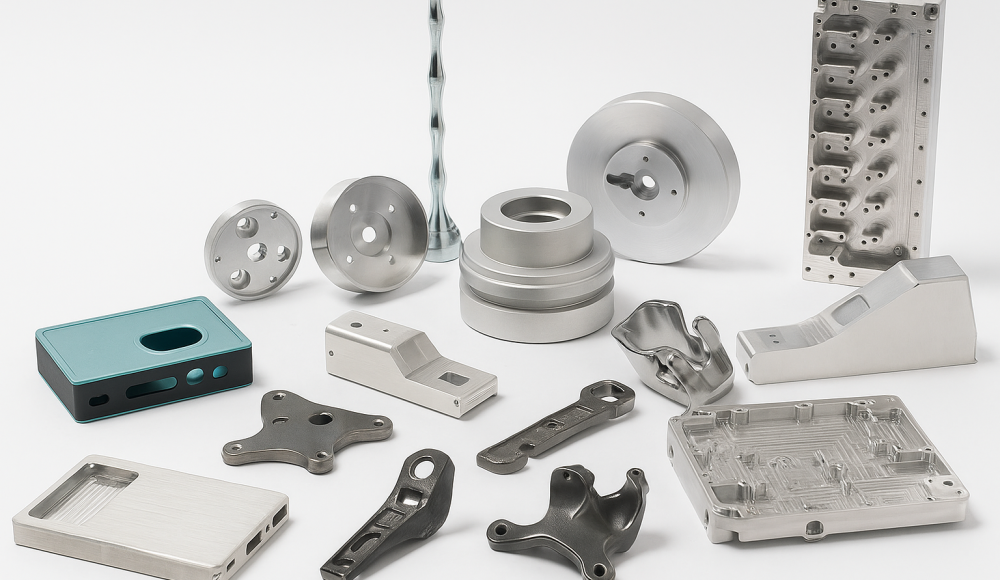
Fundición is a highly efficient metal manufacturing process used to produce precise metal parts with complex geometries. Sin embargo, the die-casting process alone does not always guarantee parts with the desired final surface appearance or properties. Por lo tanto, applying the correct surface finish is critical to achieving functional, estético, and durable fabricated parts.
En este articulo, we’ll deeply explore 13 types of surface finishes commonly used in die casting, highlighting their definitions, beneficios, suitable applications, y consideraciones.
Importance of Choosing the Right Surface Finish
Selecting the appropriate acabado superficial impacts the following critical properties:
Durabilidad: Enhances corrosion resistance and prolongs part lifespan.
Apariencia: Improves visual appeal and market value of components.
Funcionalidad: Ensures suitability for specific applications and conditions.
Choosing an incorrect surface finish can lead to premature part failures, poor aesthetics, increased maintenance, y costos innecesarios.
13 Types of Die Casting Surface Finishes
1. Arenado (Abrasive Blasting)
Sandblasting involves forcibly propelling fine abrasive particles (p.ej., arena, cuentas de vidrio) onto the part surface under high pressure.
Beneficios:
Uniform matte finish
Enhanced adhesion for coatings
Efficient removal of impurities and contaminants
Aplicaciones:
Componentes automotrices e industriales
Parts requiring high adhesion for painting or coating
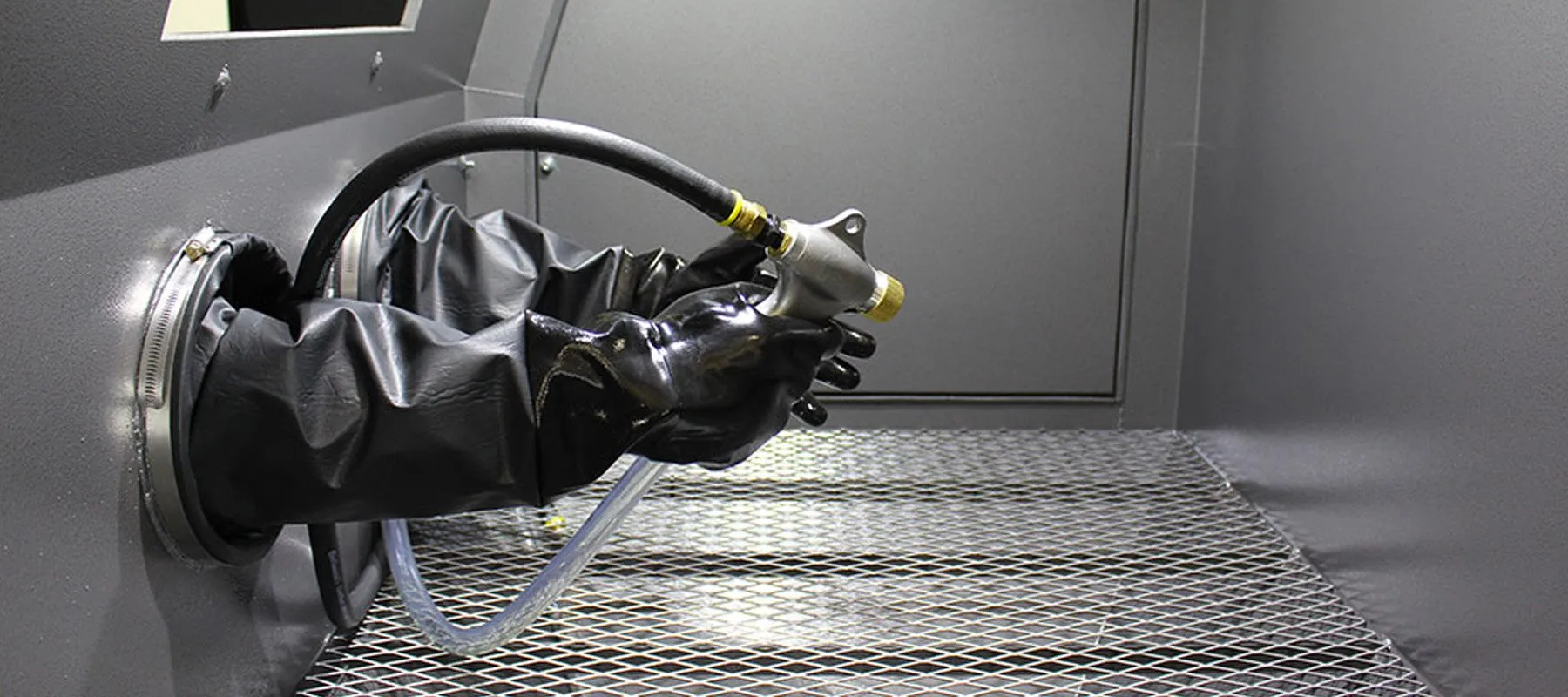
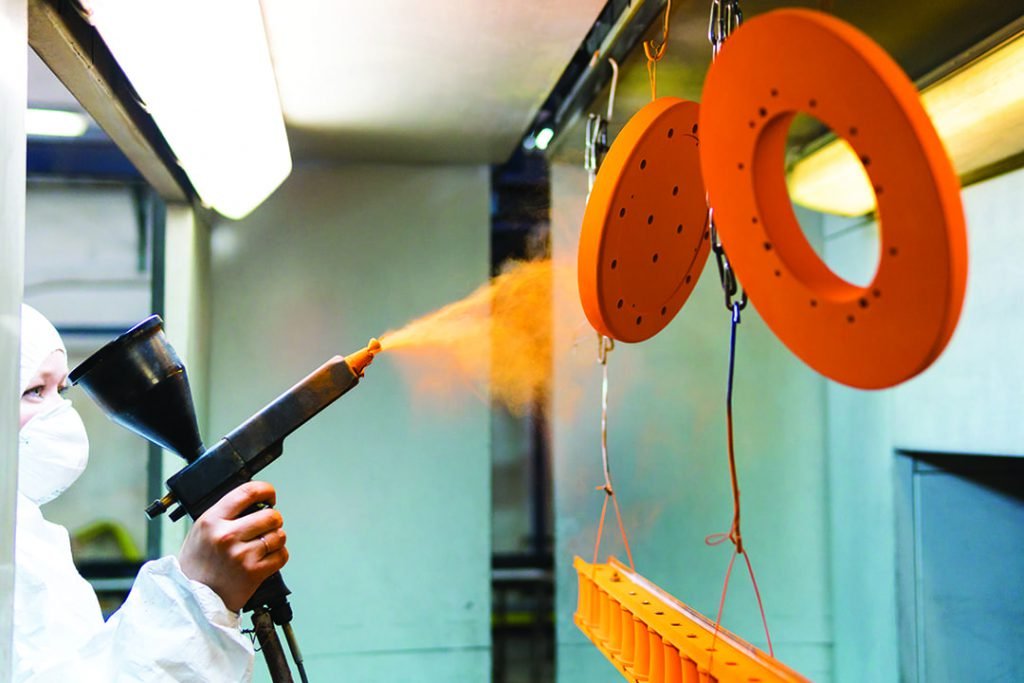
2. Recubrimiento en polvo
Powder coating is a dry finishing process involving applying electrostatically charged powdered pigments, followed by heat curing.
Beneficios:
Excellent corrosion and chemical resistance
Durable and impact-resistant surface
Available in numerous colors and finishes
Aplicaciones:
Automotive wheels and components
Electrodomésticos, trampas de electrónica, outdoor products
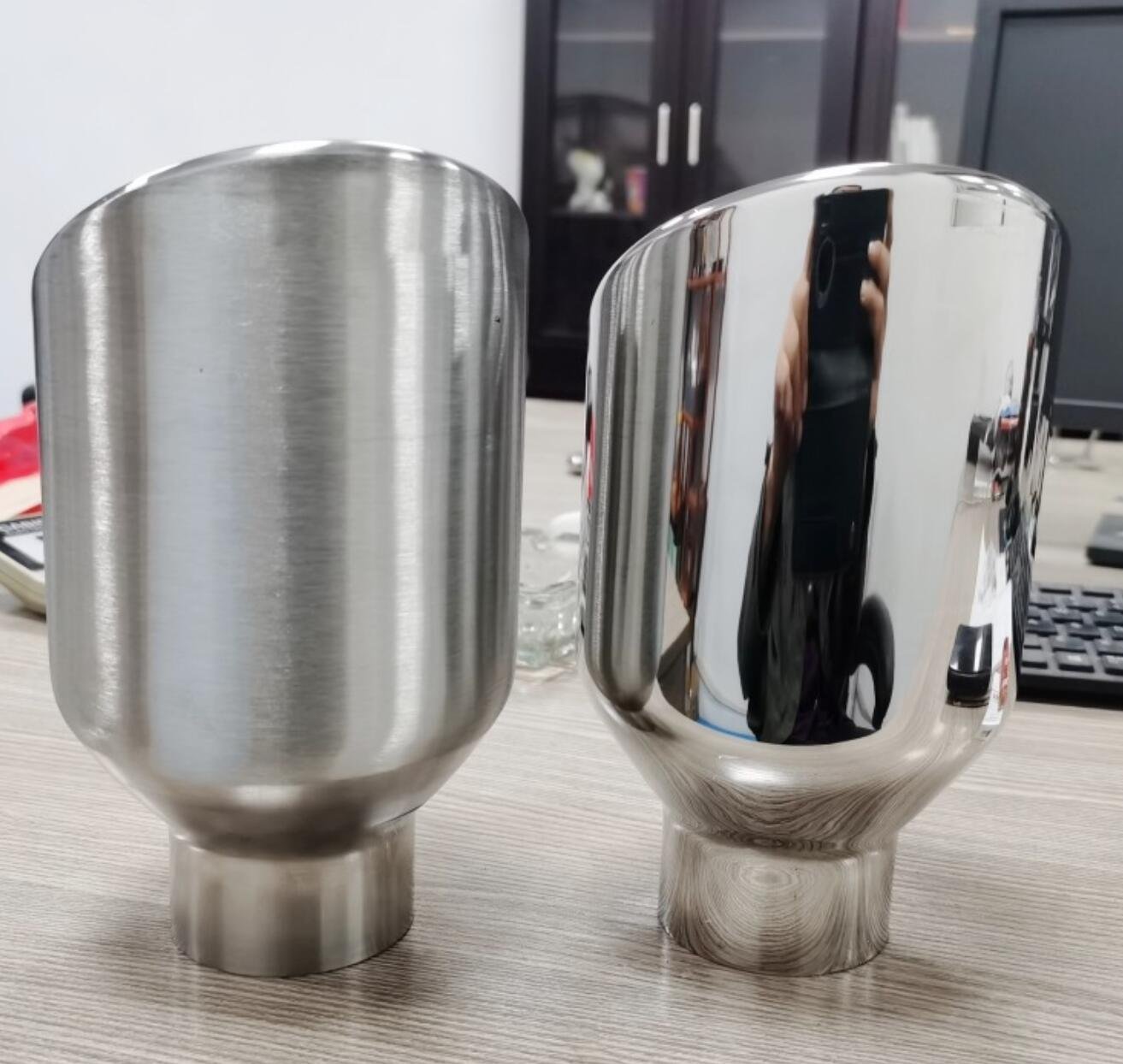
3. Pulido
Polishing removes microscopic imperfections through abrasive buffing, producing a smooth, superficie reflectante.
Beneficios:
Mirror-like, high-quality aesthetic finish
Improved cleanability and reduced friction
Aplicaciones:
Adorno automotriz, joyas, hardware decorativo, equipo medico
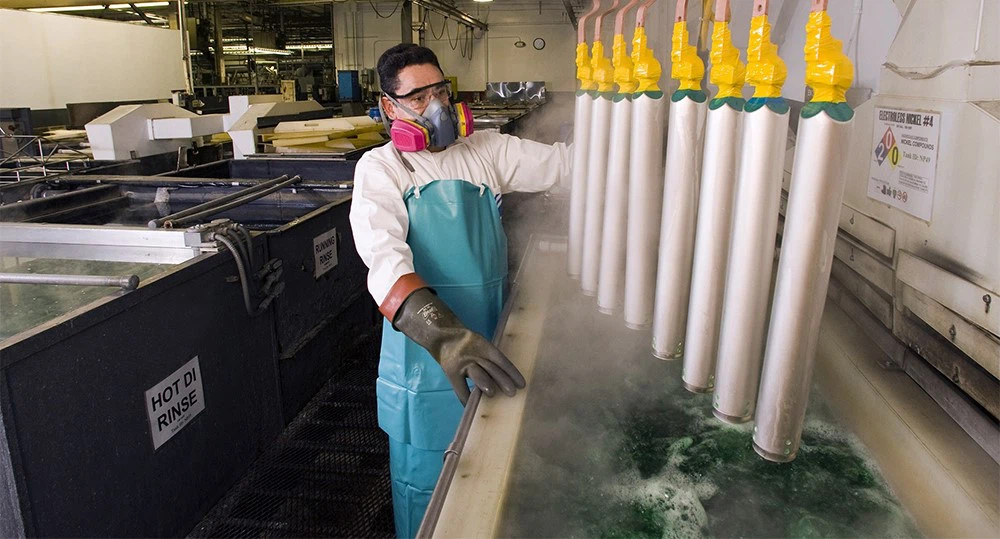
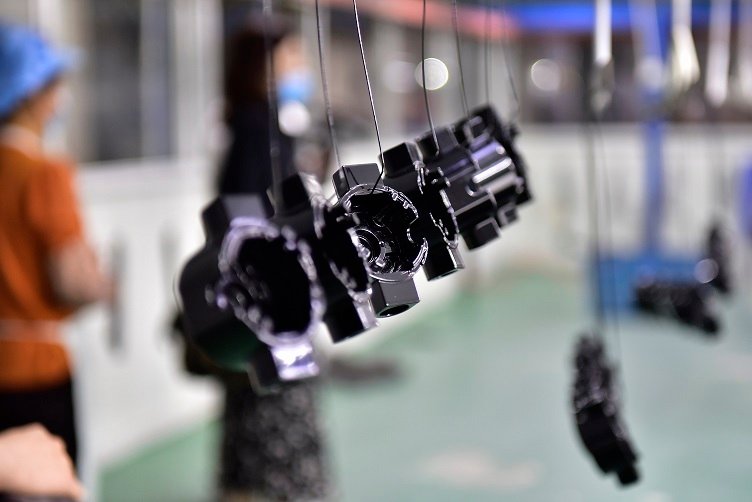
4. Enchapado (galvanoplastia & Enchapado de electrodomésticos)
Plating involves depositing a thin layer of metal (níquel, cromo, oro, etc.) onto die cast parts through chemical or electrolytic means.
Beneficios:
Enhanced corrosion protection and wear resistance
Improved electrical conductivity
Decorativo, high-gloss appearance
Aplicaciones:
Electronic components, piezas automotrices, accesorios decorativos
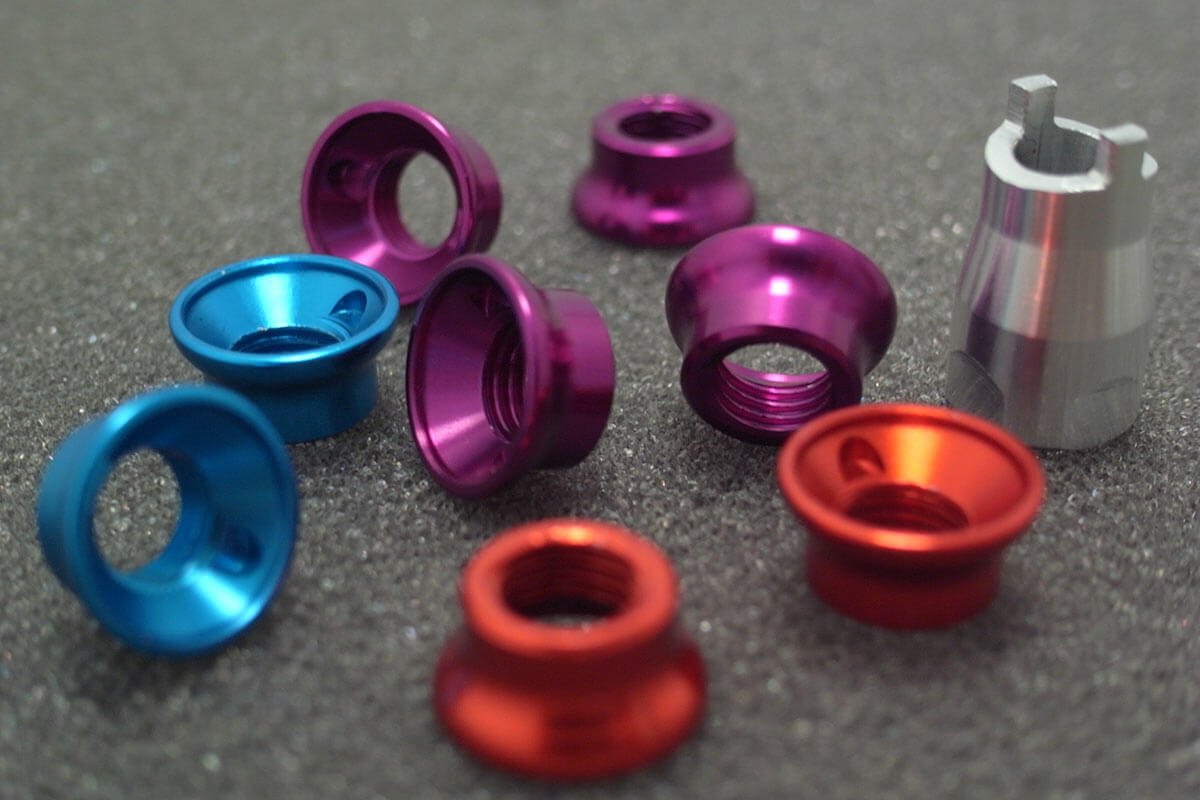
5. Anodizado
Anodizing creates a controlled oxide layer on aluminum alloy surfaces through electrolytic treatment.
Beneficios:
Superior corrosion and wear resistance
Aesthetic appearance with various color options
Increased surface hardness
Aplicaciones:
Architectural fittings, electronics enclosures, productos de consumo
6. Electrophoretic Coating (E-coating)
E-coating utilizes electrical currents to deposit paint or resin onto conductive surfaces uniformly.
Beneficios:
Excellent corrosion protection
Uniform and consistent coating thickness
Good chemical resistance and durability
Aplicaciones:
Automotive chassis components, equipo industrial, maquinaria pesada
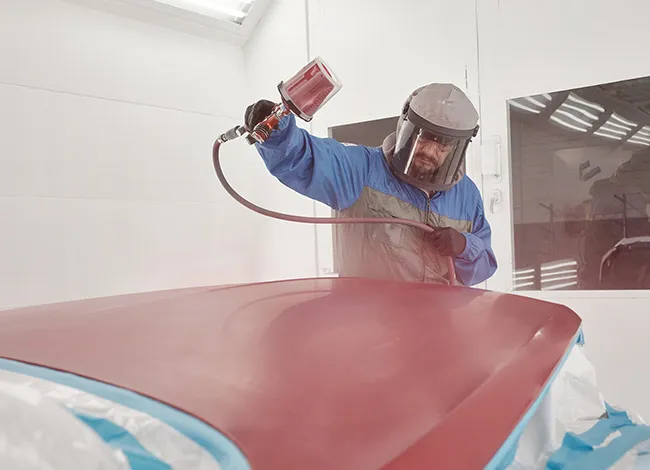
7. Cuadro
Painting involves applying liquid coatings via spray, brush, or dipping techniques to improve aesthetics and protective properties.
Beneficios:
Cost-effective with extensive color options
Easy to repair or update finishes
Aplicaciones:
Productos de consumo, automotive body parts, accesorios, muebles
8. Vibratory Deburring
This process removes burrs and sharp edges using vibrating equipment with abrasive media.
Beneficios:
Efficient deburring without manual labor
Consistent and uniform surface finish
Improved safety and handling
Aplicaciones:
Small to medium die-cast automotive parts, engranajes, sujetadores, conectores
9. Parkerizing (Fosfante)
Parkerizing involves chemically coating steel parts with phosphate solutions to create a robust corrosion-resistant layer.
Beneficios:
Cost-effective corrosion protection
Improved adhesion for subsequent coatings or paints
Durable matte-black finish
Aplicaciones:
Armas de fuego, automotive suspension components, heavy-duty industrial equipment
10. Niquelado no electrolítico
Electroless nickel plating deposits nickel-phosphorus alloy layers chemically, without external electricity.
Beneficios:
Uniform thickness distribution, even on complex shapes
Excellent wear and corrosion resistance
Increased hardness and lubricity
Aplicaciones:
Componentes aeroespaciales, industrial valves, precision automotive parts
11. Impregnation
Impregnation involves sealing microscopic porosities in die-cast parts using vacuum-assisted polymer sealants.
Beneficios:
Enhanced leak-proof properties for high-pressure components
Improved structural integrity and longevity
Reduced porosity-related defects
Aplicaciones:
Hydraulic pumps, bloques de motor para automóviles, fluid containment components
12. Deposición de vapor físico (PVD)
PVD is an advanced vacuum-based coating method vaporizing metals or ceramics onto substrates, forming ultra-thin and highly durable coatings.
Beneficios:
Superior wear and scratch resistance
Excellent aesthetic finish with various colors
High hardness and chemical resistance
Aplicaciones:
Luxury automotive parts, herramientas de corte, accesorios decorativos, instrumentos medicos
13. Pasivación
Passivation chemically enhances stainless steel’s inherent corrosion resistance by removing surface iron contaminants.
Beneficios:
Improved natural corrosion resistance
Cleaner and smoother stainless steel surface
Safer for applications in hygienic environments
Aplicaciones:
Equipos de procesamiento de alimentos, dispositivos médicos, pharmaceutical machinery
Factors Influencing Die Casting Surface Finish
Several key factors influence the outcome of die casting surface finishes:
tipo de material: Specific finishes are best suited to particular alloys or metals.
Die and Mold Quality: High-quality molds ensure consistent and smooth surfaces.
Casting Parameters: Control de temperatura, injection pressure, and cooling rates directly affect surface quality.
Post-processing Methods: Proper selection and execution determine the final surface characteristics.
How to Improve Die Cast Surface Finish
Improving surface finishes involves:
Mantenimiento del moho: Regularly clean and maintain molds to avoid imperfections.
Controlled Casting Conditions: Optimize temperature and injection parameters.
Use Appropriate Post-processing Techniques: Arenado, pulido, anodizado, and others as required.
Design Optimization: Design parts to reduce complexity and minimize surface imperfections.
Conclusión
Clearly understanding the variety of available surface finishing methods is crucial in achieving die-cast parts with optimal aesthetics, durabilidad, and functional performance. Selecting the appropriate finish according to the application requirements will significantly enhance product quality and customer satisfaction.
Consulting with professional die-casting specialists further ensures you select the ideal finishing processes tailored to your specific manufacturing needs.
Preguntas frecuentes
Q1: What is a Die Casting Surface Finish Chart?
A reference tool showing different finishes, their characteristics, materiales adecuados, y aplicaciones, assisting manufacturers in selection.
Q2: What is Typical Surface Roughness in Die Casting?
Roughness typically ranges from 1 a 5 µm depending on alloy, casting methods, and chosen finishes.
Q3: Does Die Casting Naturally Produce Good Surface Finishes?
Die casting alone provides decent surface quality, but post-processing finishes typically are needed to achieve enhanced aesthetics and functional properties.
Q4: How Can Surface Finish Be Improved in Die Casting?
By optimizing mold designs, controlling casting processes, and employing post-processing methods like polishing, enchapado, o revestimiento.
Q5: What Factors Affect Die Cast Surface Finish Quality?
Tipo de material, mold temperature, die design, casting process controls, and chosen surface treatments.