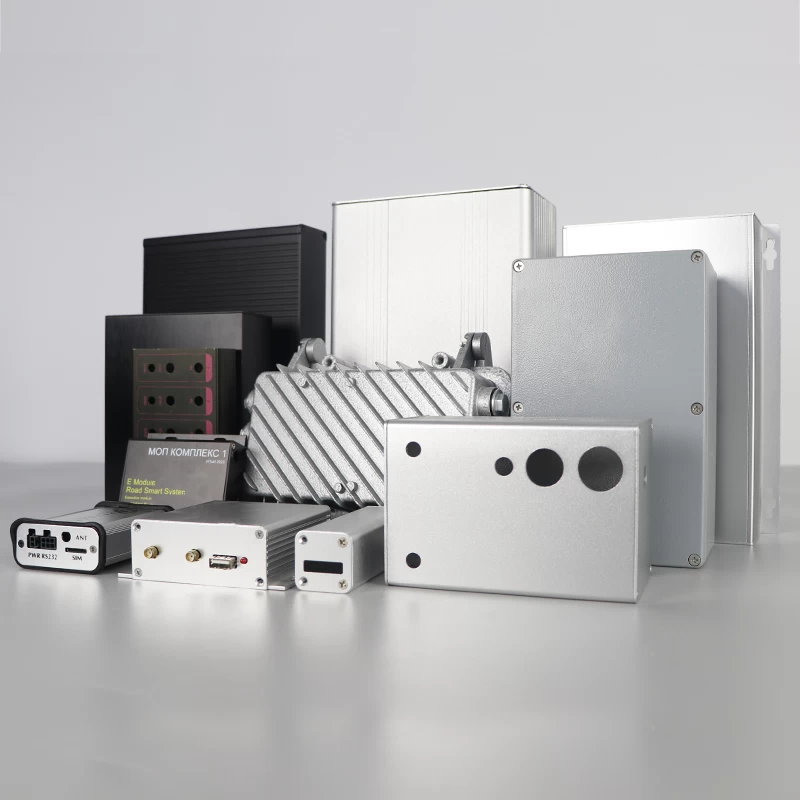
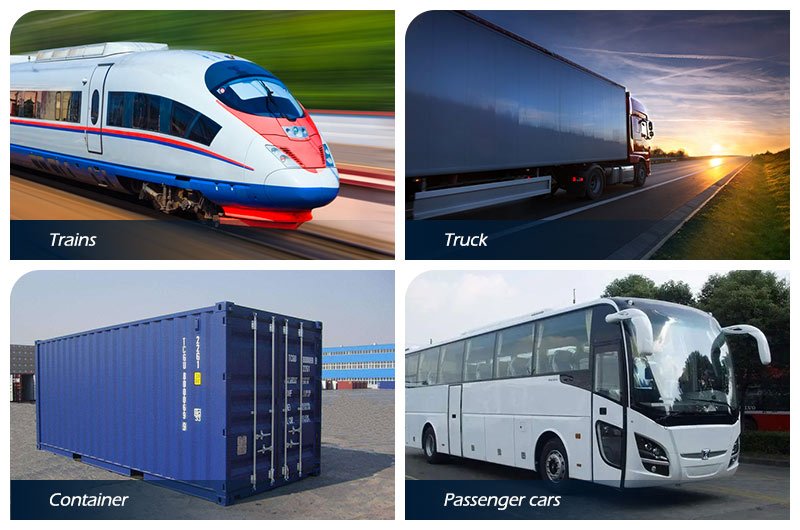
Alluminio is one of the most widely used metals in the world. It is lightweight, forte, resistente alla corrosione, easy to form, and highly recyclable. These properties make aluminum an essential material across construction, trasporto, elettronica, aerospaziale, medico, e produzione industriale.
If you are sourcing materials, designing products, or evaluating alternatives to steel or copper, capire il real-world uses of aluminum will help you make better technical and commercial decisions.
Questa guida spiega where aluminum is used, why it is chosen, and which aluminum products are most common, with practical examples from multiple industries.
1. Introduction to Aluminum
Aluminum is a non-ferrous metal known for its elevato rapporto resistenza/peso, natural corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. Unlike steel, aluminum does not rust. Unlike copper, it is much lighter and more cost-effective for large structures.
Key characteristics of aluminum:
Lightweight but structurally strong
Naturally corrosion-resistant (oxide layer protection)
Facile da lavorare, extrude, rotolo, and cast
Excellent heat and electrical conductivity
100% recyclable without loss of properties
These advantages explain why aluminum is used in both everyday consumer products E high-precision industrial systems.
2. Most Common Applications of Aluminum
You encounter aluminum daily, often without realizing it. From buildings and vehicles to electronics and packaging, aluminum supports modern infrastructure and technology.
Common application areas include:
Construction and architecture
Automotive and rail transportation
Aerospace and aviation
Electrical and electronics manufacturing
Household and kitchen products
Industrial machinery and safety systems
Compared to steel, aluminum reduces weight and maintenance. Compared to copper, it lowers cost while still providing reliable conductivity.
3. Industrial Applications of Aluminum
In industrial manufacturing, aluminum is valued for its process flexibility and long-term cost efficiency. It can be extruded into complex profiles, rolled into sheets and coils, or cast into precision components.
Industries rely on aluminum because:
It reduces total system weight
It lowers transportation and installation costs
It resists corrosion in harsh environments
It supports mass production and customization
It aligns with sustainability and recycling goals
Factories, infrastructure projects, and OEM manufacturers consistently choose aluminum for both structural and functional components.
4. Uses of Aluminum in Construction (Aluminum Building Products)
After steel, aluminum is the second most commonly used metal in construction. Unisce la forza, estetica, and durability while reducing structural load.
4.1 Structural and Architectural Applications
Aluminum Building Studs
Aluminum studs are used as vertical framing inside walls. They are lightweight, Dritto, fire-resistant, e facile da tagliare. Builders prefer them for modular layouts and modern construction.
Aluminum House Framing
Aluminum framing systems create strong, corrosion-resistant structures with minimal maintenance. They are ideal for residential and commercial buildings in humid or coastal environments.
Staircases and Safety Ramps
Aluminum staircases and ramps offer high load capacity with reduced weight. They are commonly used in public buildings, fabbriche, and accessibility projects.
4.2 Exterior Building Components
Cladding
Aluminum cladding protects buildings from weather while improving appearance. It resists UV exposure, piovere, and wind and requires minimal upkeep.
Roofing Systems
Aluminum roofs, piastrelle, and shingles are durable and lightweight. They reduce structural load while providing long service life in extreme weather conditions.
Curtain Wall Systems
Aluminum curtain walls support glass façades in high-rise buildings. Forniscono forza, flessibilità, and weather sealing without excessive weight.
Solar Panel Frames
Aluminum frames are standard in solar panels due to corrosion resistance, peso ridotto, and easy installation.
4.3 Interior Building Components
Window and Door Frames
Aluminum frames are strong, slim, e durevole. They support large glass panels and provide long-term dimensional stability.
Aluminum Skirting
Used at the base of walls, aluminum skirting resists moisture, impatto, and warping, making it superior to wood in commercial and residential interiors.
4.4 HVAC and Thermal Systems
Heating Systems and Heat Exchangers
Aluminum distributes heat evenly and efficiently. It is widely used in radiators, scambiatori di calore, and thermal transfer systems.
Air Conditioning Systems
Aluminum coils, fins, and frames improve cooling efficiency while reducing system weight and energy consumption.
5. Aluminum in Household and Daily-Use Products
5.1 Kitchen and Food-Related Products
Aluminum is widely used in cookware because it heats quickly, è facile da pulire, and is non-toxic.
Common aluminum kitchen products include:
Frying pans and pressure cookers
Kettles and baking trays
Piatti, bowls, and ladles
Cups, tumblers, and food containers
Why aluminum is used in kitchen foil
Aluminum foil blocks air, leggero, e umidità. It is flexible, food-safe, and ideal for food storage and cooking.
5.2 Furniture and Home Décor
Aluminum furniture is strong, rust-resistant, e leggero. It is widely used for:
Outdoor chairs and tables
Kitchen cabinets
Decorative panels and frames
Its durability makes it ideal for long-term indoor and outdoor use.
6. Aluminum Alloys in Aerospace Applications
Pure aluminum is too soft for aerospace use. Invece, aluminum alloys are created by adding elements such as copper, magnesio, o zinco.
These alloys provide:
High strength with low weight
Fatigue resistance
Stability under extreme conditions
Applications in aerospace include:
Aircraft fuselages and wings
Componenti del carrello di atterraggio
Engine housings
Cabin and seat frames
Aluminum alloys remain critical in both aviation and space exploration.
7. Aluminum in Electronics and Electrical Products
Aluminum is widely used in electronics due to its thermal conductivity and lightweight structure.
Le applicazioni comuni includono:
Smartphone and laptop housings
Heat sinks and cooling plates
Printed circuit boards (PCB)
Cables, connettori, and wires
LED lights and street lighting systems
Batteries and capacitors
Aluminum helps electronic devices dissipate heat efficiently and operate reliably.
8. Aluminum in Traffic and Safety Products
Aluminum is the preferred material for outdoor safety and traffic systems because it is rust-free and highly durable.
Typical aluminum traffic products include:
Traffic and road signs
Safety and warning signs
Aluminum road studs
LED sign frames
Control boxes and enclosures
Aviation obstruction lights
Aluminum ensures long service life in harsh outdoor environments.
9. Aluminum Applications in Transportation
9.1 Industria automobilistica
Automotive manufacturers use aluminum to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency.
Applications include:
Body panels and doors
Chassis and wheels
Componenti del motore
Scambiatori di calore
Lighter vehicles consume less fuel and produce lower emissions.
9.2 Rail Transportation
Trains use aluminum to increase speed and reduce energy consumption. Aluminum rail cars offer high load capacity with lower overall weight.
9.3 Industria marina
Aluminum is widely used in boats, yachts, and ships due to its resistance to saltwater corrosion. It reduces maintenance costs and improves vessel performance.
10. Aluminum in Sports and Recreation
Sports equipment manufacturers use aluminum for its strength and light weight.
Common products include:
Bicycles
Baseball bats
Tennis rackets
Hockey sticks
Gym equipment
Aluminum improves performance while reducing fatigue for athletes.
11. Aluminum in Medical and Healthcare Equipment
Nella sanità, aluminum supports hygiene, sicurezza, e precisione.
Medical applications include:
Hospital beds and frames
Diagnostic machines (X-ray, MRI housings)
Medical device enclosures
Aluminum is easy to clean and meets strict industry standards.
12. Aluminum in Packaging Industry
Aluminum packaging protects products from moisture, ossigeno, and light.
Gli usi comuni includono:
Lattine di bevande
Food trays
Foil wraps
Pharmaceutical packaging
Its recyclability makes aluminum packaging environmentally responsible.
13. Uses of Aluminum in Robotics and Automation
Robotics relies on aluminum for lightweight and precise structural components.
Applications include:
Braccia robotiche
Frames and housings
Automation equipment
Aluminum enables faster movement, higher payloads, and long-term durability.
14. Domande frequenti
Why is aluminum used in cars?
To reduce weight, improve fuel efficiency, and enhance performance.
Why does aluminum not react with water?
A protective oxide layer prevents corrosion.
È a prova di ruggine in alluminio?
SÌ, it does not rust like steel, though surface corrosion can occur in extreme conditions.
What is annealing used for in aviation?
To reduce internal stress and improve formability.
Is aluminum safe?
SÌ, aluminum is non-toxic and safe for daily use.
Is aluminum stronger than steel?
NO, but it offers better strength-to-weight efficiency.
Why is aluminum used in power lines?
It is lighter and more economical than copper while maintaining good conductivity.
Is aluminum flammable?
NO, it does not burn under normal conditions.
How long does aluminum last?
30–70+ years depending on application and environment.
15. Summary of Aluminum Uses
Aluminum is one of the most versatile engineering materials available today. From homes and vehicles to aerospace and robotics, it supports innovation while reducing weight, costo, e manutenzione.
Choosing the right aluminum grade depends on your application:
Soft aluminum for household and packaging
Structural alloys for construction and transportation
High-strength alloys for aerospace and industrial systems
Per i produttori, builders, e ingegneri, aluminum remains a future-proof material with unmatched versatility and value.