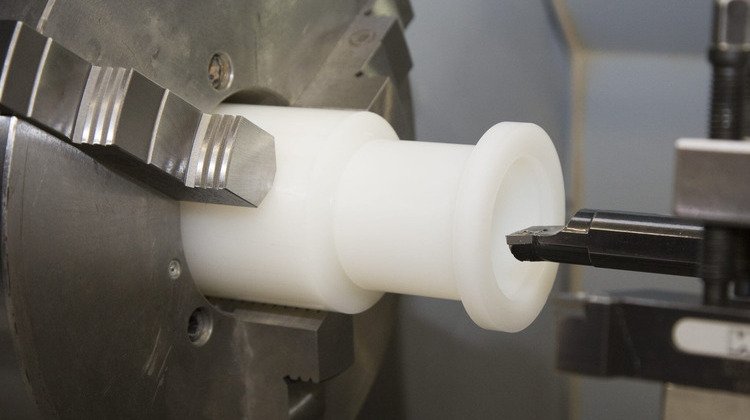
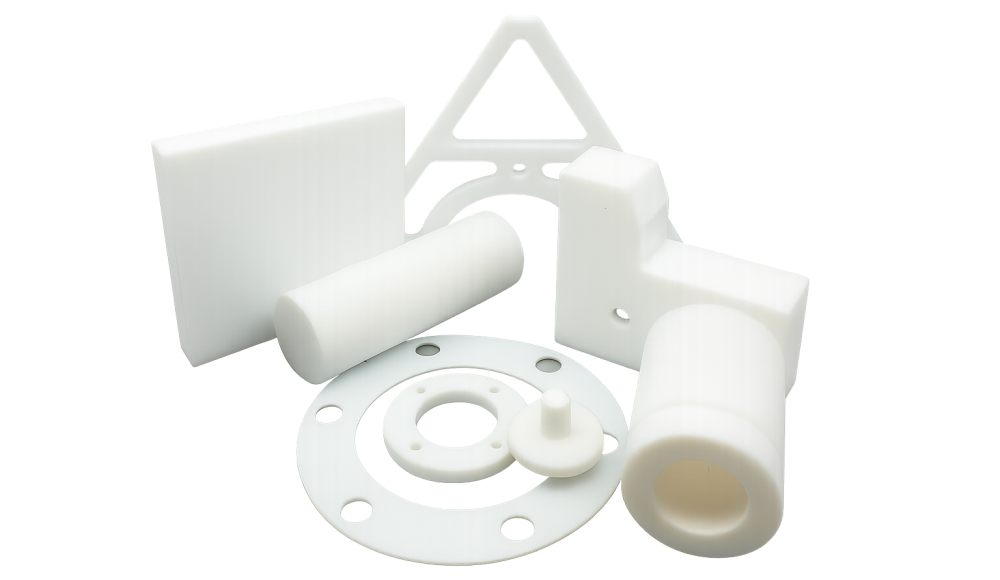
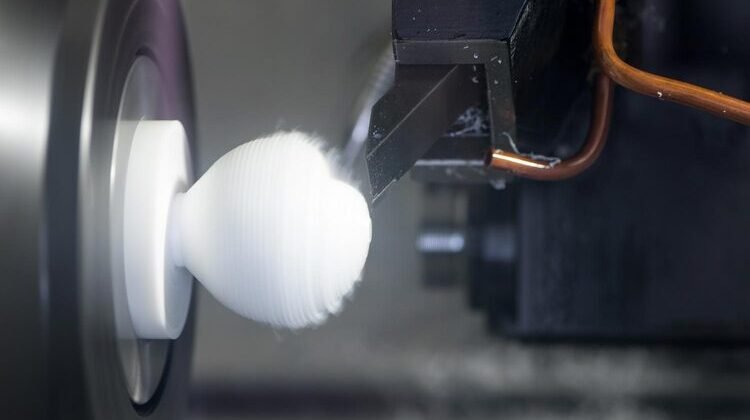
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), best known by its brand name Teflon, is one of the most chemically resistant and thermally stable plastics in the world. This fluoropolymer offers exceptional performance across demanding industries—from aerospace and pharmaceuticals to food processing and electronics. While its mechanical properties may not rival other engineering plastics, Teflon machining is a practical solution for manufacturing custom components that require low friction, high heat resistance, and inertness.
This guide provides a detailed breakdown of PTFE’s properties, the advantages and challenges of machining it, suitable applications, tooling tips, and material alternatives.
What is Teflon (PTFE)?
Teflon is a synthetic fluoropolymer made by polymerizing tetrafluoroethylene (TFE). First discovered accidentally in 1938 by DuPont, it is chemically composed of carbon and fluorine atoms, forming one of the strongest bonds in organic chemistry. This unique structure is what gives PTFE its impressive chemical and thermal resilience.
Key Properties:
Appearance: White, waxy solid
Melting Point: ~327°C (621°F)
Chemical Formula: (C₂F₄)ₙ
Structure: Linear chain of carbon atoms surrounded by fluorine atoms
Teflon is:
Hydrophobic: Repels water and most substances
Non-reactive: Extremely resistant to acids, bases, and solvents
Low-friction: Among the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid
Thermally stable: Can operate from -260°C to 260°C without degrading
Advantages of Machining Teflon
Material Advantages
Teflon’s material traits are what make it so useful in precision CNC machining:
Chemical Resistance: Inert to nearly all industrial chemicals
UV and Weather Resistance: Maintains properties under outdoor exposure
Water Resistance: Naturally hydrophobic, making it ideal for fluid systems
Electrical Insulation: Excellent dielectric strength across a wide temperature range
Thermal Stability: Can operate in cryogenic and high-temperature environments
Low Friction: Ideal for sliding or rotating parts
Food-Grade: FDA-compliant and easy to sterilize
Flame Resistance: Very low flammability
Process Advantages
Machining PTFE provides additional advantages due to its softness and machinability:
Easily Machinable: Cuts easily with minimal force
No Thermal Deformation: Stays dimensionally stable during dry or wet machining
No Hardening Needed: No need for post-machining heat treatment
Great for Prototypes: Quick to produce low-volume or custom components
Limitations of Machining Teflon
Despite its many benefits, machining Teflon presents some unique challenges:
High Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: Parts can expand or contract more than other plastics
Creep Deformation: Tends to deform slowly under long-term mechanical stress
Difficult to Hold Tolerances: Especially on thin or small features
Poor Dimensional Stability: Subject to warping during machining or post-processing
Soft Material: Can leave burrs or tool marks, requiring extra finishing
To minimize issues:
Use sharp tools
Avoid tight tolerance designs
Employ effective cooling and deburring techniques
Common Applications of CNC Machined Teflon Parts
CNC machining is a preferred method for fabricating solid PTFE components used in various industries. Some typical parts include:
| Application | Examples |
| Valves & Fittings | Pipe seals, washers, flow control parts |
| Bearings & Bushings | Low-friction wear-resistant components |
| Insulation | Electrical insulators, cable spacers |
| Laboratory Components | Chemical-resistant connectors, sample holders |
| Food-Grade Parts | Scraper blades, nozzles, sealing plates |
| Medical Devices | Implants, biocompatible tubing connectors |
| Aerospace | Lightweight gaskets and seals |
| Semiconductor | Inert fluid path components |
Machining Tips and Best Practices for Teflon
To achieve the best results when CNC machining PTFE, consider the following:
Tooling
Use carbide or HSS tools with extremely sharp edges
Single-flute or polished flute tools reduce burrs and improve finish
Coolant and Lubrication
Apply non-aromatic, water-soluble coolants
Spray mists or compressed air work well for chip removal and heat management
Speeds and Feeds
Use moderate cutting speeds and high feed rates to prevent material melting
Avoid excessive tool pressure or heat buildup
Deburring and Finishing
Use sanding, cryogenic freezing, or chemical deburring to remove soft burrs
Freezing the part before finishing can reduce softness and deformation
Design Considerations
Plan for looser tolerances (~±0.13 mm) unless the part is stress-relieved
Avoid thin walls or delicate geometries prone to warping
Alternative Materials to Teflon
For projects where Teflon’s limitations are unacceptable, the following alternatives offer similar benefits with improved strength or processability:
| Material | Key Advantage | Common Brand |
| PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy) | Better non-stick, more flexible | Teflon PFA |
| PCTFE (Polychlorotrifluoroethylene) | Lowest water vapor transmission | Kel-F |
| ECTFE (Ethylene Chlorotrifluoroethylene) | Excellent corrosion resistance | Halar |
Each of these materials can be CNC machined but may have different tooling and handling requirements.
Conclusion: Precision PTFE Machining Services from Experts
Teflon (PTFE) is a go-to material for demanding environments requiring chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low friction. However, its softness and dimensional instability mean that precision PTFE machining requires a careful approach and experienced operators.
If you’re looking to prototype or mass-produce custom Teflon components, partner with a manufacturer familiar with engineering plastics. At Tops Precision, we offer advanced PTFE CNC machining with expert support—from design assistance to final quality inspection.
Contact our team today to get a free quote or learn how we can help with your next project.
FAQs
1. What makes Teflon (PTFE) the preferred material for low-friction applications?
Teflon (PTFE) has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, comparable to wet ice sliding on wet ice. This unique property stems from the uniform blanket of fluorine atoms surrounding the carbon backbone. This structure prevents other molecules from forming strong bonds with the PTFE surface, making it extremely “slippery” and ideal for bearings, bushings, seals, and sliding surfaces where wear resistance and minimal energy loss are critical.
2. Is PTFE the same as the non-stick coating found on cookware?
Yes, chemically, it is the same material. PTFE is the base ingredient for most high-quality non-stick cookware coatings. However, in cookware, the PTFE is applied as a thin, high-temperature-cured coating. In CNC machining, PTFE is worked as a solid block (often referred to as billet or rod) to produce thick, structural, custom parts like gaskets, insulators, or pump components.
3. What is “Creep Deformation,” and why is it a significant limitation for machined PTFE parts?
Creep is the tendency of a solid material to slowly and permanently deform or flow under mechanical stress below its yield strength. Since PTFE is a relatively soft material with a low glass transition temperature, it is highly susceptible to creep, especially under continuous load or at slightly elevated temperatures. This means that PTFE gaskets or seals under constant compression may eventually lose their thickness and fail to seal properly over time.
4. Why is cryogenic deburring often used for finishing machined PTFE parts?
Because PTFE is very soft, traditional mechanical deburring (scraping or sanding) can easily smear the material, damage the surface finish, or cause slight dimensional changes. Cryogenic deburring involves freezing the PTFE part using liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide until it becomes temporarily hard and brittle. The soft burrs then become brittle and are easily removed by tumbling or light blasting without damaging the underlying, tougher material.
5. What is the biggest machining challenge when holding tight tolerances on PTFE?
The biggest challenge is PTFE’s High Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE). A small change in temperature (even from ambient heat or machine friction) causes the part to expand or contract significantly more than other plastics or metals. Furthermore, the material’s inherent poor dimensional stability and tendency to stress-relieve and warp after material removal make achieving and holding tolerances tighter than $\pm 0.13 \text{ mm}$ difficult without specialized stress-relieving procedures.
6. When should PFA or PCTFE be used as an alternative instead of standard PTFE?
The alternatives are chosen to overcome PTFE’s specific limitations:
-
PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy): Used when melt processability is needed (for complex molding) while maintaining PTFE’s low friction and chemical resistance.
-
PCTFE (Polychlorotrifluoroethylene): Used when the key requirement is the lowest possible water vapor transmission rate (impermeability) and higher mechanical strength, making it ideal for pharmaceutical packaging or cryogenic seals where moisture must be absolutely excluded.
7. Why is a high feed rate sometimes beneficial when machining PTFE despite its softness?
Using a high feed rate (the speed at which the tool advances into the material) can be beneficial because it allows the tool to make a thicker, cleaner chip. This action rapidly removes the material and helps prevent the tool from simply rubbing or smearing the soft plastic. A thicker chip also carries heat away more efficiently and helps reduce the formation of soft, difficult-to-remove burrs.