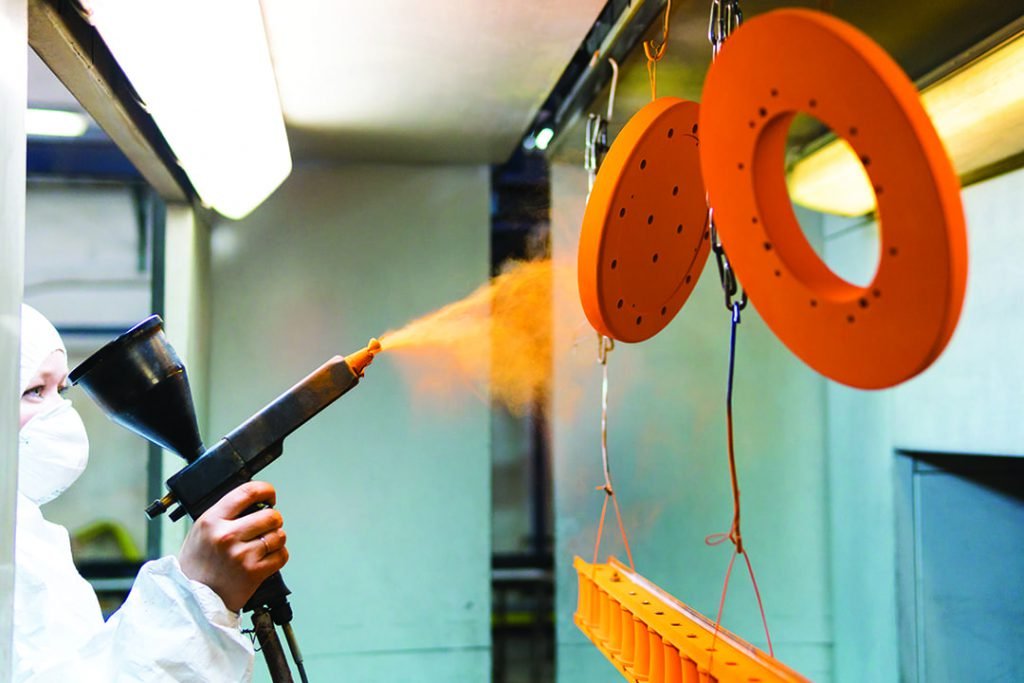
2. Revêtement en poudre
Le revêtement en poudre est un processus de finition sec impliquant l'application de pigments en poudre chargés électrostatiquement, suivi d'un durcissement thermique.
Avantages:
Excellente corrosion et résistance chimique
Surface durable et résistante à l'impact
Disponible en de nombreuses couleurs et finitions
Applications:
Roues et composants automobiles
Appareils de ménage, Enveloppes électroniques, produits extérieurs
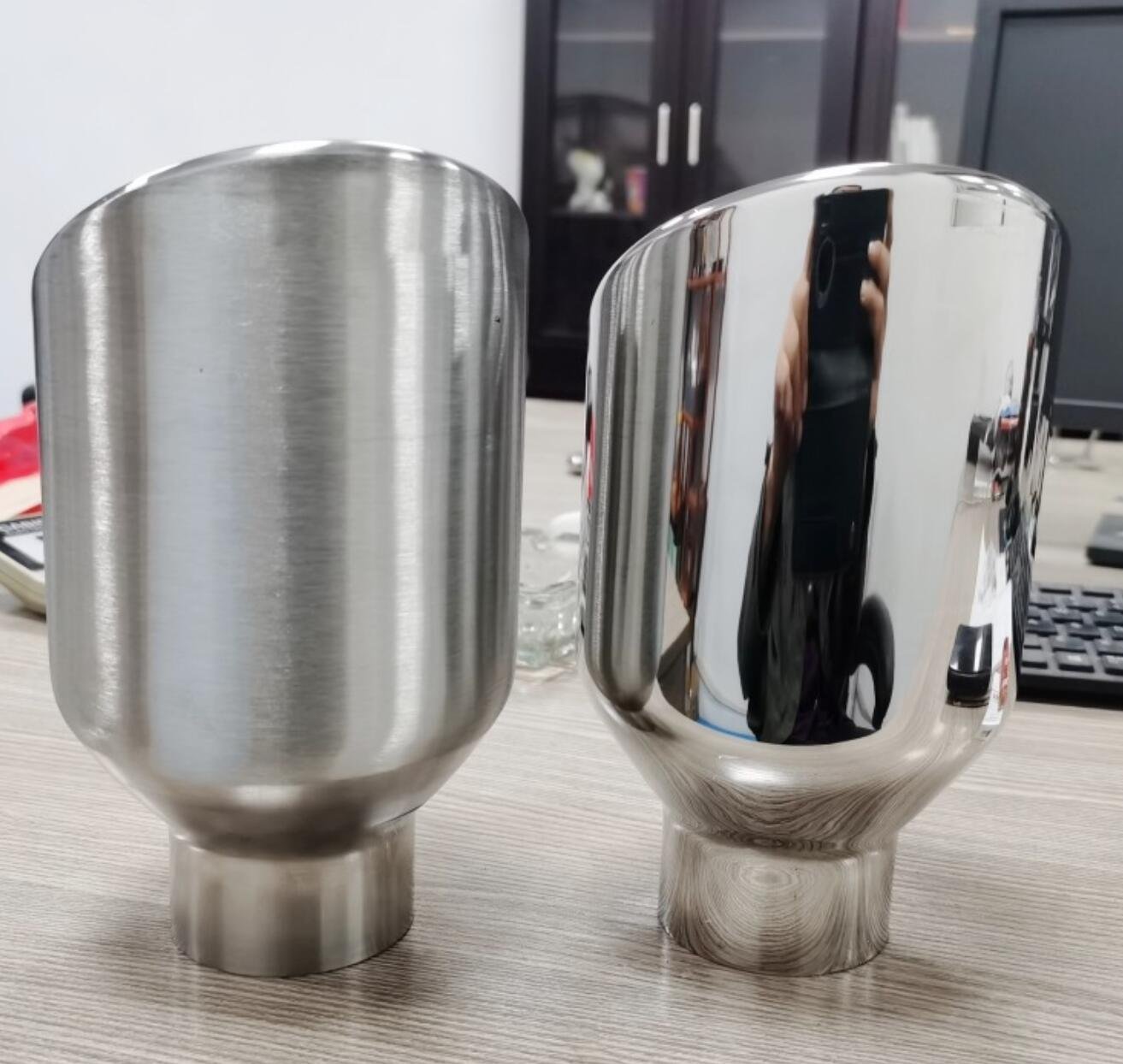
3. Polissage
Le polissage supprime les imperfections microscopiques par le polissage abrasif, produisant un lisse, surface réfléchissante.
Avantages:
Miroir, finition esthétique de haute qualité
Amélioration de la nettoyabilité et des frottements réduits
Applications:
Garniture automobile, bijoux, matériel décoratif, équipement médical
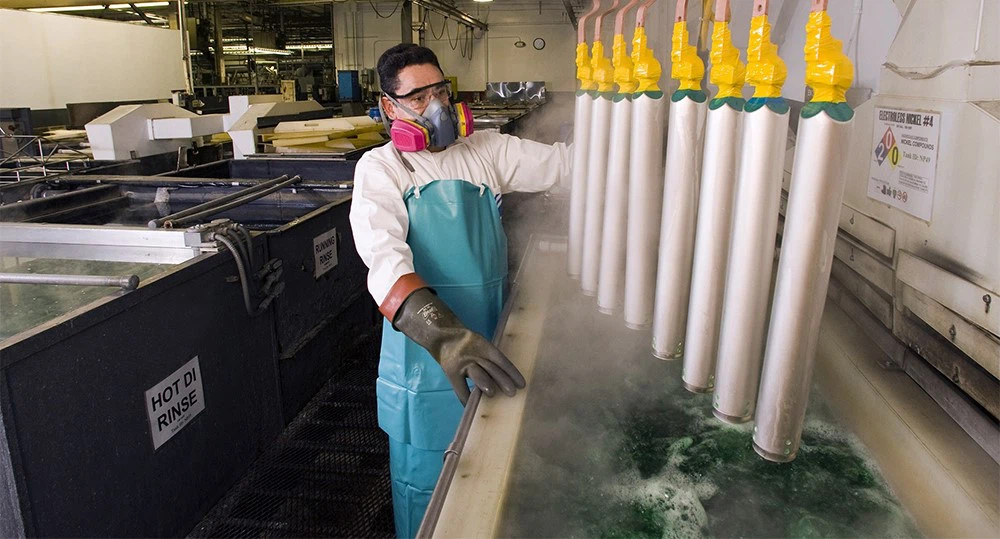
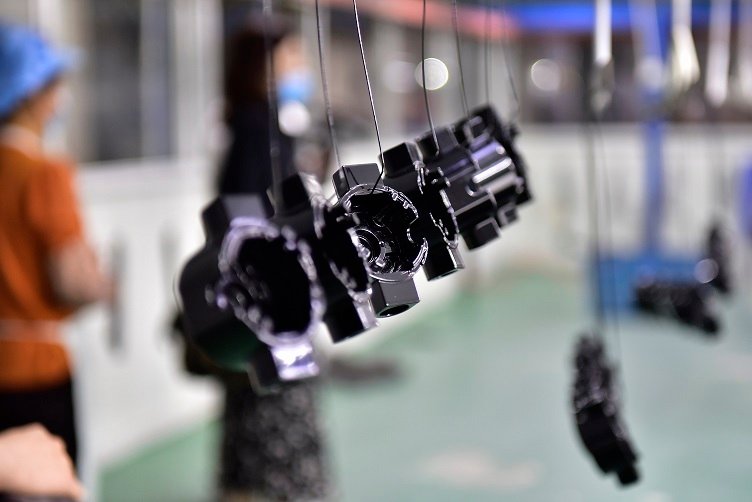
4. Placage (Galvanoplastie & Placage électrolytique)
Le placage implique le dépôt d'une fine couche de métal (nickel, chrome, or, etc.) sur des pièces moulées par des moyens chimiques ou électrolytiques.
Avantages:
Amélioration de la protection de la corrosion et de la résistance à l'usure
Amélioration de la conductivité électrique
Décoratif, apparence brillante
Applications:
Composants électroniques, pièces automobiles, accessoires décoratifs
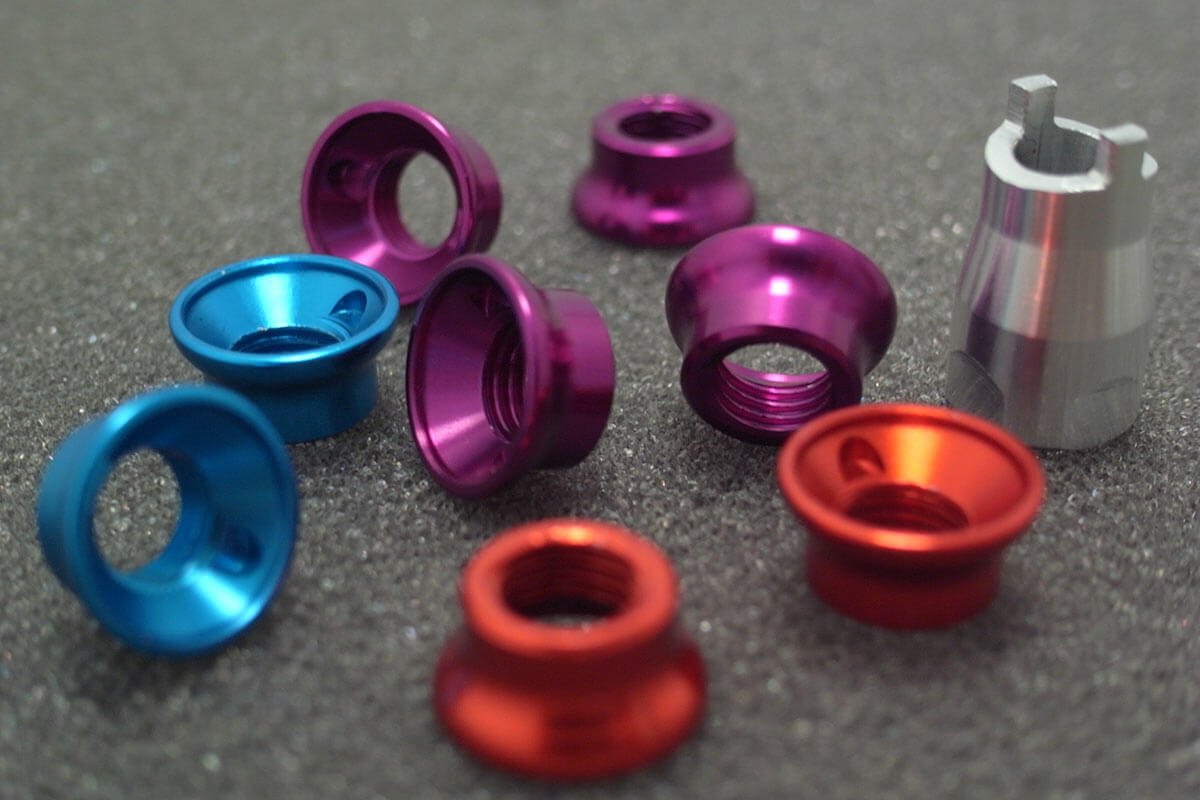
5. Anodisation
L'anodisation crée une couche d'oxyde contrôlée sur les surfaces en alliage en aluminium par traitement électrolytique.
Avantages:
Corrosion supérieure et résistance à l'usure
Apparence esthétique avec différentes options de couleurs
Augmentation de la dureté de surface
Applications:
Accessoires architecturaux, enclos électronique, produits de consommation
6. Revêtement électrophorétique (E-revêtement)
Le revêtement électronique utilise des courants électriques pour déposer uniformément de la peinture ou de la résine sur des surfaces conductrices.
Avantages:
Excellente protection contre la corrosion
Épaisseur de revêtement uniforme et cohérente
Bonne résistance chimique et durabilité
Applications:
Composants du châssis automobile, équipement industriel, machinerie lourde
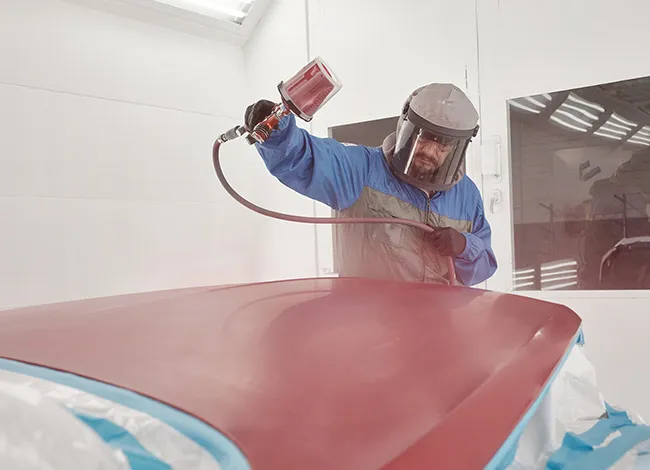
7. Peinture
La peinture implique l'application de revêtements liquides via le spray, brosse, ou des techniques de trempage pour améliorer l'esthétique et les propriétés de protection.
Avantages:
Corparement avec des options de couleurs étendues
Finies faciles à réparer ou à mettre à jour
Applications:
Produits de consommation, parties du corps automobile, appareils électroménagers, meubles
8. Vibratoire
Ce processus supprime les bavures et les bords tranchants en utilisant un équipement vibrant avec des supports abrasifs.
Avantages:
Unburring efficace sans travail manuel
Finition de surface cohérente et uniforme
Amélioration de la sécurité et de la manipulation
Applications:
Parties automobiles coulées petites à moyennes, engrenages, attaches, connecteurs
9. Parkérisant (Phosphation)
La parkéririsation implique des pièces en acier chimiquement enrobage avec des solutions de phosphate pour créer une couche robuste résistante à la corrosion.
Avantages:
Protection de corrosion rentable
Adhésion améliorée pour les revêtements ou peintures ultérieures
Finition mate-noir durable
Applications:
Armes à feu, composants de suspension automobile, équipement industriel en service lourd
10. Placage autocatalytique au nickel
Dépôts de nickel électrolyl, sans électricité externe.
Avantages:
Distribution d'épaisseur uniforme, Même sur des formes complexes
Excellente résistance à l'usure et à la corrosion
Augmentation de la dureté et de la lubricité
Applications:
Composants aérospatiaux, vannes industrielles, Pièces automobiles de précision
11. Imprégnation
L'imprégnation consiste à sceller les porosités microscopiques dans des pièces moulées à l'aide de scellants en polymère assisté sous vide.
Avantages:
Propriétés améliorées à l'épreuve des fuites pour les composants à haute pression
Amélioration de l'intégrité structurelle et de la longévité
Réduction des défauts liés à la porosité
Applications:
Pompes hydrauliques, blocs moteurs automobiles, composants de confinement fluide
12. Dépôt de vapeur physique (PVD)
Le PVD est une méthode de revêtement avancée basée sur le vide vaporisant les métaux ou la céramique sur des substrats, formant des revêtements ultra-minces et très durables.
Avantages:
Usure supérieure et résistance aux rayures
Excellente finition esthétique avec différentes couleurs
Haute dureté et résistance chimique
Applications:
Pièces automobiles de luxe, outils de coupe, accessoires décoratifs, instruments médicaux
13. Passivation
La passivation améliore chimiquement la résistance à la corrosion inhérente de l'acier inoxydable en éliminant les contaminants du fer de surface.
Avantages:
Amélioration de la résistance à la corrosion naturelle
Surface en acier inoxydable plus propre et plus lisse
Plus sûr pour les applications dans des environnements hygiéniques
Applications:
Équipement de transformation des aliments, Équipement médical, machines pharmaceutiques
Facteurs influençant la finition de la coulée de la matrice
Plusieurs facteurs clés influencent le résultat des finitions de surface de moulage de la matrice:
type de materiau: Les finitions spécifiques sont les mieux adaptées à des alliages ou des métaux particuliers.
Die et qualité de moisissure: Les moules de haute qualité garantissent des surfaces cohérentes et lisses.
Paramètres de coulée: Contrôle de la température, pression d'injection, et les taux de refroidissement affectent directement la qualité de la surface.
Méthodes de post-traitement: Une sélection et une exécution appropriées déterminent les caractéristiques de surface finales.
Comment améliorer la finition de surface de la moule Die
L'amélioration des finitions de surface implique:
Entretien de moisissure: Nettoyez régulièrement et maintenez les moules pour éviter les imperfections.
Conditions de coulée contrôlées: Optimiser les paramètres de température et d'injection.
Utilisez des techniques de post-traitement appropriées: Sablage, polissage, anodisation, et d'autres au besoin.
Optimisation de conception: Concevoir des pièces pour réduire la complexité et minimiser les imperfections de surface.
Conclusion
Comprendre clairement la variété des méthodes de finition de surface disponibles est crucial pour réaliser des pièces moulées avec une esthétique optimale, durabilité, et performances fonctionnelles. La sélection de la finition appropriée en fonction des exigences de l'application améliorera considérablement la qualité des produits et la satisfaction du client.
La consultation avec des spécialistes professionnels de la mise en poupe de la détérioration vous garantit en outre les processus de finition idéaux adaptés à vos besoins de fabrication spécifiques.
FAQ
T1: Qu'est-ce qu'un graphique de finition de surface de moulage de moulage?
Un outil de référence montrant différentes finitions, leurs caractéristiques, matériaux adaptés, et applications, Aider les fabricants dans la sélection.
T2: Qu'est-ce que la rugosité de surface typique dans la coulée de la matrice?
La rugosité varie généralement de 1 à 5 µm selon l'alliage, méthodes de coulée, et finitions choisies.
T3: Die la coulée produit naturellement de bonnes finitions de surface?
Le moulage de matrice seul offre une qualité de surface décente, Mais les finitions de post-traitement sont généralement nécessaires pour obtenir une esthétique et des propriétés fonctionnelles améliorées.
T4: Comment s'améliorer la finition de surface dans le moulage de la matrice?
En optimisant les conceptions de moisissures, Contrôle des processus de coulée, et utiliser des méthodes de post-traitement comme le polissage, placage, ou revêtement.
Q5: Quels facteurs affectent la qualité de finition de surface moulée?
Type de matériau, température de moisissure, design, Contrôles de processus de coulée, et traitements de surface choisis.