Casting de aluminio es uno de los procesos de fabricación más esenciales en el paisaje industrial actual. Combinando las propiedades livianas del aluminio con la precisión del moldeo de alta presión, Esta técnica produce complejo, piezas de alta resistencia de manera eficiente y a escala.
Esta guía proporciona una descripción completa del proceso de fundición de aluminio., incluyendo aleaciones clave, acabados superficiales, Consideraciones de diseño, y aplicaciones en las principales industrias.
Introducción
El aluminio es un peso ligero, metal resistente a la corrosión con alta conductividad térmica y eléctrica. Estas propiedades lo hacen ideal para producir componentes intrincados con tolerancias estrechas a través de la fundición a la matriz. Entre todos los procesos de formación, La fundición de aluminio se destaca por su repetibilidad, precisión dimensional, y rentabilidad, especialmente para la producción de alto volumen.
¿Cuál es el proceso de fundición de aluminio??
Definición
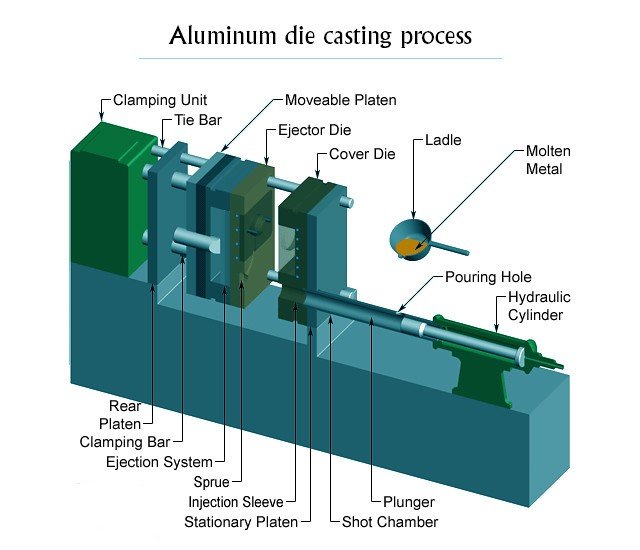
La fundición de aluminio es un método de fabricación de alta presión que inyecta aluminio fundido en un molde de acero (morir) para producir complejo, piezas de metal precisas. Se realiza principalmente usando Máquinas de fundición de la cámara fría Debido al alto punto de fusión del aluminio (~ 660 ° C o 1220 ° F), que dañaría los componentes sumergidos en una máquina de cámara caliente.
Proceso paso a paso:
Derritiendo: Los lingotes de aluminio se derriten en un horno separado.
Tirador: El metal fundido está en la manga de disparo manual o robóticamente en la manga de disparos.
Inyección: Un pistón obliga al aluminio fundido a la cavidad del moho a alta presión (10–175 MPA).
Solidificación: El metal se enfría y se endurece dentro del dado, típicamente en segundos.
Expulsión: El molde se abre y se expulsa la parte, a menudo con pasadores de eyector automatizados.
Recorte y acabado: Exceso de material (destello) se elimina, y se aplica el acabado de superficie opcional.
Die Casting Dies se puede reutilizar miles de veces, Hacer este método ideal para carreras de producción de gran volumen.
Ventajas de la fundición de troqueles de aluminio
El casting de aluminio ofrece varios beneficios técnicos y económicos:
✅ Acabado superficial superior: Superficies suaves que requieren poco o ningún postprocesamiento.
✅ Alta precisión dimensional: Se pueden lograr tolerancias tan apretadas como ± 0.1 mm.
✅ Alta relación resistencia-peso: Las piezas son ligeras y estructuralmente sólidas.
✅ Excelente térmico & Conductividad eléctrica: Ideal para disipadores y recintos de calor.
✅ Porosidad mínima: La ventilación y las actividades avanzadas reducen los vacíos internos.
✅ Flexibilidad de diseño: Admite geometrías complejas y secciones de paredes delgadas (<1.5 milímetros).
✅ Rentabilidad: Moldes reutilizables, tiempos de ciclo rápido, y la automatización reduce el costo por parte.
✅ Sostenibilidad: El aluminio es 100% Reciclable sin pérdida de rendimiento.
Aleaciones de fundición de died de aluminio comunes
Elegir la aleación correcta es crucial para el rendimiento, durabilidad, y castabilidad. Aquí están las calificaciones más utilizadas de fundición a muerte:
| Aleación | Características clave | Aplicaciones |
| A380 | Excelente moldeabilidad, fortaleza, resistencia a la corrosión | Soportes, herramientas eléctricas, recintos electrónicos |
| A390 | Alta dureza, resistencia al desgaste, baja ductilidad | Bloques de cilindro, componentes hidráulicos |
| A360 | Opresión, resistencia a la corrosión superior | 5G CONSEJOS, conchas de controlador |
| A413 | Buena fluidez, opresión | Partes complejas de paredes delgadas |
| ADC-12 | Estándar japonés; Similar a A383 | Componentes automotrices e industriales |
| ADC-1 | Fuerza mejorada, menos contracción | Molduras de alta precisión |
Cada aleación difiere en propiedades mecánicas, comportamiento térmico, maquinabilidad, y resistencia a la corrosión o grietas.
Características clave de las aleaciones de aluminio
Las aleaciones de aluminio fundidas a troqueles ofrecen una poderosa combinación de propiedades mecánicas y funcionales:
Ligero: Reduce la masa general y mejora la eficiencia energética.
Resistente a la corrosión: Forma una capa de óxido natural para proteger de la óxido.
Térmicamente eficiente: Excelente disipación de calor para recintos electrónicos.
Conductivo eléctrico: Ideal para blindaje EMI/RFI.
Fuerza de alta tensión y rendimiento: Confiable para cargas estructurales.
Totalmente reciclable: Ambientalmente sostenible con una degradación mínima.
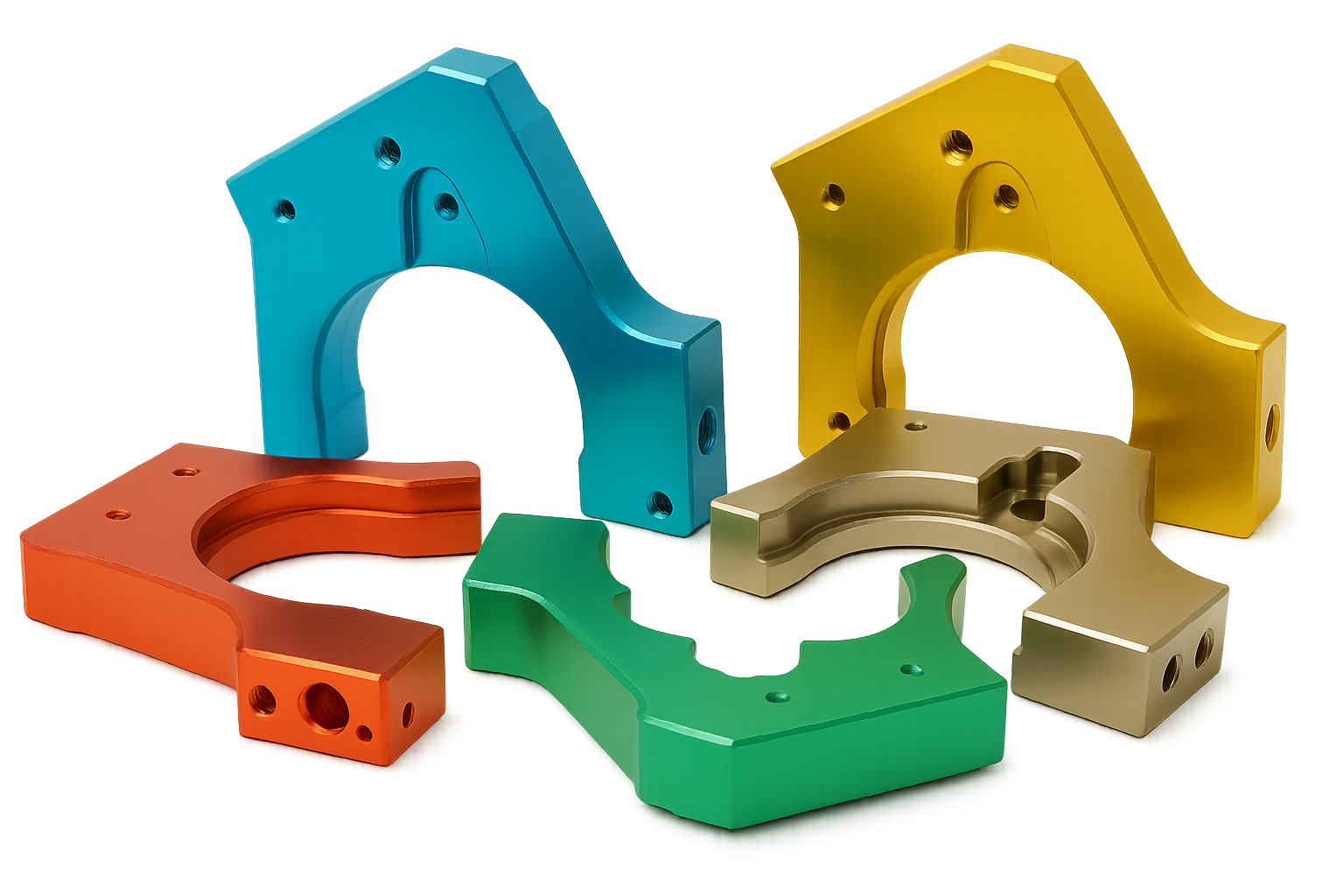
Opciones de acabado de superficie para aluminio fundido
Aunque las fundiciones de aluminio a menudo tienen un acabado suave y liso, Los tratamientos superficiales se aplican para mejorar la apariencia o el rendimiento funcional.
Anodizado
Convierte la superficie en una capa de óxido de aluminio.
Mejora el desgaste y la resistencia a la corrosión.
Eléctricamente no conductor, Bueno para el aislamiento.
Recubrimiento en polvo
Agrega un grueso, vistoso, y capa protectora duradera.
Rascar, ultravioleta, y resistente a la corrosión.
Flexibilidad estética: mate, brillo, o acabados texturizados.
Película química (Recubrimiento de conversión de cromato)
Proporciona resistencia a la corrosión mientras mantiene la conductividad eléctrica.
Ideal para piezas aeroespaciales y de grado militar.
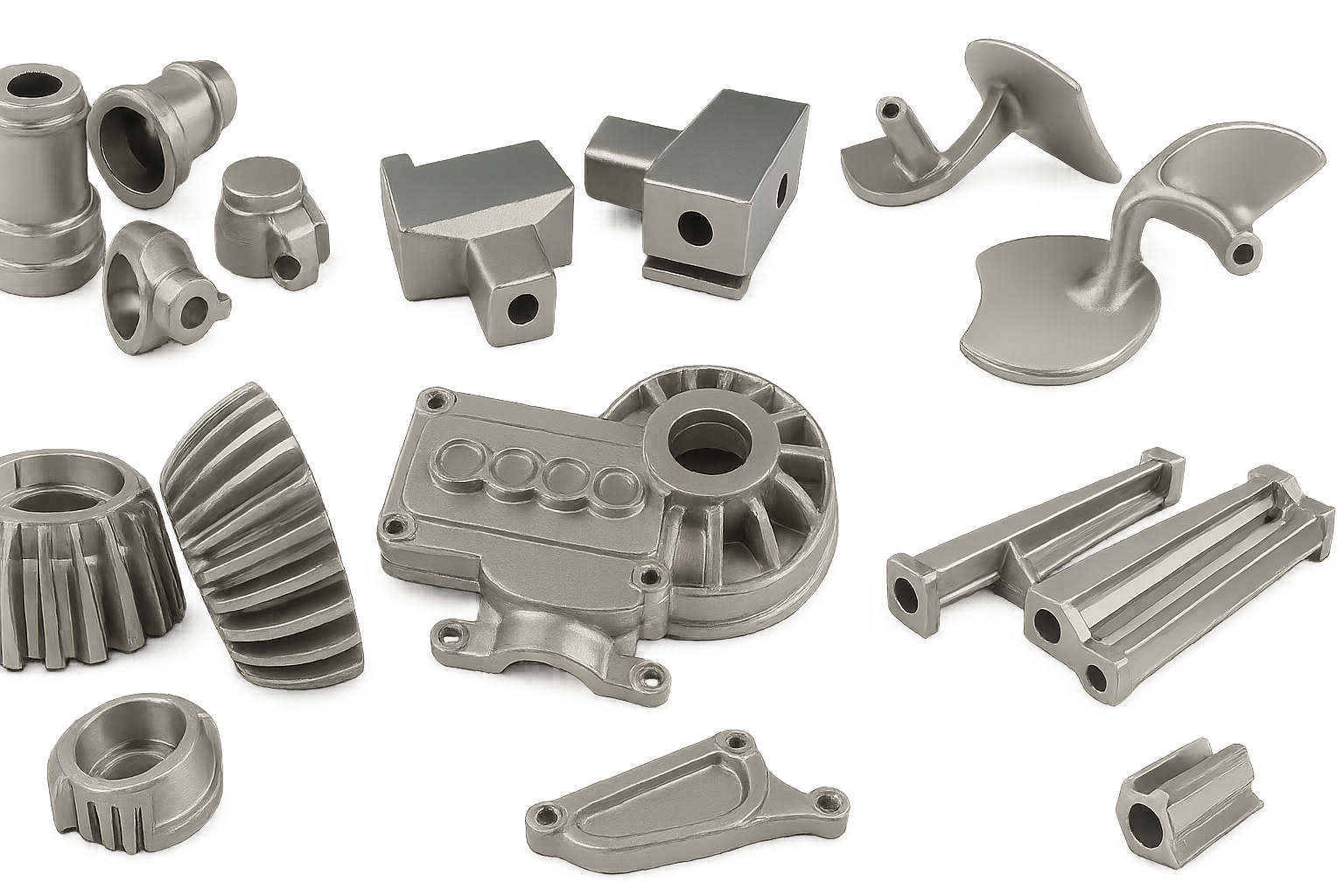
Aplicaciones de fundición a died de aluminio
Construcción
Marcos de ventana, soportes de pared de cortina, estructuras de soporte.
Aumento del uso en puentes y sistemas de construcción modulares.
Automotor
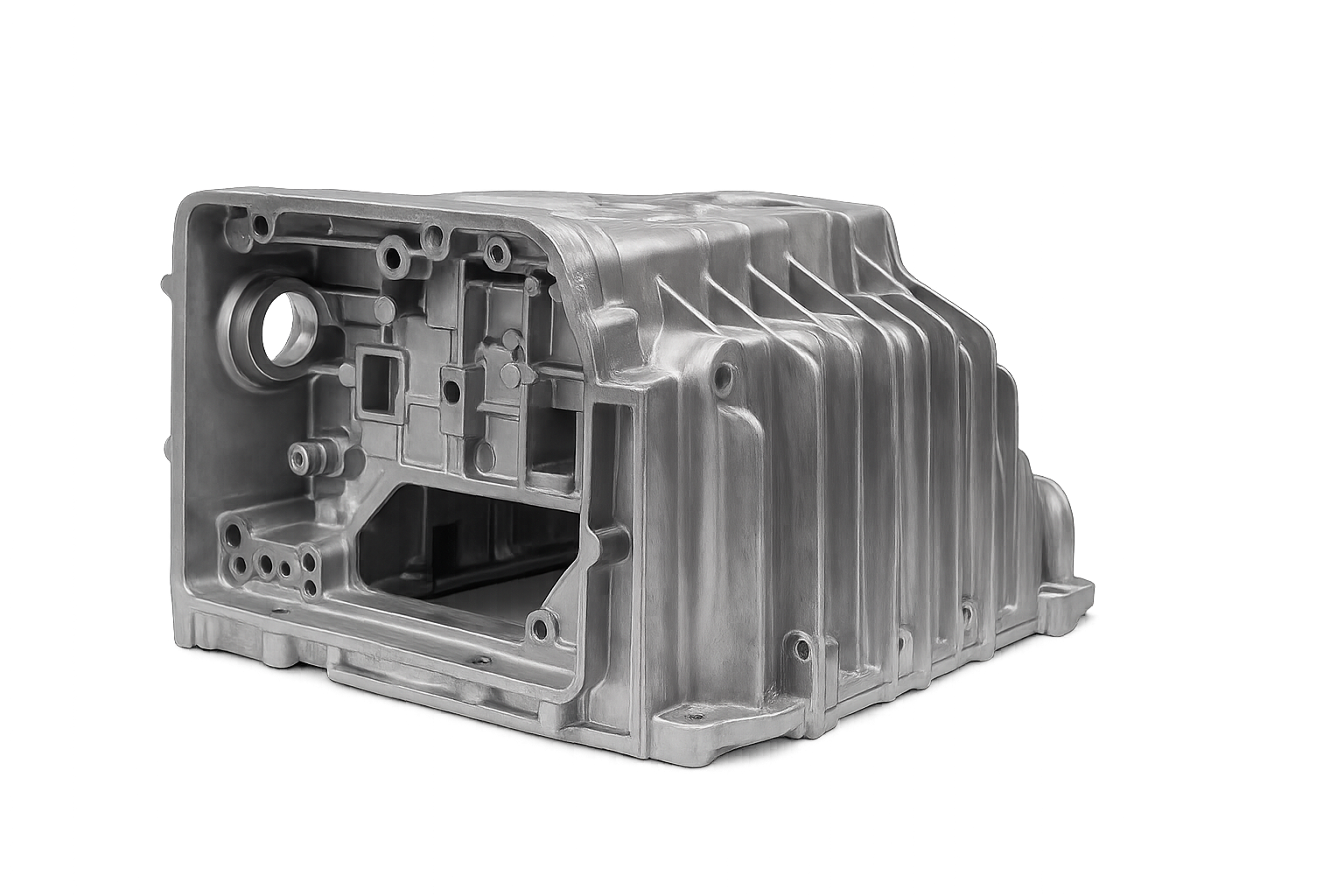
Carcasa de transmisión, bloques de motor, soportes, sartenes.
Ayuda a reducir el peso del vehículo y las emisiones.
Electrónica
Disipadores de calor, recintos, marcos de teléfonos inteligentes, 5G Costas de antena.
Combina la gestión térmica con EMI blindaje.
Muebles
Componentes duraderos pero elegantes como bases de silla, manejas, y cerraduras.
Aeroespacial
Cabezales de pistón, carcasa de equipo, recintos de iluminación, piezas del motor.
Combina bajo peso con alto rendimiento de tracción.
Consideraciones de diseño para piezas de aluminio fundidas
Diseño de moldes
Optimizar el flujo de metal liso y la eyección fácil.
Definir líneas de separación claras y agregar ángulos de borrador.
Punto de inyección
Crítico para reducir el aire atrapado y garantizar el relleno completo.
Es posible que se necesiten múltiples puertas para piezas complejas.
Espesor de la pared
Las paredes más delgadas reducen el peso pero deben mantener la integridad estructural.
Apunte a un grosor de pared uniforme para evitar puntos calientes y deformación.
Factores de costo de fundición de aluminio
La fundición de aluminio es más rentable a escala. Las variables de precios clave incluyen:
Costos de herramientas: Por lo general, $ 7,000– $ 75,000 dependiendo de la complejidad.
Volumen: Los altos volúmenes reducen los costos por unidad debido a la reutilización de moho.
Parte de geometría: Las formas complejas requieren herramientas más intrincadas y tiempos de ciclo más largos.
Material & Tiempo de máquina: Tipo de aleación y parte Duración del ciclo de impacto de masa y costos de material.
Mano de obra: Configuración, guarnición, y el tiempo de inspección contribuye a los costos laborales.
Servicios de fundición de aluminio - Ejemplo de RapidDirect
Ofertas de precisión de Tops:
Tolerancias tan apretadas como ± 0.004 " (0.1 milímetros)
YO ASI 9001:2015 procesos certificados
Comentarios de DFM y citas rápidas de modelos CAD
Prototipos completos para la capacidad de producción en masa
Beneficios:
Hasta 30% ahorro de costes
Acabados y especificaciones personalizados
Control de calidad de extremo a extremo
Conclusión
La fundición de aluminio es una alta precisión, escalable, y método de fabricación rentable. Es particularmente ideal para aplicaciones que requieren componentes livianos pero fuertes con tolerancias ajustadas y acabados limpios. Al trabajar con volúmenes de producción más grandes, Die Casting ofrece un valor inigualable en el rendimiento, velocidad, y repetibilidad.
Si está construyendo componentes automotrices, electrónica, o piezas arquitectónicas, Elegir la aleación correcta, estrategia de diseño, y el socio de servicio puede afectar significativamente el éxito de su proyecto.
Preguntas frecuentes
Q1: ¿Cómo difieren la fundición de aluminio??
Die Casting usa moldes de acero para precisión; La fundición de arena utiliza moldes de arena prescindibles.
La fundición de la matriz tiene una mejor precisión dimensional y acabado superficial, pero un costo de herramientas más alto.
Traje de fundición de arena de bajo volumen, producción de gran parte; El casting de dado sobresale en carreras de alto volumen.
Q2: ¿Es caro de fundición de aluminio??
Las herramientas son costosas por adelantado, pero el proceso se vuelve altamente rentable para lotes grandes.
Q3: ¿Qué tan rápido es el lanzamiento??
Una vez que las herramientas están configuradas, Los tiempos de ciclo van desde 30 segundos a unos pocos minutos por parte.
Artículos relacionados:
Die Casting VS. Mecanizado CNC
Fundición a presión versus fundición a la cera perdida
Aluminio mecanizado versus aluminio fundido





1 pensamiento en “Guía completa para la fundición de died de aluminio: Proceso, Aleaciones, Refinamiento & Aplicaciones”