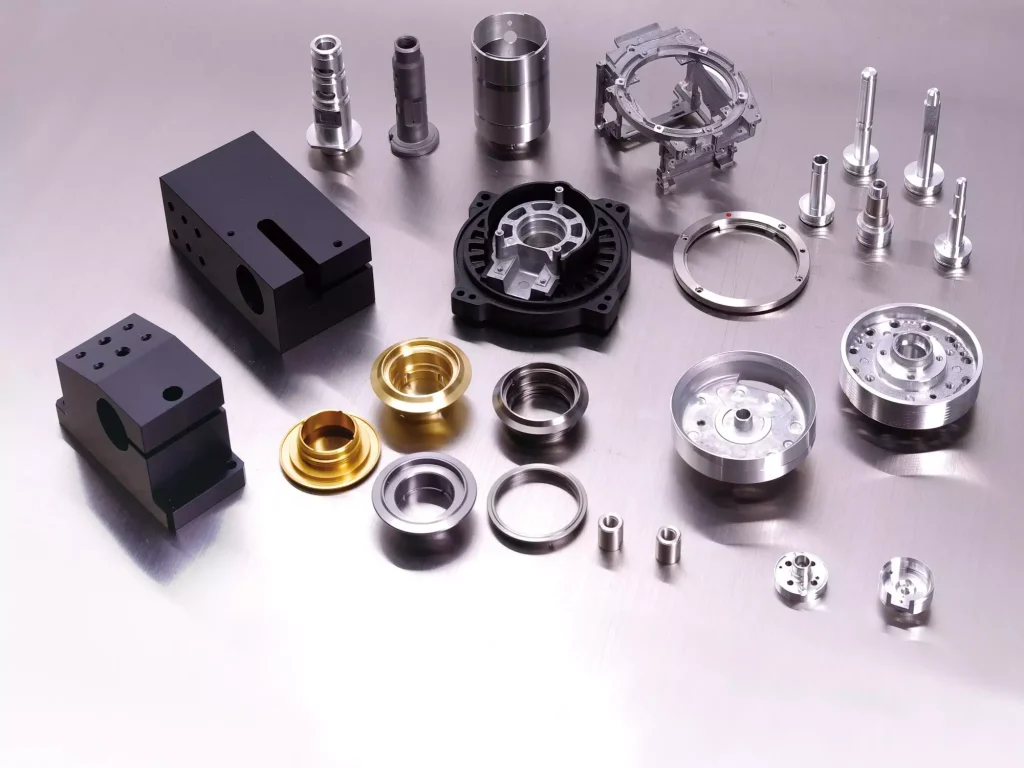
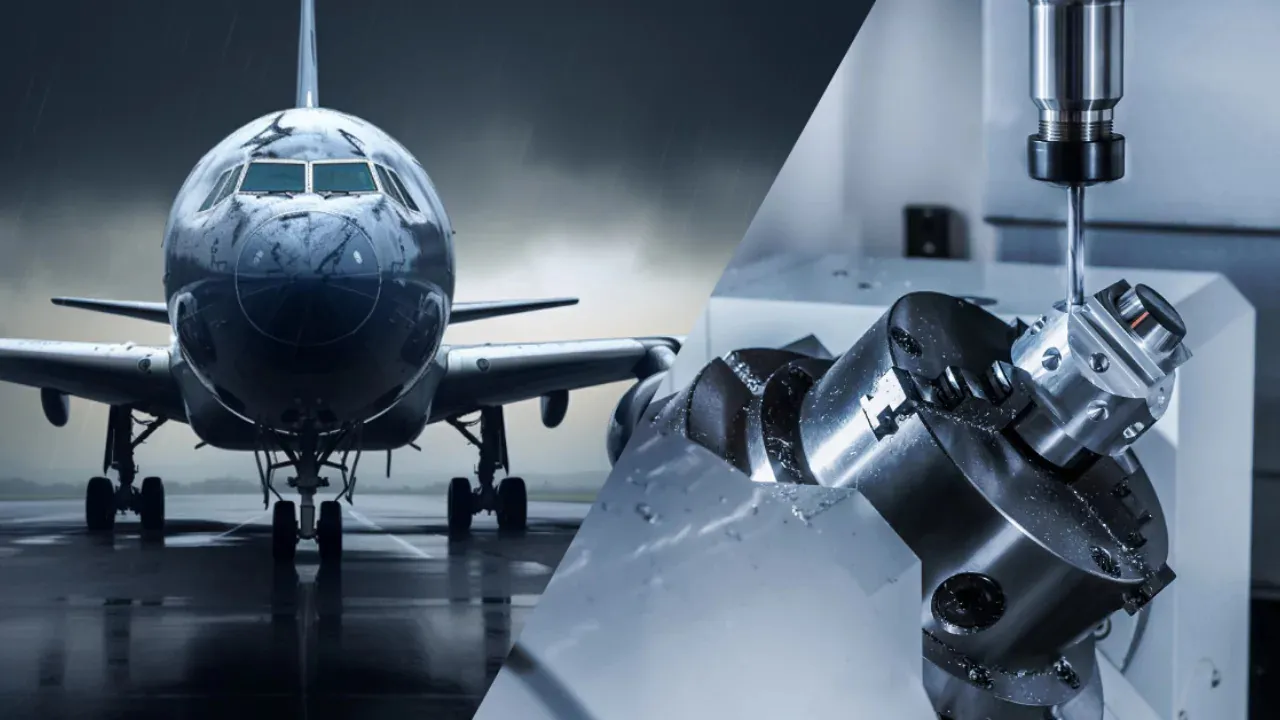
Why does CNC machining matter so much across different industries? Because it brings consistency. From the first piece to the millionth, a CNC machine delivers identical, high-quality results. And when industries like aerospace or healthcare demand perfection—where a single error can cost millions or even lives—CNC machining rises as the gold standard.
This article will explore 30 industries where CNC machining is indispensable. We’ll go beyond surface-level descriptions and dive deep into the specific roles CNC plays, the types of components it produces, and why it continues to be the preferred choice for manufacturers worldwide. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of how CNC machining fuels everything from airplanes to jewelry.
What is CNC Machining?
At its core, CNC machining is the marriage of computers and mechanical tools. Instead of manually controlling lathes, mills, drills, or grinders, a computer takes over. Engineers feed a digital design—usually in the form of CAD (Computer-Aided Design) files—into the CNC system, and the machine interprets it into precise movements. The result? A flawless part cut, drilled, or shaped exactly as designed.
There are several types of CNC machines:
CNC Milling Machines – Used to cut, drill, and shape solid materials.
CNC Lathes – Perfect for creating symmetrical objects like shafts and screws.
CNC Routers – Ideal for cutting softer materials like wood, plastics, and composites.
CNC Grinders – Used when ultra-smooth finishes are required.
Unlike traditional machining, where human error is always a risk, CNC machining thrives on automation and repeatability. Once a design is uploaded, the machine can reproduce it with the same accuracy hundreds or thousands of times. This not only speeds up production but also dramatically reduces waste and cost.
Another key distinction is the ability to handle complex geometries. Traditional tools might struggle with intricate patterns or curved designs, but CNC machines can carve, mill, or drill with surgical precision. For example, components like aircraft turbine blades or custom medical implants would be nearly impossible to make by hand with such accuracy.
In short, CNC machining is more than just a tool—it’s a manufacturing revolution. It bridges the gap between imagination and production, turning digital blueprints into physical reality with unmatched precision.
Benefits of CNC Machining
CNC machining’s success across industries stems from its multitude of benefits. Let’s break down the key advantages that make it indispensable:
Precision and Accuracy
CNC machines achieve tolerances as tight as a few microns. For industries like aerospace or healthcare, where even the smallest error could lead to catastrophic outcomes, this level of accuracy is life-saving.
Speed and Efficiency
Once programmed, CNC machines can work 24/7 without fatigue. What used to take weeks can now be done in days—or even hours. Automation allows manufacturers to meet tight deadlines without sacrificing quality.
Scalability and Repeatability
Need a single prototype? CNC can do that. Need 10,000 identical parts? CNC can do that too—without losing consistency. This makes it the ideal choice for both prototyping and mass production.
Versatility with Materials
CNC machines handle a wide range of materials, from metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium to plastics, composites, wood, and even ceramics. This flexibility means industries from aerospace to jewelry can all benefit from the same technology.
Cost-Effectiveness
While CNC machines require a significant upfront investment, they reduce long-term costs by cutting down on waste, speeding up production, and minimizing human errors. Over time, this makes CNC machining economically unbeatable.
Complexity Made Simple
Modern CNC machines, especially 5-axis models, can handle designs that once seemed impossible. Imagine carving a sculpture out of solid titanium—CNC makes such complex jobs feasible and efficient.
These advantages explain why CNC machining has become the foundation of modern manufacturing, powering industries as diverse as aerospace, automotive, and even entertainment.
Aerospace Industry
Few industries demand precision as much as aerospace. A single airplane is made up of millions of parts, and even the tiniest flaw could result in disaster. That’s why CNC machining is not just useful—it’s mission-critical for aerospace.
Key Components Produced
Engine Parts: Turbine blades, fuel systems, and nozzles
Landing Gear: High-strength components that endure extreme stress
Airframe Structures: Fuselage, wings, and support brackets
Cabin and Interior Parts: Seats, cockpit instruments, storage bins
These parts are typically made from aluminum, titanium, and composites, chosen for their strength-to-weight ratios. CNC machines can handle these tough materials with ease, producing lightweight yet durable components.
Why CNC is Essential in Aerospace
Safety Standards: Precision is non-negotiable; tolerances are razor-thin.
Durability: Aerospace parts face extreme temperatures and pressures.
Customization: Prototypes and new designs are quickly tested using CNC.
For instance, creating a jet turbine blade requires machining curves, holes, and complex geometries. A manual approach would take months and still risk flaws. CNC machines handle this challenge in hours with flawless accuracy.
In short, CNC machining is the unsung hero of aviation and space travel, making modern flight possible.
Automotive Industry
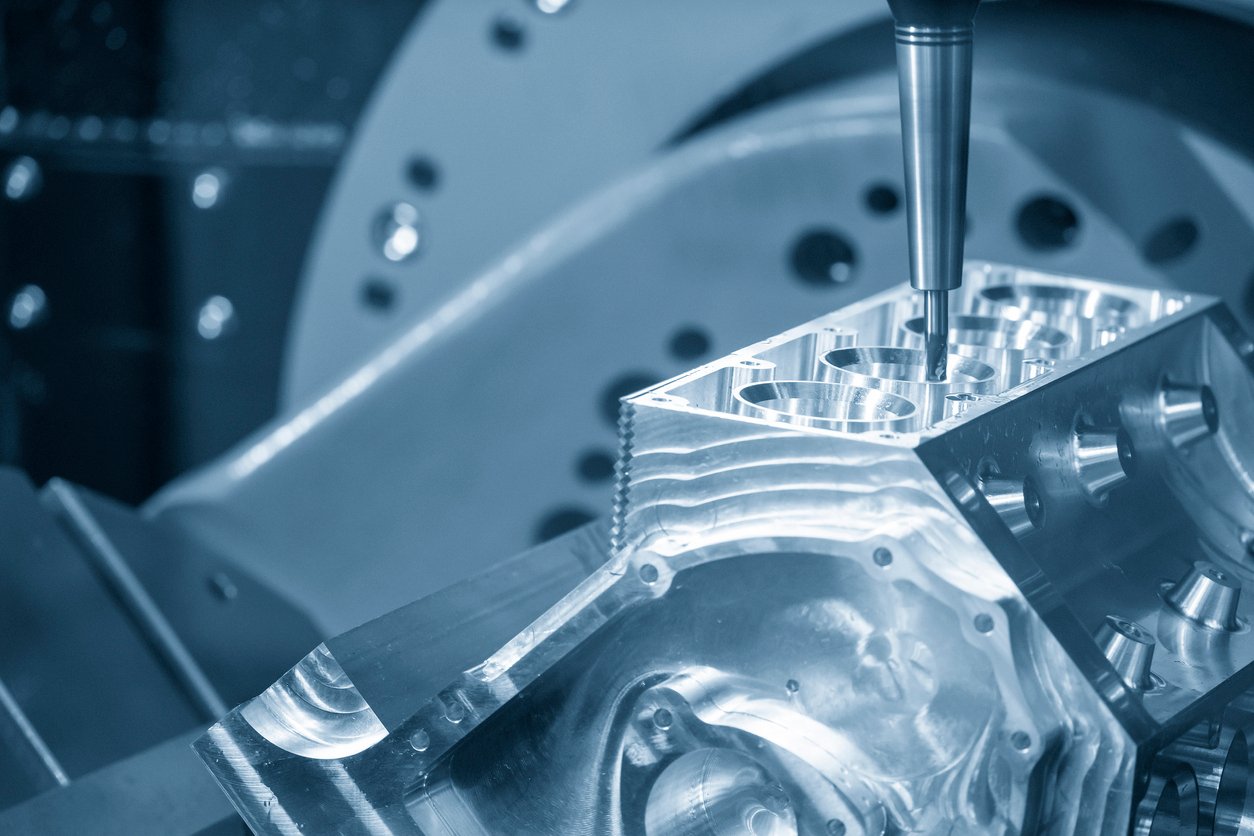
The 5-axis machining center cutting the v8-engine cylinder block. The 5-axis milling machine cutting the aluminum cylinder block manufacturing process.
The automotive sector is another heavy user of CNC machining. From designing a sleek sports car to producing everyday commuter vehicles, CNC plays a critical role in making cars faster, safer, and more reliable.
Key Automotive Applications
Engine Components: Pistons, cylinder heads, and valve blocks
Transmission and Gearboxes: Precision gears and casings
Suspension and Steering: Shock absorbers, steering racks, and joints.Alloy Wheels: Lightweight alloy wheels that require tight tolerances for safety, balance, and performance
Prototyping: Concept car designs and testing parts before mass production
Body and Interior Parts: Dashboards, door panels, and steering wheels
CNC machining ensures each part fits perfectly, which is vital for vehicle safety and performance. Imagine a piston that’s just slightly off—it could compromise the entire engine.
Why CNC Matters in Automotive
Mass Production: CNC enables millions of identical components.
Prototyping Speed: Designers can test concepts rapidly.
Durability: CNC-machined metals withstand heat, friction, and stress.
Customization: Luxury carmakers use CNC for personalized features.
For example, when companies like Tesla or BMW prototype new vehicles, CNC machining allows them to move from design to testing in record time. Meanwhile, manufacturers like Toyota rely on CNC for large-scale production, ensuring every car rolling off the assembly line meets strict standards.
Simply put, CNC machining keeps the automotive world moving, balancing mass production with innovation.
Medical Industry
Few industries demand precision and reliability as much as the medical sector. Here, the difference between success and failure can be measured in human lives. CNC machining has revolutionized medical manufacturing by enabling the production of highly accurate, sterile, and complex parts that meet stringent healthcare standards.
Applications in Medicine
Surgical Instruments: Scalpels, forceps, clamps, and bone saws require microscopic accuracy.
Orthopedic Implants: Titanium hip joints, knee replacements, and dental implants must fit patients perfectly.
Diagnostic Equipment: MRI scanners, CT scanners, and ultrasound machines contain CNC-machined housings and components.
Micro Devices: Pacemaker housings and tiny screws for orthopedic surgery are often CNC-produced.
Why CNC is Indispensable
Precision for Patient Safety: Even a fraction of a millimeter can determine whether an implant integrates properly.
Sterile Production: CNC machines can work with medical-grade materials like stainless steel, titanium, and biocompatible plastics.
Customization: Patients often need personalized implants, and CNC machining makes custom designs feasible.
A clear example is the production of dental implants. Each patient’s jawbone structure is unique, and CNC machining allows for the creation of implants tailored to an individual’s exact measurements. This customization would be impractical with traditional machining.
By ensuring accuracy, repeatability, and biocompatibility, CNC machining has become a cornerstone of modern healthcare, enabling longer lives and better treatment outcomes.
Electronics Industry
The electronics sector thrives on miniaturization and precision—two qualities where CNC machining excels. From smartphones to advanced communication systems, CNC technology ensures that delicate components are manufactured with pinpoint accuracy.
Applications in Electronics
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): CNC routers and mills are used for drilling micro-holes and shaping boards.
Enclosures and Casings: Protective covers for laptops, phones, and routers.
Heat Sinks: CNC machines cut grooves and fins for efficient thermal management.
RF Components: Connectors, antenna housings, and waveguides.
Why CNC is Crucial in Electronics
Micro-Precision: Many electronic parts are smaller than a fingernail but require exact fits.
Material Versatility: CNC can machine plastics, aluminum, copper, and composites—all widely used in electronics.
Scalability: Electronics manufacturing often involves mass production of small, intricate parts.
Innovation: Prototyping new gadgets is faster with CNC machines.
Take smartphones as an example. The sleek aluminum bodies of iPhones or Samsung devices are CNC-machined to perfection, ensuring a seamless fit for glass panels and internal components. Similarly, heat sinks for CPUs rely on CNC to maintain exact dimensions for efficient cooling.
In a world where electronics are getting smaller and more powerful, CNC machining provides the accuracy and consistency to keep up with consumer demands.
Military and Defense
The defense industry relies on CNC machining for producing components that must withstand extreme conditions—heat, pressure, corrosion, and impact. Here, failure is not an option, making CNC technology a vital part of defense manufacturing.
Applications in Military and Defense
Weapons Systems: Barrels, firing mechanisms, and precision scopes.
Vehicles and Aircraft: Armored vehicles, drones, and helicopters contain numerous CNC-machined parts.
Communication Equipment: Secure radios, radar housings, and satellite components.
Protective Gear: Helmets, armor plates, and tactical equipment housings.
Why CNC is Vital
Reliability Under Stress: CNC-machined parts can endure combat environments.
Precision Targeting: Weapon accuracy depends on flawless components.
Rapid Prototyping: Defense contractors can test new designs quickly.
Security Standards: Defense parts must meet the highest quality certifications.
For instance, fighter jet components—from turbine blades to cockpit housings—are CNC-machined with tight tolerances. Similarly, advanced weaponry like guided missile systems relies on CNC parts to ensure flawless performance.
The defense sector trusts CNC machining because it combines precision, durability, and scalability, enabling nations to maintain strong, reliable defense capabilities.
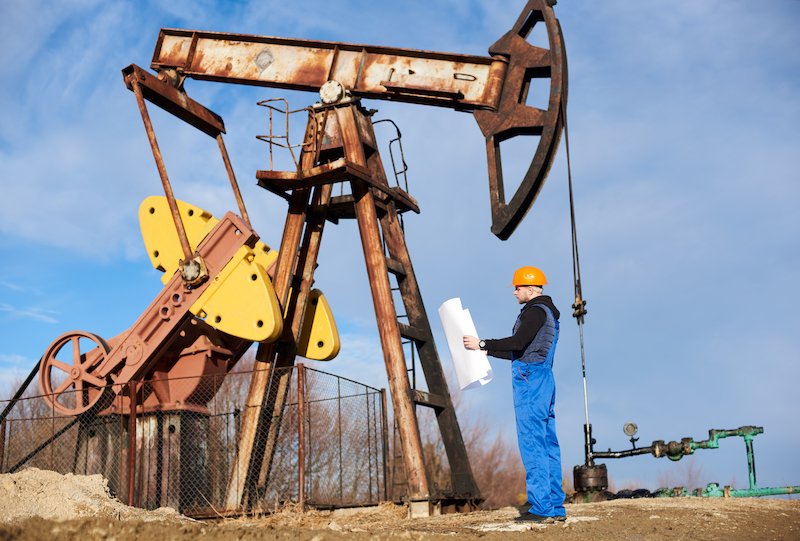
Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry operates in some of the harshest environments on Earth—deep seas, deserts, and arctic regions. Equipment here must handle extreme pressure, heat, and corrosive conditions, making CNC machining a necessity.
Applications in Oil and Gas
Drilling Tools: Drill bits, pipes, and couplings.
Valves and Fittings: High-pressure components that regulate fluid flow.
Pumps and Compressors: Precision-machined housings and impellers.
Subsea Equipment: Components designed to resist corrosion in saltwater environments.
Why CNC Matters
Material Strength: CNC machining works with hardened steel, titanium, and exotic alloys.
Reliability: Failures can lead to catastrophic oil spills or gas leaks.
Efficiency: CNC allows for faster production of replacement parts, minimizing downtime.
Customization: Different oil rigs require specialized parts that CNC can produce.
Consider a deep-sea drilling operation: every part, from drill heads to valve systems, must withstand crushing pressures and corrosive seawater. CNC machining ensures these components meet the industry’s demanding standards.
By providing strength, precision, and durability, CNC machining keeps the energy sector running smoothly—even under the toughest conditions.
Renewable Energy Industry
As the world shifts toward sustainable energy, CNC machining is playing a central role in building the infrastructure for wind, solar, and hydro power. Renewable energy components often require large, complex, and precise parts, which CNC machining delivers with efficiency.
Applications in Renewable Energy
Wind Turbines: Rotor hubs, shafts, and gearbox components.
Solar Power: Aluminum frames, mounts, and tracking systems.There are many solar panel suppliers that rely on precision-made metal parts, such as HBOWA.
Hydroelectric Plants: Turbine blades and housing parts.
Energy Storage: CNC-machined casings for battery systems.
Why CNC is Important
Scalability: Renewable projects often require large-scale production.
Durability: Components must last decades in outdoor environments.
Material Flexibility: CNC machines work with composites, metals, and alloys.
Innovation-Friendly: As renewable technologies evolve, CNC supports prototyping and custom parts.
For example, wind turbine gearboxes are massive yet must be machined with microscopic tolerances to function reliably for 20+ years. Similarly, CNC machining is used to create solar panel mounts that can withstand constant exposure to sun, wind, and rain.
By providing the backbone for renewable energy infrastructure, CNC machining is helping power the global shift toward a greener future.
Consumer Goods Industry
The consumer goods sector is vast, spanning everything from household appliances to toys and personal electronics. What ties them together is the need for cost-effective, durable, and aesthetically appealing products—and CNC machining plays a major role in delivering them.
Applications in Consumer Goods
Appliances: Washing machine drums, blender blades, and coffee machine parts.
Electronics: Laptop housings, speaker enclosures, and gaming consoles.
Toys and Gadgets: Precision plastic or metal components for moving parts.
Luxury Goods: High-end watches, designer accessories, and custom tools.
Why CNC Matters in Consumer Products
Consistency: Consumers expect every item to look and function identically.
Customization: Personalized phone cases, engraved items, or tailored gadgets are CNC-friendly.
Durability: CNC machining ensures longer-lasting parts compared to mass-molded plastics.
Design Flexibility: CNC allows designers to experiment with intricate forms.
Take the example of high-end headphones. The aluminum housing around the speakers isn’t just aesthetic—it protects delicate electronics and ensures proper sound quality. CNC machining delivers the precise dimensions required for both performance and style.
In essence, CNC machines empower manufacturers to deliver reliable, stylish, and affordable goods that meet consumer expectations in today’s fast-paced market.
Railway Industry
The railway industry depends on parts that can endure heavy loads, constant friction, and outdoor conditions. Since trains run for decades, durability and safety are non-negotiable. CNC machining provides the precision and strength that modern railway systems require.
Applications in Railways
Engines: Cylinders, housings, and pistons.
Braking Systems: Brake discs and pads requiring high tolerance.
Track Components: Switches, fastening systems, and rail joints.
Car Interiors: Seating structures, panels, and fittings.
Why CNC is Key for Railways
Longevity: Train parts must last years with minimal wear.
Safety Standards: Even a small defect could cause derailments.
Customization: Each railway system has unique infrastructure needs.
Scalability: CNC enables large-batch production for entire fleets.
For example, braking systems must function reliably under massive loads. CNC machining ensures exact tolerances so that brakes engage uniformly, reducing accident risks. Similarly, precision machining of rail joints ensures smoother rides and less wear on both trains and tracks.
Ultimately, CNC machining helps the railway industry deliver safe, reliable, and long-lasting transportation systems.
Robotics Industry
The robotics sector is one of the fastest-growing fields today, and CNC machining is at its heart. Robots require complex, lightweight, and highly accurate components, making CNC machining the go-to method for production.
Applications in Robotics
Frames and Chassis: Structural skeletons of industrial and service robots.
Gears and Actuators: High-precision movement parts.
Electronic Housings: Enclosures for sensors and processors.
Prototyping: Custom robotic arms, joints, and attachments.
Why CNC Powers Robotics
Tight Tolerances: Robots need precision for repeatable motion.
Material Versatility: Robotics uses metals, plastics, and composites.
Customization: CNC enables unique builds for specialized robots.
Innovation: Rapid prototyping supports new designs.
For instance, industrial robots used in car assembly lines require gears machined with micrometer accuracy to ensure consistent performance under stress. Meanwhile, service robots like drones use CNC-machined lightweight aluminum or carbon fiber parts to maximize efficiency.
Simply put, CNC machining fuels robotics by providing the precision and adaptability required for this cutting-edge industry.
Mining Industry
The mining industry operates in environments that are tough on machinery—dust, abrasion, moisture, and constant wear. CNC machining provides the rugged, durable, and reliable parts that allow mining operations to continue without costly breakdowns.
Applications in Mining
Drilling Equipment: Drill heads, rods, and couplings.
Excavation Machinery: Buckets, gears, and structural components.
Crushing Systems: Precision parts for crushers and pulverizers.
Conveyor Systems: Rollers, shafts, and supports.
Why CNC is Vital in Mining
Durability: CNC parts resist wear and tear from abrasive materials.
Material Strength: CNC machining can handle hardened steel and alloys.
Reliability: Downtime in mining is costly—precision reduces failures.
Scale: Large components for heavy machinery can be machined efficiently.
Take a rock crusher as an example. Its gears must endure constant grinding without wearing down quickly. CNC machining ensures gears are not only durable but also precisely matched to minimize breakdowns.
In short, CNC machining ensures that the mining industry’s machinery remains reliable, strong, and productive in even the harshest environments.
Optics Industry
The optics industry demands microscopic precision, and CNC machining provides exactly that. From manufacturing camera lenses to telescope assemblies, CNC machines deliver the flawless accuracy needed for optical clarity.
Applications in Optics
Lens Molds: Precision molds for glass or plastic lenses.
Mounts and Housings: Structural frames for microscopes and telescopes.
Micro-Optics: Tiny components for endoscopes and laser systems.
Optical Benches: Complex assemblies for scientific research.
Why CNC Excels in Optics
Micron-Level Accuracy: Essential for clear imaging.
Smooth Finishes: CNC grinding ensures flawless optical surfaces.
Customization: CNC enables unique lens configurations.
Material Handling: Glass, plastics, and metal housings all benefit.
For example, in medical endoscopes, tiny optical components must align perfectly for doctors to see clearly inside the human body. CNC machining ensures those alignments are consistent and reliable.
In essence, CNC machining is the reason optical devices—from cameras to telescopes—deliver sharp, reliable, and precise vision.
Food Processing Industry
Food processing machinery must be sanitary, durable, and efficient. CNC machining plays a critical role in producing food-safe equipment that can withstand constant cleaning, cutting, and packaging operations.
Applications in Food Processing
Cutting Blades: Precision blades for slicing bread, meat, or vegetables.
Molds and Dies: Shapes for cookies, pasta, or chocolate.
Conveyor Systems: Rollers, shafts, and mechanical parts.
Packaging Equipment: Jaws, sealing components, and forming tubes.
Why CNC Matters in Food Industry
Hygiene Standards: CNC machines produce smooth surfaces that resist bacteria.
Durability: Stainless steel and food-grade plastics withstand cleaning chemicals.
Efficiency: CNC machining ensures long-lasting, sharp cutting tools.
Customization: Different foods require tailored molds and tools.
For instance, pasta molds are CNC-machined to precise shapes, ensuring uniform products every time. Similarly, food packaging equipment relies on CNC parts to seal bags and boxes quickly and reliably.
Without CNC machining, food production would be slower, less hygienic, and far less efficient.
Textile Industry
The textile industry uses CNC machining to enhance fabric production, embroidery, and weaving. While often overlooked, CNC contributes to the accuracy and durability of modern textile machinery.
Applications in Textiles
Embroidery Machines: CNC-made components for precision stitching.
Weaving Machines: Loom parts, spindles, and bobbins.
Cutting Tools: Blades for fabric cutting.
Pattern Making: CNC routers for creating complex textile designs.
Why CNC Supports Textiles
Consistency: Ensures smooth production without defects.
Durability: Textile machinery operates continuously—CNC parts extend lifespan.
Customization: Unique textile patterns require precision tools.
Efficiency: CNC reduces downtime with high-quality, long-lasting parts.
For example, loom spindles must spin flawlessly for fabric to weave evenly. CNC machining guarantees this precision, reducing errors and waste in textile manufacturing.
This makes CNC machining an invisible yet essential partner in producing clothes, fabrics, and fashion accessories worldwide.
Entertainment Industry
The entertainment industry thrives on creativity—and CNC machining helps bring imagination to life. From stage sets to movie props, CNC makes complex designs practical and repeatable.
Applications in Entertainment
Props and Models: Weapons, costumes, and replicas for movies.
Stage Sets: CNC-carved panels, frameworks, and scenery pieces.
Musical Instruments: Guitar necks, violin bodies, and drum shells.
Theme Parks: Ride components and decorative structures.
Why CNC Fuels Creativity
Complex Designs: CNC machines cut intricate shapes impossible by hand.
Repeatability: Props and set pieces can be replicated for productions.
Durability: CNC ensures strong, long-lasting parts for repeated use.
Customization: Every creative project demands unique designs.
For example, in Hollywood movies, realistic sci-fi props like weapons or helmets are CNC-machined for precision and durability. Meanwhile, musical instrument makers use CNC to carve wood bodies with consistent sound quality.
CNC machining makes it possible to turn fantasy into reality, supporting creative industries with engineering precision.
Telecommunications Industry
The telecommunications industry relies on CNC machining to create the physical infrastructure for global communication. Whether it’s smartphones, satellites, or antenna towers, CNC ensures durability and precision.
Applications in Telecom
Connectors: Precision-machined plugs and sockets.
Antenna Components: Bases, brackets, and housings.
Enclosures: Protective casings for telecom equipment.
Heat Management: Heat sinks for 5G systems.
Why CNC Matters in Telecom
Precision: Telecom relies on exact fits for high-frequency signals.
Durability: Outdoor antennas must withstand weather extremes.
Customization: Unique installations require custom brackets.
Scalability: CNC supports mass production of standardized parts.
Think of 5G infrastructure—antennas require CNC-machined housings and mounts for flawless performance. Without CNC precision, connectivity would be unreliable.
This makes CNC machining essential in keeping the world connected and communicating.
Research & Development (R&D)
The R&D sector thrives on innovation, and CNC machining is one of its most powerful tools. From concept models to experimental devices, CNC makes ideas tangible.
Applications in R&D
Prototyping: Rapid creation of testable parts.
Testing Equipment: Precision housings and fixtures.
Custom Components: One-off designs for experiments.
Educational Models: Teaching aids in universities and labs.
Why CNC Empowers R&D
Speed: Quickly turns ideas into physical prototypes.
Flexibility: Handles diverse designs and materials.
Accuracy: Provides reliable test results by eliminating part errors.
Innovation: Supports industries in pushing technological boundaries.
For instance, biotech researchers might design a custom instrument for DNA sequencing. CNC machining allows them to prototype and refine this tool without long delays.
In essence, CNC machining is the bridge between imagination and innovation, enabling scientists and engineers to test and perfect their ideas.
Furniture Manufacturing Industry
The furniture industry has embraced CNC machining to meet the growing demand for custom designs, durability, and mass production efficiency. Gone are the days when handcrafted furniture was the only option—today, CNC machines make it possible to achieve both artistry and scalability.
Applications in Furniture
Frameworks: Chairs, tables, and bed frames.
Decorative Elements: Intricate carvings and engravings.
Custom Furniture: Bespoke designs tailored to client needs.
Cabinetry and Panels: Kitchen and office furniture parts.
Why CNC Matters in Furniture
Design Precision: CNC can reproduce detailed carvings consistently.
Customization: Customers can request personalized shapes or patterns.
Material Flexibility: Works with wood, composites, metals, and plastics.
Efficiency: Speeds up mass production while maintaining quality.
For example, a luxury dining table might feature ornate carvings along its edges. CNC machines replicate these intricate designs flawlessly, ensuring every unit looks identical without requiring hundreds of hours of hand labor.
In short, CNC machining combines craftsmanship with technology, allowing the furniture industry to deliver both creativity and efficiency.
Pharmaceutical Industry
In pharmaceuticals, precision and hygiene are essential. CNC machining ensures that the equipment used in drug manufacturing, packaging, and testing meets the industry’s strict safety standards.
Applications in Pharmaceuticals
Production Equipment: Mixers, encapsulation machines, and tablet presses.
Packaging Machinery: Forming dies, sealing jaws, and filling systems.
Laboratory Equipment: Custom tools for experiments and testing.
Why CNC is Vital
Sterile Standards: CNC machining creates smooth, bacteria-resistant surfaces.
Durability: Machines often run 24/7 and need reliable parts.
Precision: Accurate dosing and packaging depend on flawless machinery.
Customization: Unique research projects need specialized components.
For example, pill presses rely on CNC-machined dies that ensure every tablet is identical in shape and dosage. Without this consistency, drug safety could be compromised.
CNC machining plays a hidden but critical role in ensuring safe, effective, and reliable medications reach patients worldwide.
Biotechnology Industry
The biotechnology sector pushes the boundaries of science, often requiring unique, complex, and miniature components. CNC machining is the go-to technology for producing these highly specialized tools.
Applications in Biotechnology
Medical Devices: DNA sequencers, microscopes, and lab instruments.
Research Equipment: Specialized housings and precision parts.
Custom Components: One-off builds for experimental research.
Why CNC Supports Biotech
Micron Accuracy: Essential for micro-scale devices.
Material Compatibility: Works with stainless steel, titanium, and biocompatible plastics.
Rapid Prototyping: Helps researchers test new designs quickly.
Innovation: Enables breakthroughs by providing unique solutions.
For example, a DNA sequencing machine relies on CNC-machined housings to align optical and electronic components with extreme precision. Without CNC, such intricate assemblies would be impossible.
By enabling cutting-edge scientific research, CNC machining is a cornerstone of biotechnology’s rapid progress.
Sporting Goods Industry
The sporting goods sector blends performance with durability, and CNC machining ensures equipment meets those demands. From bicycles to baseball bats, CNC brings consistency and customization to sports gear.
Applications in Sports
Bicycles: Frames, gears, and braking systems.
Golf Clubs: Custom heads and shafts.
Outdoor Gear: Knives, skateboards, and camping tools.
Protective Equipment: Helmets and support structures.
Why CNC Matters in Sports
Performance Precision: Small differences can impact athletic performance.
Customization: Athletes often need gear tailored to their style.
Durability: CNC-machined metals and composites last longer.
Mass Production: CNC ensures identical quality across product lines.
For instance, professional golfers often use CNC-machined custom clubs that match their swing style perfectly. Similarly, high-performance bicycles rely on CNC-machined gears and brake systems for safety and speed.
CNC machining guarantees that sporting goods not only look good but also deliver top-tier performance on the field.
Space Technology Industry
When it comes to space exploration, the stakes couldn’t be higher. A single component failure in space could mean mission failure—or worse. CNC machining ensures parts are built to the most demanding standards on Earth.
Applications in Space
Satellite Parts: Antennas, housings, and brackets.
Rocket Components: Engines, casings, and fuel systems.
Spacecraft Assemblies: Scientific instrument housings, panels, and connectors.
Why CNC is Critical in Space Tech
Ultra-High Precision: Space components must fit perfectly.
Material Durability: CNC machines titanium and alloys that withstand extreme conditions.
Reliability: No room for failure in space missions.
Innovation: CNC enables prototypes for next-gen spacecraft.
For example, rocket engine housings require flawless machining to withstand extreme heat and pressure during launches. CNC machining makes this possible with unmatched consistency.
Simply put, CNC machining is the backbone of space exploration, turning science fiction into scientific reality.
Chemical Processing Industry
The chemical industry requires machinery that can endure corrosive materials and high temperatures. CNC machining delivers parts tough enough to survive these demanding conditions.
Applications in Chemical Processing
Reactors: Precision-machined vessels for chemical reactions.
Pumps and Valves: Parts designed to handle aggressive fluids.
Heat Exchangers: Components that require precise tolerances.
Why CNC is Essential
Corrosion Resistance: CNC machines exotic alloys resistant to chemicals.
Precision: Ensures accurate control of chemical processes.
Durability: Extends equipment lifespan in harsh environments.
Safety: Reduces the risk of leaks or accidents.
For instance, valve components in chemical plants must fit perfectly to prevent leaks of dangerous chemicals. CNC machining guarantees the required precision.
Without CNC machining, chemical plants would struggle to maintain the safety and reliability needed in their operations.
Educational Sector
Even education benefits from CNC machining. Schools, colleges, and training institutes use CNC machines for hands-on learning and research projects.
Applications in Education
Training Machines: CNC equipment for student practice.
Research Tools: Prototyping for university experiments.
Educational Models: Teaching aids and demonstrations.
Why CNC Matters in Education
Skill Development: Prepares students for modern manufacturing.
Innovation: Enables students to experiment with real-world designs.
Accessibility: Affordable CNC machines make learning easier.
Industry-Relevant Training: Creates a skilled future workforce.
For example, engineering students often build robotic prototypes using CNC-machined parts, learning valuable real-world skills.
CNC machining helps education bridge the gap between theory and practical application, empowering the next generation of innovators.
Jewelry Manufacturing Industry
The jewelry sector has been transformed by CNC machining, which allows for intricate, repeatable, and customized designs.
Applications in Jewelry
Custom Pieces: Name pendants, rings, and bracelets.
Intricate Designs: Patterns that were once hand-carved.
Mold Making: CNC-machined molds for mass production.
Why CNC Matters in Jewelry
Precision Detailing: Even the smallest patterns are possible.
Customization: Personalization is easy with CNC design.
Efficiency: Reduces labor costs while boosting production.
Material Flexibility: Works with gold, silver, platinum, and more.
For example, a diamond ring setting must hold gems perfectly in place. CNC machining ensures exact tolerances for both security and style.
Thanks to CNC, jewelry makers can combine creativity and technology, producing stunning, personalized pieces at scale.
Water Treatment Industry
The water treatment sector requires parts that can withstand constant use and exposure to water and chemicals. CNC machining ensures durability and reliability.
Applications in Water Treatment
Pump Components: Shafts, impellers, and housings.
Valve Parts: Control systems for fluid flow.
Filtration Systems: Frames and precision parts for filters.
Why CNC is Crucial
Durability: Handles corrosive and high-pressure conditions.
Precision: Ensures clean and reliable water flow.
Efficiency: Extends the life of treatment equipment.
Safety: Reduces risk of contamination.
For instance, filter housings require CNC machining to exact specifications so that no impurities leak into treated water.
By enabling safe and efficient water treatment, CNC machining plays a vital role in public health.
HVAC Industry
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems rely on CNC machining for reliable, efficient, and customized parts.
Applications in HVAC
Ductwork: CNC-cut panels and fittings.
Fan Blades: Precision-machined for efficiency.
Compressors and Valves: Tight-tolerance parts for performance.
Custom Installations: Unique parts for large-scale systems.
Why CNC Matters in HVAC
Energy Efficiency: CNC machining ensures precision components for optimal airflow.
Customization: Buildings often need tailored HVAC systems.
Durability: CNC-machined parts last longer under continuous use.
Scalability: Enables both small and large-scale manufacturing.
Take fan blades as an example. Even a small imbalance can waste energy. CNC machining ensures blades are perfectly balanced, boosting efficiency and reducing noise.
Thus, CNC machining is central to creating comfortable, energy-efficient indoor environments.
Wrapping Up
From aerospace to jewelry, CNC machining has proven itself as the backbone of modern industry. Its ability to deliver precision, durability, customization, and scalability makes it indispensable across sectors.
As technology advances, with 5-axis machining, automation, and AI integration, CNC machines will only become more powerful. The future promises even faster production, greater customization, and new industries that will rely on CNC in ways we can’t yet imagine.
In short, CNC machining doesn’t just support industries—it drives innovation worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the top 10 applications of CNC machining?
Aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, defense, renewable energy, construction, robotics, sporting goods, and HVAC are among the most common applications. - What materials can be machined with CNC?
CNC machines handle aluminum, steel, titanium, brass, copper, plastics, wood, composites, and even ceramics. - What is CNC machining most commonly used for?
It’s most commonly used for precision manufacturing of metal and plastic parts, from prototypes to mass production. - Why is CNC machining better than traditional machining?
Because CNC offers speed, repeatability, precision, and scalability—all while reducing human error. - What industries benefit most from CNC machining?
While almost every industry benefits, aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics are the top sectors relying heavily on CNC.