Die casting is a highly efficient and precise manufacturing process where molten metal is injected into a steel mold under high pressure. It’s widely used for creating complex metal components that are difficult or expensive to machine by conventional methods. However, the success of any die casting project depends heavily on the quality of the design. A well-thought-out design ensures structural integrity, minimizes defects, reduces cost, and enhances manufacturability.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to die casting design tips, highlighting critical variables that every engineer and designer should consider when developing parts for this process.
Major Considerations for Die Casting Design
Designing an effective die cast part requires balancing multiple factors. Here are the most important considerations:
Material Selection
Die casting can be performed with various alloys, such as:
Aluminum (lightweight, corrosion-resistant)
Zinc (high fluidity, suitable for intricate parts)
Magnesium (lightest structural metal)
Each alloy has different properties like shrinkage, thermal conductivity, and fluidity, all of which affect design decisions such as wall thickness, fillet radii, and cooling requirements.
Die Design
The die must be strong enough to withstand high pressure and temperature without warping. Accurate machining of the die ensures dimensional consistency in every cycle.
Ejection and Cores
Parts should be designed for easy ejection to avoid damage and reduce cycle time. Core designs must also allow easy removal without sticking or distorting the part.
Functionality
Die cast parts used in high-load or critical applications (e.g., automotive, aerospace) require specific reinforcements and tolerances compared to cosmetic or lightweight applications.
Top Design Tips for Die Casting – Key Variables
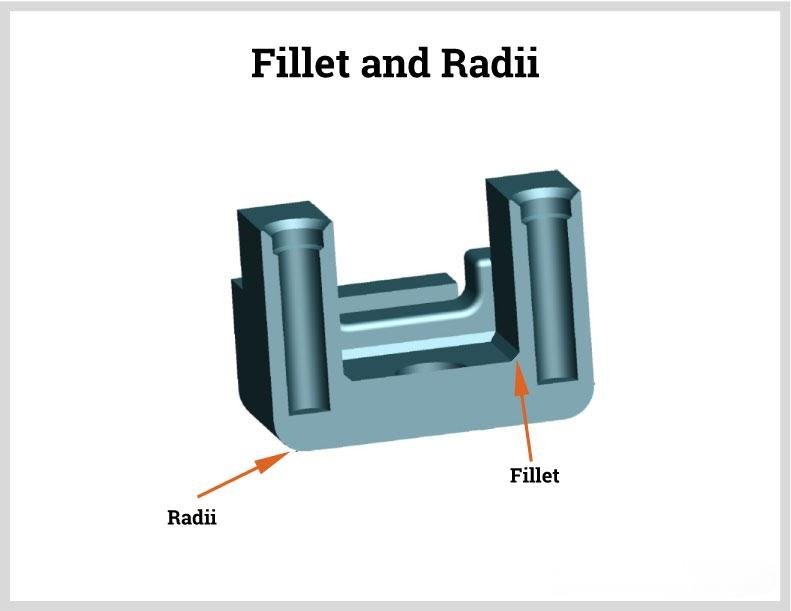
Fillets and Radii
Fillets and radii are crucial to eliminate sharp corners, reduce stress concentrations, and improve metal flow.
Tips:
Avoid sharp internal corners
Use a radius of at least 1 mm (larger in high-stress zones)
Apply consistent radii throughout the design
Incorporate draft angles (typically 1–3°) to aid in part removal
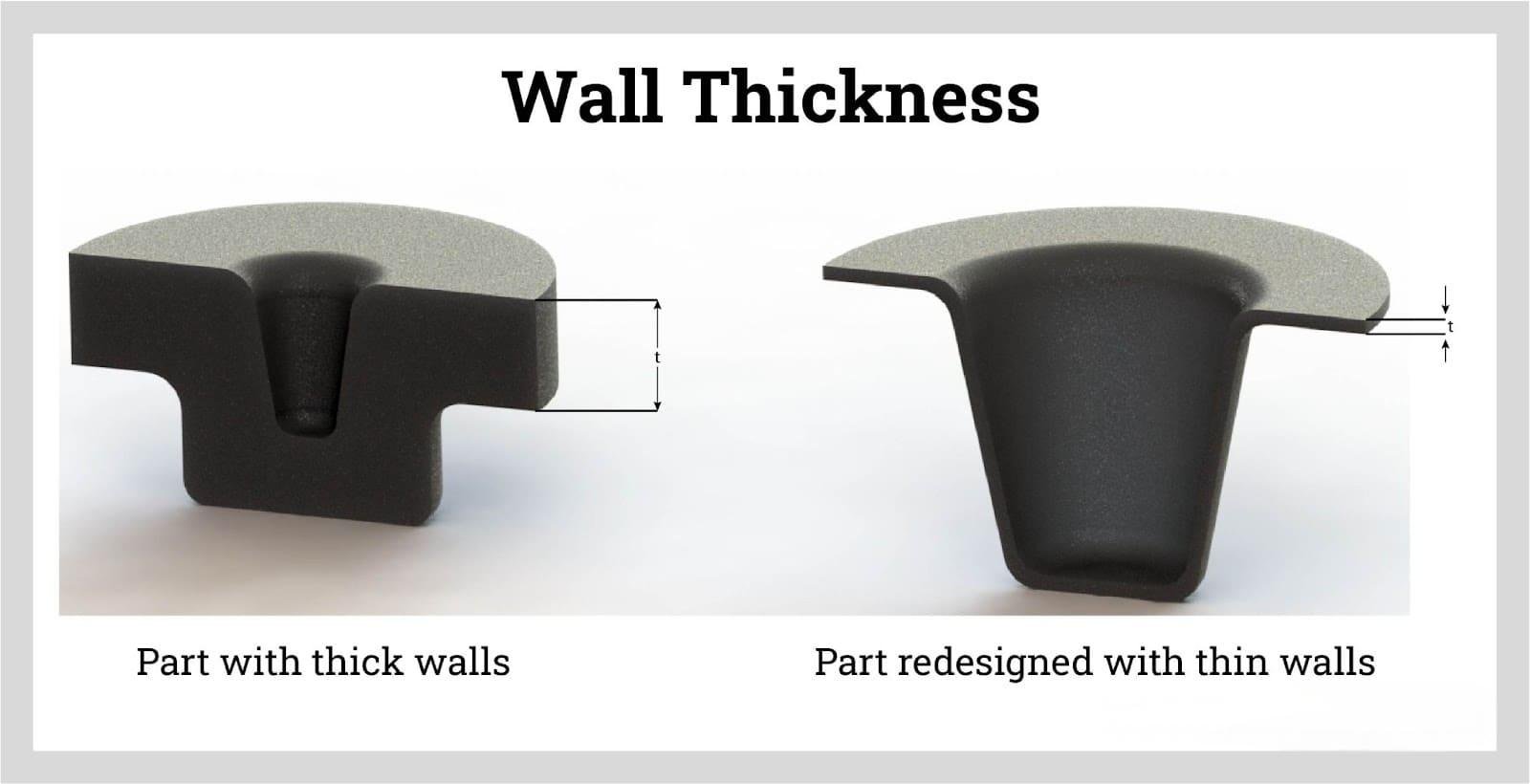
Wall Thickness
Wall thickness affects cooling time, casting pressure, and overall part weight. Maintaining uniform wall thickness prevents issues such as porosity and warping.
Recommended Minimum Wall Thickness:
| Material | Small Parts (mm) | Large Parts (mm) |
| Aluminum | 1.016 | 2.032 |
| Zinc | 0.381 | 0.889 |
| Magnesium | 1.016 | 2.540 |
Avoid abrupt changes in wall thickness to prevent hotspots and shrinkage cavities.
Ribs and External Corners
Ribs are added to strengthen thin walls without significantly increasing weight. External corners need careful attention to avoid stress buildup.
Tips:
Prioritize rib placement on the thinnest sections
Maintain uniform rib spacing
Avoid sharp external corners; use generous radii instead
Rib thickness should be about 50–60% of wall thickness
Windows and Holes
Windows (cutouts) and holes are often required for assembly, airflow, or material savings, but they can weaken a part if not designed properly.
Tips:
Round all edges of holes and cutouts
Keep features away from corners and load-bearing areas
Apply generous draft angles on side-wall holes
Avoid unnecessary post-machining when possible
Post-Machined Features
Some geometries like threads, undercuts, or tight-tolerance bores may need post-machining, which adds time and cost.
Design Guidelines:
Keep post-machining to a minimum
Design features for easy tool access
Use cores to avoid secondary machining where possible
Set realistic tolerances to avoid unnecessary scrap
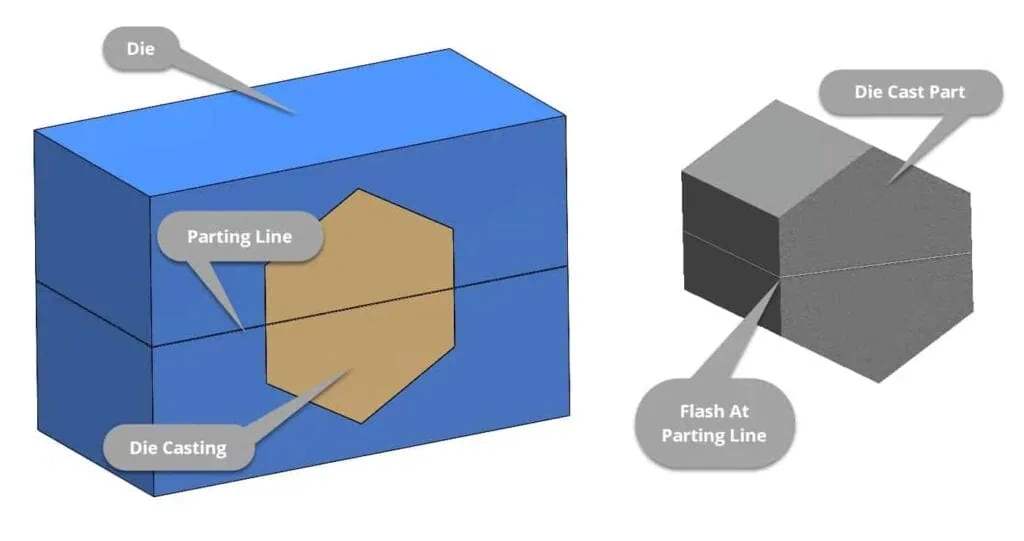
Parting Lines
Parting lines are the visible seams where two die halves meet. Their location impacts both function and appearance.
Tips:
Place parting lines in less visible areas
Avoid placing them on functional surfaces
Expect some flash that must be removed in post-processing
Balance aesthetic requirements with manufacturability
Surface Finishing Grades
Die cast parts have different finishing levels based on their end use. Each grade balances cost, appearance, and functional requirements.
| Grade | Name | Typical Use Case | Finish Quality |
| 1 | Utility Grade | Internal or protected components | ⭐ |
| 2 | Functional Grade | Spot-polished, painted parts | ⭐⭐ |
| 3 | Commercial Grade | Structural and semi-cosmetic use | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 4 | Consumer Grade | Visible surfaces, good appearance | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 5 | Superior Grade | High-end aesthetic or sealing use | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Choose the lowest necessary grade to minimize cost while meeting functional needs.
Die Casting Services by TOPS
At TOPS Precision, we offer high-precision die casting services for aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys. Our team supports you from design to production, offering expert advice on material selection, cost reduction strategies, and optimal manufacturing methods.
How to Get Started:
Send your CAD file to us by email
Receive an instant quote with material and quantity options
Adjust your design online to evaluate cost-saving opportunities
Whether you need prototypes or production-scale parts, TOPS helps you achieve high-quality results with efficient lead times and cost control.
Conclusion
Designing for die casting is both a technical and creative process. By considering the proper wall thickness, fillets, ribs, draft angles, and finishing options, you can drastically improve your part’s performance and reduce manufacturing costs. Remember, the success of a die casting project lies in the details—so use these tips to make your next design smarter and more efficient.
For reliable die casting services, material expertise, and design feedback, TOPS is your trusted partner.
Read More:
Meta Title:
Design Tips for Die Casting: Best Practices for Functional & Cost-Effective Parts
Meta Description:
Explore expert die casting design tips including fillets, wall thickness, ribs, post-machining, and surface finishing. Learn how to optimize your parts with TOPS Precision.
Suggested Keywords:
die casting design tips
aluminum die casting
die casting wall thickness
post-machined features
rib design in die casting
draft angles in casting


2 thoughts on “Design Tips for Die Casting: A Complete Guide for Optimized Parts”