Dans l’environnement manufacturier mondial d’aujourd’hui, La qualité et la précision des dimensions critiques du produit et de ses éléments sont d'une importance cruciale. Dans des domaines comme l'automobile, aérospatial, électronique, et ainsi de suite où une mesure stricte est requise dans les composants ou les structures que les appareils de mesure jouent un rôle essentiel. Cet appareil assure aux fabricants qu'aucun de leurs produits ne sort de la ligne de production sans répondre à certaines normes. Néanmoins, D'autres questions importantes doivent être répondues: À quoi se réfère l'abréviation à l'abréviation et quel type de machine est une machine CMM? Comment cela fonctionne-t-il et pourquoi il est devenu un facteur important dans la fabrication contemporaine? Cet article vous aidera à comprendre tous ces concepts.
Qu'est-ce qu'un Machine CMM?
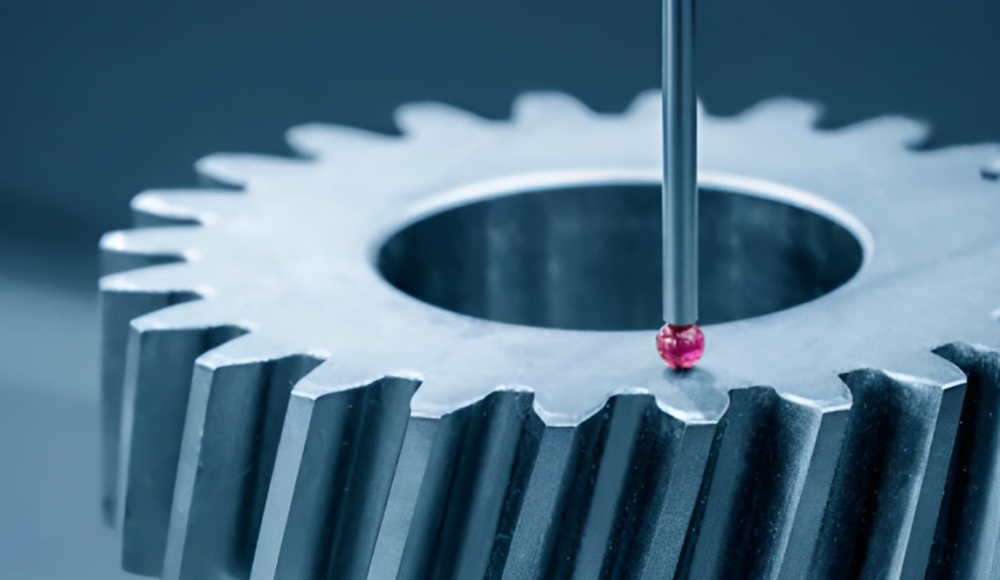
Une machine CMM communément appelée machine à mesure de coordonnées est un instrument utilisé pour mesurer les attributs géométriques physiques d'un objet. Il utilise une sonde pour quantifier avec précision les coordonnées se trouvant à un point à la surface d'un objet. Cela aide les fabricants à vérifier si les dimensions d'une pièce sont correctes sur la conception. Le CMMS est utilisé dans les industries où la précision dimensionnelle et les limites de tolérance sont importantes.
HOW fait que la machine CMM fonctionne?
Une machine CMM fonctionne par contact ou sans contact, la méthode de contact utilise une sonde tactile et l'autre utilise un laser ou un système optique. La sonde acquiert des mesures détaillées pour trouver X, Oui, et les coordonnées Z qui décrivent des points particuliers dans la peau de l'objet. Ces mesures sont ensuite comparées à la mesure spécifiée pour savoir si l'objet testé fonctionne ou non selon les tolérances requises.. La machine fonctionne selon les étapes suivantes:
1. Initialisation
D'abord, CMM est calibré pour référencer des objets afin de garantir l'exactitude des mesures. La température et les vibrations qui agissent sur la structure sont contrôlées pour garantir que les normes de mesure souhaitées sont atteintes.
2. Sondage
La sonde en copie carbone est constituée de touches tactiles, laser, ou optique qui touche la surface de l'objet et acquiert le X, Oui, et coordonnées Z de certains points. Il peut être commandé numériquement par ordinateur (CNC) ou guidé manuellement.
3. Analyse des données
Les données obtenues sont comparées aux spécifications de conception qui ont été définies. Le logiciel montre les écarts par rapport à une certaine tolérance permettant ainsi aux ingénieurs d'identifier les erreurs.
4. Génération de rapports
Les impressions supplémentaires incluent des rapports détaillés pour indiquer si la pièce répond aux spécifications et si elle doit être modifiée d'une certaine manière.
Types de machines de mesure des coordonnées (MMT)
Le tableau suivant nous donne des informations sur les différents types de machines CMM disponibles sur le marché:
| Type de cmm | Description | Précision | Plage de taille | Meilleures applications |
| Pont cmm | Cadre fixe, le type le plus courant | Haut (±0,001 mm) | Petites à moyens parties (jusqu'à 2 m) | Ingénierie de précision, automobile |
| Cantilever cmm | Ouvert d'un côté, permet l'accès depuis trois côtés | Haut (± 0,002 mm) | Petites pièces (jusqu'à 1 m) | Électronique, petites pièces de précision |
| Portique cmm | À grande échelle, fixé, et très stable | Très élevé (±0,001 mm) | Grosses pièces (jusqu'à 10 m) | Aérospatial, grands composants automobiles |
| Bras horizontal cmm | Structure ouverte, bon pour les pièces plus grandes ou flexibles | Modéré (±0,01 mm) | Grosses pièces (jusqu'à 5 m) | Tôle, cadres automobiles |
| Cmm portable | Poids léger, mobile, utilise le laser ou les sondes | Modéré (± 0,02 mm) | Petites à très grandes pièces (jusqu'à 10 m) | Mesures sur le terrain, construction, matériel lourd |
Pourquoi ai-je besoin d'une machine CMM?
Les fabricants ont besoin de machines CMM pour plusieurs raisons:
- Précision améliorée: Le CMMS fournit des mesures avec une précision significative pour mesurer une faible variabilité des dimensions. Ceux-ci peuvent faire une différence dans la fabrication de produits durables pour les applications, c'est à dire. Fabrication de l'équipement aérospatial ou médical.
- Contrôle de qualité: Voici les avantages d'une gestion de documents efficace. Ils aident à maintenir la qualité des produits car toute erreur est repérée à temps.
- Automatisation: Les machines CMM sont généralement utiles car elles contribueront à l'automatisation de certaines mesures qui sont sujettes à de nombreuses erreurs.
- Efficacité: Des degrés élevés d'automatisation du travail ont rendu le nombre d'inspections considérablement inférieures. Ainsi, Les machines CMM économisent du temps et de l'argent pendant les processus de fabrication.
- Polyvalence: Il sera également vu à partir de diverses fonctionnalités comment ces machines de mesure très flexibles peuvent être utilisées dans la fabrication. Donc, il peut tout mesurer, des composants aux grands assemblages.
Avantages des machines CMM
Les machines CMM offrent les avantages suivants:
- Haute précision: Haute précision avec peu de fluctuation entre l'idéal et le réel.
- Polyvalence: Il peut mesurer tous les objets de taille et de forme variées.
- Gâchis de temps: Cela contraste fortement avec les méthodes d'inspection conventionnelles qui prendront beaucoup de temps lorsqu'elles seront effectuées manuellement.
- Capacité d'automatisation: Élimine le besoin des grands rôles des personnes. Donc, cela entraînera une augmentation de la précision.
- Analyse des données: Permet la collecte d'informations factuelles et de données de recherche pour améliorer les décisions vers la résolution de problèmes.
Limites des machines CMM
Voici quelques limites des machines CMM:
- Coût: Leurs coûts initiaux sont élevés en fonction du type de modèle, Type d'usinage CNC
- Exigences de formation: Les opérateurs de la machine doivent être professionnels et bien informés dans la bonne manipulation de la machine.
- Sensibilité environnementale: Vibrations, changements de température, et l'humidité peut influencer les opérations de CMMS.
- Limitations de taille: Certains CMM ne peuvent pas s'adapter à d'énormes mesures d'objets pendant le processus de mesure.
- Besoins de maintenance: Certaines de ces complications nécessitent un entretien et un étalonnage constants pour fonctionner comme requis à l'avenir.
Applications des machines CMM
Voici quelques-unes des applications courantes des machines CMM:
- Industrie automobile: Pour mesurer les parties généralement complexes d'un moteur, Gears à utiliser, et parties de carrosserie.
- Industrie aérospaciale: La bavure élimine les inexactitudes dans les morceaux plus fins tels que les lames d'une turbine ou des parties d'un avion.
- Équipement médical: Indispensable pour la fabrication de matériel médical et d'instruments chirurgicaux.
- Fabrication d'électronique: Utilisé dans la mesure des circuits imprimés et/ou des boîtiers électroniques.
- Machinerie lourde: Ils étaient utilisés pour vérifier les dimensions d'énormes pièces mécaniques dont les mesures ne pouvaient pas être facilement prises avec un micromètre traditionnel..
Différence entre CMMS portable vs outils de mesure traditionnels
Voici un tableau comparatif des machines MMT portables par rapport aux outils de mesure traditionnels:
| Fonctionnalité | MMT portables | Outils de mesure traditionnels |
| Portabilité | Très portable, pèse ~5-10 kg | Non portable, appareils fixes (20-50 kilos) |
| Vitesse | Mesures en quelques minutes | Prend jusqu'à 2-5 fois plus longtemps |
| Plage de mesure | Peut mesurer des objets jusqu'à 10 mètres | Limité aux petits objets (jusqu'à 1 mètre) |
| Précision | ±0,01 mm | ±0,05mm |
| La flexibilité | Peut mesurer des complexes, grand, et petites pièces | Limité aux plus petits, objets simples |
| Facilité d'utilisation | Facile à utiliser, formation minimale requise | Nécessite une expertise et une opération manuelle |
| Analyse des données | Automatisé, traitement des données en temps réel | Nécessite des calculs manuels |
Pourquoi parlons-nous de la vitesse CMM tout le temps?
La vitesse de mesure CMM joue un facteur important dans les machines CMM. C'est le temps plus court pour la production de régénération de mesure. Évidemment, dans la fabrication à volume élevé, Le temps pris pour inspecter chaque partie doit être minimisé pour réaliser de grosses économies. Les fabricants essaient d'atteindre des objectifs clairement définis pour la minimisation du temps. mis-à-part, Il aide à augmenter l'efficacité et l'efficacité de la machine lorsqu'il entreprend son travail d'inspection. Les principaux domaines de développement de la technologie CMM sont centrés sur les améliorations de la vitesse réalisées grâce à des stratégies de sondage améliorées, logiciel, et l'équipement.
Conclusion
En conclusion, Une machine CMM est un équipement important dans les processus de production actuels car il améliore la précision et la vitesse des contrôles de qualité. Si vous êtes de l'automobile, aérospatial, ou industrie de la fabrication d'électronique, Un CMM garantit que les produits de l'entreprise servent à fixer des exigences de conception. Tout en possédant des coûts d'acquisition élevés, Les avantages dérivés de la technologie d'automatisation pour la précision, Exigence de temps d'efficacité, et l'analyse des données dépassent les coûts pour les entreprises manufacturières. Donc, Ils peuvent améliorer la qualité et réduire les coûts grâce à l'utilisation d'outils d'amélioration de la qualité efficaces.
Questions fréquemment posées:
1. Que représente CMM?
CMM est un acronyme de la machine à mesure des coordonnées, qui est un appareil utilisé pour mesurer différentes dimensions d'un objet.
2. Quel est le rôle majeur d'un cmm?
Un CMM est utilisé pour déterminer les paramètres géométriques d'un objet pour vérifier sa conformité à la taille requise.
3. Comment la précision de CMM est-elle contrôlée?
Le CMM est précis et précis et est rendu possible grâce à l'étalonnage de maintenance et de conditions environnementales appropriées telles que la température et l'humidité.
4. Un cmm peut-il quantifier les matériaux doux?
Oui, Toutes sortes de CMM peuvent mesurer des matériaux plus doux sans endommager le matériau dans le processus.
5. Où est l'application des machines CMM très utilisées?
Les machines CMM sont utilisées dans l'automobile, aérospatial, électronique, et industries médicales.
6. Quelle est la différence entre CNC CMM et manuel CMM?
CNC CMMS sont des machines par ordinateur. Ils sont automatisés, alors que, Les CMM manuels sont exploités par l'homme.





4 réflexions sur "Qu'est-ce qu'une machine MMT? Son processus de travail, Les types, et applications”