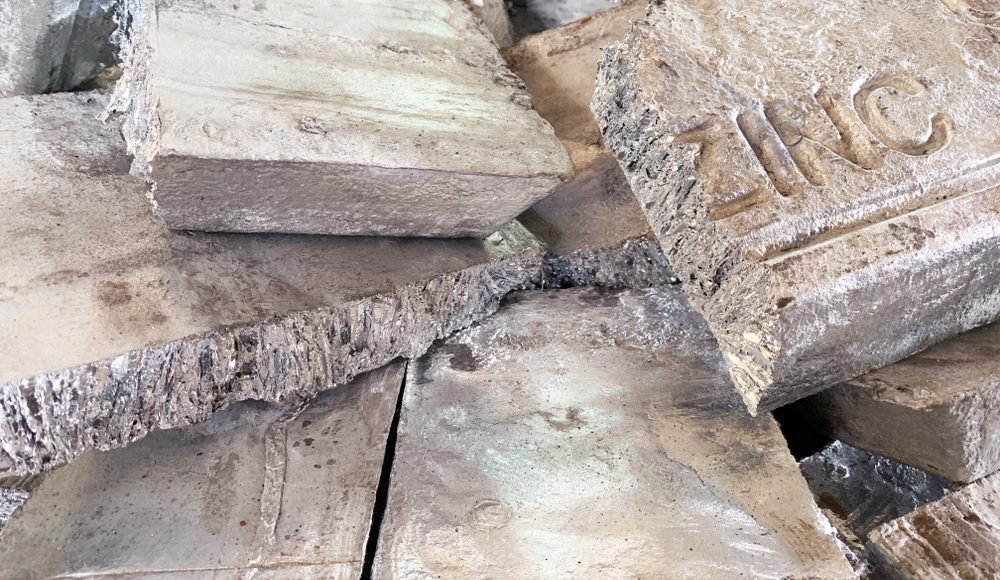
Zinc has been used for centuries in various industries, from construction and automotive manufacturing to consumer goods and electronics. Es conocido por su resistencia a la corrosión., fortaleza, and ability to form alloys that enhance other metals’ properties. But beyond its industrial applications, zinc stands out because of its recyclability.
Unlike many materials that degrade after repeated recycling, zinc maintains its original quality no matter how many times it is recycled. This makes it an excellent candidate for circular economy practices, where waste is minimized, and resources are continually reused. De hecho, zinc recycling contributes significantly to reducing mining activities, conserving energy, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
When we talk about sustainable manufacturing, zinc is at the center of the conversation. It bridges the gap between industrial growth and environmental responsibility. And because industries like die casting depend heavily on zinc, the ability to recycle it without losing performance ensures that businesses can thrive while still supporting global sustainability goals.
Recycling Rate of Zinc

Recycling Rate of Zinc
One of the most remarkable facts about zinc is its high recycling rate. Globally, zinc boasts a recycling rate of 70% a 90%, meaning that out of every 100 tons of zinc used, entre 70 y 90 tons can be recovered and reused. This statistic alone highlights zinc’s vital role in promoting a circular economy.
To put this into perspective, many common materials have significantly lower recycling rates. Plástica, por ejemplo, often have recycling rates below 20%, while even some metals struggle to match zinc’s efficiency. This positions zinc as one of the leaders in sustainable material usage.
The benefits of this high recycling rate extend beyond numbers. Each ton of zinc that is recycled instead of mined saves valuable natural resources, reduces energy consumption, and cuts back on water usage. The energy required to recycle zinc is substantially lower than the energy needed to extract and process new zinc ore. This energy efficiency translates into reduced carbon emissions, making recycled zinc a win-win solution for both industries and the environment.
Además, high recycling rates also create resilience in the supply chain. With fluctuating raw material prices and geopolitical tensions impacting global trade, relying on recycled zinc ensures a more stable and cost-effective supply for manufacturers. This stability is particularly important in industries like automotive manufacturing, construcción, y electrónica, where zinc is a critical component.
Why Zinc is Ideal for Recycling

Why Zinc is Ideal for Recycling
Entonces, what makes zinc stand out among metals when it comes to recycling? The answer lies in its purity and durability. Zinc is a pure metal, and unlike composite materials or plastics that degrade after multiple recycling cycles, zinc retains its full integrity. This means recycled zinc is chemically identical to primary zinc extracted from ore.
In practical terms, this ensures that recycled zinc can be used in the same applications as newly mined zinc. Manufacturers do not have to worry about reduced strength, altered performance, or compromised safety. Whether it’s being used for galvanizing steel, producing alloys, or creating die-cast parts, recycled zinc performs just as well as its primary counterpart.
Another key advantage is that zinc does not accumulate impurities when recycled properly. With modern purification processes, contaminants like lead, níquel, or tin are effectively removed, leaving behind high-quality zinc that meets industrial standards. This makes zinc an endlessly recyclable material, one that aligns perfectly with circular economy principles.
Beyond the technical aspects, zinc recycling also has a cultural and economic dimension. Communities and industries are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, and zinc recycling fits seamlessly into this shift. From large-scale industrial recycling systems to small collection initiatives, zinc’s recyclability ensures it can contribute across all levels of society.
The Zinc Recycling Process
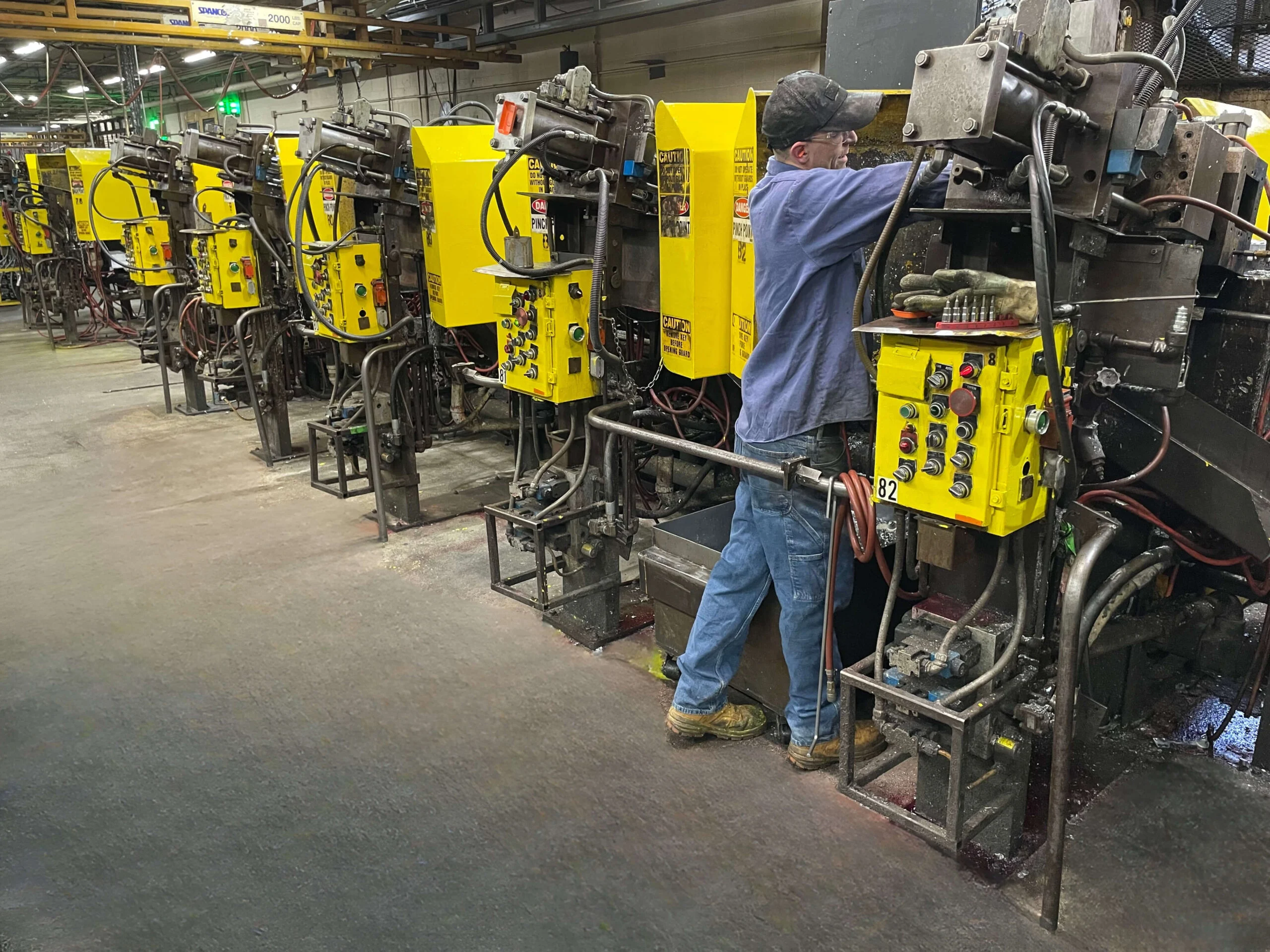

The Zinc Recycling Process
The journey of zinc from discarded material to a valuable industrial resource is a fascinating process. Unlike some complex recycling methods, zinc recycling is relatively straightforward yet highly efficient. It involves several key stages: collection, pretreatment, fusión, and finally, casting into usable forms.
At the heart of this process is the ability to recover zinc from various waste streams. Everything from galvanized steel scrap and die-cast alloys to zinc oxide residues can serve as raw material for recycling. Instead of being treated as waste, these materials are transformed into valuable inputs for manufacturing.
Once collected, the materials undergo pretreatment, a critical stage where impurities are removed. Substances like lead, estaño, and nickel must be eliminated to ensure the recycled zinc meets purity standards. Advanced purification methods make it possible to achieve the same quality as newly mined zinc, ensuring no compromise in performance.
After pretreatment, the cleaned materials are sent to the melting stage. Inside high-temperature furnaces, zinc is melted down to create molten metal. En este punto, the zinc is free of contaminants and ready to be shaped into usable forms.
The final stage is fundición, where molten zinc is transformed into ingots, hojas, or molds depending on the intended application. These products then re-enter the manufacturing cycle, where they can be used in industries like die casting, construcción, or consumer goods.
This closed-loop process not only conserves natural resources but also dramatically reduces environmental impact. It minimizes the need for mining, cuts back on water and energy consumption, and lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
Collection and Sorting
The recycling journey begins with the collection of zinc-containing materials. These can come from both industrial and consumer sources. On the industrial side, scrap from galvanized steel, die-cast zinc aleaciones, and zinc oxide by-products are major contributors. Consumer products like batteries, accesorios de plomería, and old appliances also provide recyclable zinc.
Sorting is an essential step here. Different sources of zinc may contain varying levels of impurities, and separating them correctly ensures efficient recycling later in the process. Por ejemplo, zinc from construction scrap might have different contaminants than zinc recovered from consumer electronics. Proper sorting helps optimize the purification stage, making the entire process more cost-effective and sustainable.
Pretreatment and Purification
Once collected and sorted, zinc materials go through pretreatment. This stage focuses on removing impurities such as lead, níquel, y estaño. If these contaminants are not removed, the final recycled product may not meet industrial standards.
Purification techniques can include chemical treatments, thermal processes, and mechanical separation. Modern technology allows recyclers to achieve extremely high levels of purity, ensuring recycled zinc is indistinguishable from primary zinc.
The pretreatment stage is not just about quality—it’s also about safety. Removing toxic elements prevents harmful substances from re-entering the manufacturing cycle, protecting both workers and the environment.
Melting and Casting
The final stages of zinc recycling involve melting and casting. Pretreated zinc is fed into furnaces where it is melted at high temperatures, transforming it into molten zinc. This molten metal is then shaped according to industry needs.
Manufacturers may cast zinc into ingots, which serve as raw material for future production. Alternativamente, molten zinc can be directly used in fundición a presión, where it is molded into specific shapes for automotive parts, carcasas para electrónica, or decorative items.
These steps showcase zinc’s versatility. Whether destined for construction materials, productos de consumo, or high-tech applications, recycled zinc is ready to meet the demand without compromising performance.
Benefits of Recycled Zinc in Manufacturing
Recycled zinc offers a wide range of advantages for industries. It is not just about reducing environmental impact—it’s also about ensuring calidad, eficiencia, y adaptabilidad in manufacturing processes.
Quality and Performance: Recycled zinc retains the same strength, durabilidad, and structural integrity as primary zinc. This means manufacturers do not have to compromise on product performance when choosing recycled materials. Whether used in die-cast parts, galvanizante, o aleaciones, recycled zinc delivers consistent results.
Rentabilidad: Recycling zinc is more cost-effective than extracting it from ore. The process uses less energy and water, and transportation costs are reduced since recycled zinc is often sourced locally. These savings contribute directly to a lower production cost for manufacturers.
Personalización: Zinc’s versatility makes it ideal for industries that demand precise specifications. Recycled zinc can be shaped and modified to meet the exact requirements of manufacturers, opening up a wide range of design possibilities.
Sostenibilidad: Perhaps the most significant benefit is sustainability. Using recycled zinc reduces the need for mining, lowers carbon emissions, and conserves natural resources. For industries looking to meet environmental targets and corporate social responsibility goals, recycled zinc is a practical and impactful solution.
When these benefits are combined, it becomes clear why recycled zinc is gaining traction across industries. It is not just an environmentally friendly option—it is also a smart business decision.
Environmental Benefits of Recycled Zinc

Environmental Benefits of Recycled Zinc
The environmental impact of using recycled zinc instead of primary zinc is profound. Mining and refining new zinc require massive amounts of energy and resources, not to mention the disruption it causes to ecosystems. By recycling zinc, we reduce the need for mining activities, conserve natural resources, and dramatically cut carbon emissions.
One of the most significant benefits is the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Producing primary zinc from ore involves energy-intensive processes such as mining, crushing, roasting, and smelting. Recycling bypasses most of these steps, leading to much lower energy consumption. Studies have shown that recycling zinc can save up to 75% of the energy needed for primary production, directly lowering CO₂ emissions.
Another environmental advantage is the conservation of water resources. Mining and refining processes consume vast amounts of water for ore processing and cooling. En comparación, zinc recycling requires far less water, reducing pressure on already strained freshwater supplies.
Además, zinc recycling contributes to waste reduction. Instead of zinc-containing products ending up in landfills, where they can pose environmental hazards, recycling ensures these materials are repurposed. Por ejemplo, galvanized steel scrap and old batteries can be converted into valuable zinc for industrial use.
Perhaps most importantly, recycling helps minimize the ecological damage of mining. Extracting zinc ore often involves deforestation, soil erosion, and habitat destruction. By relying more on recycled zinc, industries can reduce the demand for new mining projects, protecting biodiversity and preserving natural landscapes.
Economic Benefits of Recycled Zinc
Beyond environmental gains, zinc recycling delivers strong economic benefits. For businesses, cost efficiency is one of the biggest motivators. Recycling zinc is cheaper than mining and refining primary zinc because it uses significantly less energy, agua, and transportation. Lower production costs translate into competitive pricing, helping companies remain profitable in challenging markets.
Another economic advantage lies in the stability of supply chains. Raw material prices often fluctuate due to geopolitical factors, trade restrictions, or mining constraints. By investing in recycling, industries secure a steady stream of high-quality zinc that is less affected by global uncertainties. This reliability reduces dependence on imports and strengthens local economies.
Zinc recycling also creates job opportunities. The recycling industry requires workers at every stage—from collection and sorting to processing and casting. This generates employment across multiple sectors, from waste management to advanced metallurgy. In regions where traditional mining jobs are declining, recycling offers a sustainable alternative for economic growth.
Además, companies that embrace zinc recycling gain a competitive edge. As governments and consumers demand greener practices, businesses that integrate recycled materials into their operations are better positioned to win contracts, attract customers, and enhance their brand reputation. Many industries now market their use of recycled metals as part of their sustainability credentials, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
Finalmente, there is a long-term financial benefit. As natural resources become scarcer and environmental regulations stricter, the cost of primary zinc production is expected to rise. Companies that invest in recycling infrastructure today will be better shielded from future price hikes, making recycled zinc not just a sustainable choice but also a financially strategic one.
Industrial Applications of Recycled Zinc

Industrial Applications of Recycled Zinc
Recycled zinc is not limited in its applications; En realidad, it is used across a wide range of industries, proving that sustainability and performance can go hand in hand.
Industria automotriz
One of the largest users of recycled zinc is the sector automotriz. Zinc alloys are essential in die casting for parts such as door handles, carburadores, soportes, and precision components. The durability and corrosion resistance of zinc ensure vehicles remain safe and long-lasting. By using recycled zinc, automotive manufacturers reduce production costs while meeting strict environmental regulations.
Industria de la construcción
En construcción, recycled zinc is commonly used for galvanizing steel. Galvanization provides a protective layer that prevents rust and extends the lifespan of steel structures. From bridges and roofing to pipes and guardrails, recycled zinc plays a critical role in modern infrastructure. The benefit here is twofold: not only does recycling conserve natural resources, but it also supports the development of long-lasting, sustainable buildings.
Bienes de consumo
Recycled zinc also finds its way into productos de consumo. Everything from household appliances and plumbing fixtures to electronic housings and decorative items can be made with recycled zinc. Manufacturers value zinc for its ability to be molded into complex shapes without losing strength, making it ideal for high-quality consumer goods.
Electronics and Batteries
The electronics industry uses recycled zinc in batteries and electrical components. With the rising demand for portable devices, vehículos eléctricos, and renewable energy storage systems, the role of zinc in batteries is becoming more important. Recycling zinc ensures a sustainable supply for these fast-growing markets.
These examples highlight zinc’s adaptability and reliability across different industries. Recycled zinc performs just as well as primary zinc, making it a cornerstone of sustainable industrial growth.
Recycled Zinc and the Circular Economy
One of the most compelling aspects of zinc recycling is its role in the economía circular. The circular economy model is based on reducing waste, reusing resources, and designing products with longevity in mind. Zinc fits seamlessly into this framework because it can be recycled indefinitely without losing quality.
In a circular economy, products are not seen as disposable but as part of a continuous loop. For zinc, this means materials like galvanized steel or die-cast parts can be collected at the end of their life, reciclado, and reintroduced into production without degradation. This closed-loop system minimizes waste and maximizes resource efficiency.
Zinc recycling also supports extended product life cycles. Por ejemplo, galvanized steel structures last decades due to zinc’s protective coating, and once they reach the end of their lifespan, the zinc can be recovered and reused again. This ensures that the same material continues to deliver value for generations.
Case studies from around the world illustrate the success of zinc recycling initiatives. En Europa, Por ejemplo, large-scale recycling networks have been established to collect and process zinc-containing scrap. These efforts not only reduce waste but also support local economies by creating jobs and securing a steady supply of recycled materials.
The role of zinc in the circular economy is clear: it is not just a material but a sustainability enabler. By continually cycling through collection, recycling, and reuse, zinc demonstrates how industries can thrive without depleting natural resources.
Future of Zinc Recycling
Looking ahead, the future of zinc recycling is bright, driven by both technological innovation and global sustainability goals.
One key development is the advancement of recycling technology. New methods of purification and recovery are making it possible to extract zinc more efficiently from complex waste streams. Por ejemplo, innovations in hydrometallurgical processes allow recyclers to recover zinc from lower-grade materials that were previously considered unusable.
Governments and organizations are also providing policy and regulatory support. Many countries are implementing stricter recycling targets and offering incentives for businesses that adopt sustainable practices. This regulatory environment encourages investment in zinc recycling infrastructure and ensures long-term growth.
The demand for zinc is also expected to increase globally, particularly in construction, automotor, and energy storage industries. As this demand grows, recycling will play a vital role in meeting it sustainably. Without recycling, the strain on natural resources would be immense, leading to environmental and economic challenges.
Finalmente, the cultural shift toward sustainability-conscious consumers will further accelerate zinc recycling. Buyers are increasingly interested in the origin of the products they purchase, favoring companies that use recycled materials. This trend ensures that businesses embracing recycled zinc will stay competitive in the future market.
Conclusión
Zinc recycling is more than just a manufacturing practice—it is a sustainability strategy that benefits industries, economies, and the environment alike. From its outstanding recycling rate of 70–90% to its ability to retain full strength and performance after countless recycling cycles, zinc proves to be a material uniquely suited for the circular economy.
The environmental benefits are undeniable: reduced greenhouse gas emissions, conservation of water and natural resources, and minimized ecological damage from mining. Al mismo tiempo, the economic gains—cost efficiency, stable supply chains, job creation, and long-term financial security—make recycled zinc a smart investment for businesses across the globe.
Industries ranging from automotive and construction to consumer goods and electronics rely heavily on zinc, and recycling ensures these sectors can continue to grow without depleting the planet’s limited resources. By playing a pivotal role in the circular economy, zinc not only closes the loop but also helps extend product life cycles, Reducir el desperdicio, and inspire innovation in sustainable manufacturing.
Looking to the future, zinc recycling will only become more important. With rising demand for zinc in infrastructure, clean energy, y tecnología, coupled with stronger regulations and consumer awareness, the case for recycled zinc is stronger than ever. It is not simply an option—it is a necessity for building a greener, more resilient, and sustainable world.
Preguntas frecuentes
1. Is recycled zinc as strong as primary zinc?
Sí. Recycled zinc maintains the exact same chemical and physical properties as primary zinc. This means it delivers identical performance in terms of strength, resistencia a la corrosión, y durabilidad, making it suitable for demanding applications like automotive parts, materiales de construcción, y electrónica.
2. What industries use the most recycled zinc?
The construction and automotive industries are the largest users of recycled zinc. En construcción, it is used primarily for galvanizing steel, while in automotive manufacturing, it is widely used in die casting. Además, electrónica, baterias, and consumer goods industries rely heavily on recycled zinc due to its adaptability and strength.
3. How does zinc recycling reduce environmental impact?
Zinc recycling significantly reduces energy and water usage compared to mining new zinc. It cuts greenhouse gas emissions by up to 75% and prevents waste from entering landfills. Lo más importante, it reduces the demand for mining, which often causes deforestation, soil erosion, and biodiversity loss.
4. Can zinc be recycled indefinitely?
Sí, zinc is one of the few metals that can be recycled indefinitely without losing its quality. Because it is a pure metal, its chemical composition remains unchanged throughout recycling cycles. This makes zinc a perfect material for the circular economy.
5. What is the biggest challenge in zinc recycling today?
One of the main challenges is collecting and sorting zinc-containing materials efficiently. Many zinc-containing products, such as small electronics or batteries, often end up in landfills instead of recycling facilities. Improving collection systems, consumer awareness, and recycling infrastructure is essential to maximizing zinc recovery.