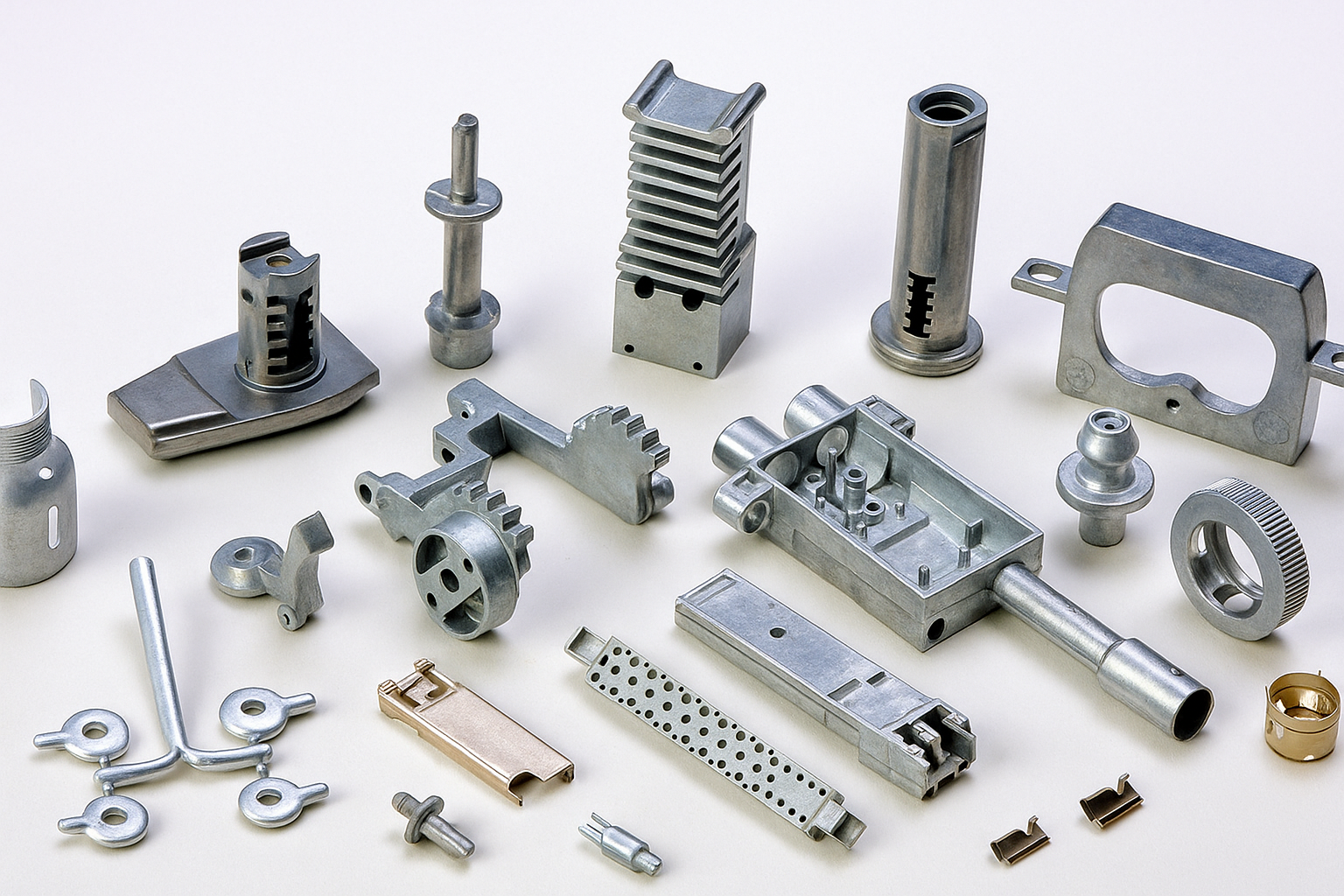
Zinc die casting is a widely used manufacturing process involving the injection of molten zinc or zinc alloys into molds under high pressure, primarily utilizing the hot chamber method. Known for precision and strength, zinc die casting has specific advantages and some notable drawbacks. This article provides a comprehensive understanding of both the benefits and limitations of zinc die casting, as well as insights into its applications and how it compares with other common metals.
Advantages of Zinc Die Casting
Higher Precision and Strength Compared to Aluminum
Zinc die-cast components offer significantly better dimensional accuracy and mechanical strength than aluminum parts. Zinc alloys have excellent castability, enabling manufacturers to produce intricate, detailed, and structurally robust components suitable for demanding engineering applications.
Lower Melting Point for Easy Reshaping
The relatively low melting point of zinc alloys (around 380–420°C) simplifies the process of reshaping or redesigning components when necessary. This flexibility can reduce production delays, lower rework costs, and enable quick adjustments during manufacturing.
Superior Fluidity for Thin-Walled Components
One of zinc’s standout features is its exceptional fluidity. This characteristic enables the production of components with thinner walls and intricate shapes that might be impossible or impractical to cast accurately using other metals.
Capability to Form Complex Designs
Zinc alloys possess excellent flow characteristics that allow manufacturers to achieve complex geometric shapes with high precision and consistently smooth surfaces. This property is invaluable in applications that require aesthetic appeal or exacting standards for tight tolerances.
Easy and Versatile Surface Treatment Options
Zinc die-cast parts support a wide array of surface treatments. Processes such as grinding, painting, electroplating, anodizing, powder coating, and chromate treatments are easily applicable, enhancing corrosion resistance, aesthetics, and overall part functionality.
Longer Die Life Due to Lower Melting Temperature
The lower casting temperatures associated with zinc alloys reduce thermal fatigue and stress on the dies. Consequently, tooling used for zinc die casting typically enjoys significantly longer service life, minimizing tooling costs and maintenance.
Better Mechanical Properties
Zinc alloys like Zamak 2 and Zamak 3 exhibit superior hardness, strength, and toughness compared to many other non-ferrous alloys, making zinc an excellent choice for structural components requiring enhanced durability and reliability.
Disadvantages of Zinc Die Casting
Higher Density and Heavier Parts
Despite its advantages, zinc’s relatively high density (approximately 6.6 g/cm³ compared to aluminum’s 2.7 g/cm³) results in heavier components. This property makes zinc alloys less suitable for lightweight and weight-sensitive applications, particularly in industries like aerospace or where fuel efficiency is critical.
Reduced Corrosion Resistance when Alloyed with Tin or Lead
When zinc is alloyed with metals like tin or lead to alter its properties, corrosion resistance diminishes. These alloys also tend to become less ductile and more brittle, limiting their application in environments exposed to harsh conditions or heavy impacts.
Sensitivity to High Temperatures
Exposing zinc alloys to excessively high temperatures can lead to a significant reduction in tensile strength. Components subjected to elevated temperatures become brittle and more susceptible to fractures, restricting their use in high-temperature applications.
Poor Impact Resistance at Low Temperatures
At significantly low temperatures, zinc die-cast components lose their impact resistance dramatically, becoming vulnerable to cracking or catastrophic failures under sudden impacts or shock loading.
TOPS Precision: Leading Zinc Die Casting Manufacturer
Tops Precision has extensive experience specializing in zinc die casting, focusing on high-quality standards and precise components. With a strong emphasis on delivering consistently superior products, Tops Precision has established itself as a trusted supplier globally.
Tops Precision Services
Comprehensive Die Casting Solutions
Sunrise Metal provides complete die casting solutions, including:
Rapid prototyping to validate designs quickly.
Die casting tooling with precision-engineered dies.
Zinc die casting production at volume and scale.
CNC machining for precise dimensional control.
Advanced Casting Equipment
Utilizing state-of-the-art hot chamber die casting machines with clamping forces up to 250 tons, Tops Precision l handles complex, large-scale projects effectively.
Exceptional Quality Control
Tops Precision emphasizes meticulous quality control procedures, employing advanced measuring instruments and testing methods to meet stringent dimensional and mechanical standards.
Extensive Alloy Selection
They offer a broad spectrum of zinc alloys, including standard Zamak alloys (Zamak 2, 3, 5, 7), ZA8, ZA27, and custom alloy formulations to meet specific project requirements.
Applications of Zinc Die Casting
Zinc alloys are preferred for various applications across different industries due to their specific properties:
Automotive Industry
Automotive components frequently made from zinc alloys include:
Engine and transmission parts
Bearings
Brake systems components
Steering system components
The strength, durability, and dimensional precision of Zamak 2 specifically make it ideal for these high-stress applications.
Electronics Industry
Zinc die-cast components serve essential roles in electronic assemblies:
Energy regulators
Switch housings
Connectors and terminals
Control panels
Ceramic resistor casings
Zamak 3 alloy is particularly suited for electronic applications requiring consistent dimensional stability over long periods.
Appliance Industry
Zinc casting is common for household and consumer products:
Razors and grooming accessories
Buckles, keychains, and decorative items
Door locks and handles
Furniture fittings and hardware components
These products benefit from zinc’s combination of strength, affordability, and ease of finishing.
Choosing Zinc Die Casting vs. Other Metals
Zinc vs. Aluminum
Zinc is superior for precision parts with intricate details, thin walls, and excellent machinability.
Aluminum is lighter and more suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor.
Zinc vs. Magnesium
Zinc offers greater strength, better elongation, and superior castability at a lower cost compared to magnesium alloys.
Magnesium alloys are lighter but often more expensive and less mechanically robust.
High-Strength Applications Similar to Steel
Zinc alloys can offer comparable strength and performance to steel in certain scenarios, providing an efficient alternative when steel’s weight, complexity, or machining costs are prohibitive.
Conclusion
Zinc die casting presents significant advantages for manufacturing complex, precise, and strong components. Although limitations such as higher density and temperature sensitivity must be considered, zinc alloys remain indispensable in various applications. By carefully evaluating the specific requirements for each project, manufacturers can confidently select zinc alloys to achieve optimal balance between performance, quality, and cost-effectiveness.