Los plásticos son materiales integrales utilizados en numerosas industrias, ofreciendo versatilidad, durabilidad, y rentabilidad. La fabricación de plástico implica transformar materiales plásticos crudos en componentes útiles o productos terminados a través de varios métodos. Comprender estas técnicas, sus aplicaciones, y los criterios de selección apropiados son cruciales para los diseñadores, ingenieros, y fabricantes. Esta guía completa cubrirá los métodos de fabricación de plástico más utilizados., materiales, y factores para la selección de métodos.
¿Qué es la fabricación de plástico??
La fabricación de plástico abarca técnicas utilizadas para dar forma, moho, o manipular materiales plásticos crudos, ya sea termoplásticos o termoestables, en productos terminados. Los termoplásticos se pueden derretir y remodelar repetidamente, Mientras que las termosets se establecen permanentemente después de la formación inicial.
Los procesos de fabricación de plástico generalmente implican calentamiento, moldura, organización, mecanizado, o ensamblar materiales plásticos crudos en geometrías definidas. Las técnicas de fabricación comunes incluyen moldeo por inyección, colocación de aspiradoras, extrusión, Mecanizado CNC, y fabricación aditiva (3impresión D).
Métodos clave de fabricación de plástico
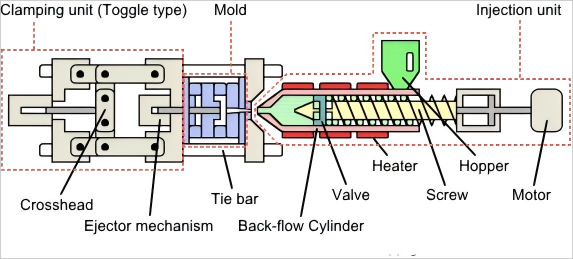
Moldeo por inyección
Qué es?
El plástico fundido se ve forzado a un molde, enfriado, y luego sale como una parte terminada.
Cuando usar:
Ideal para producir muchas partes idénticas rápidamente, como los bloques de Lego, tazas de plástico, y paneles de autos.
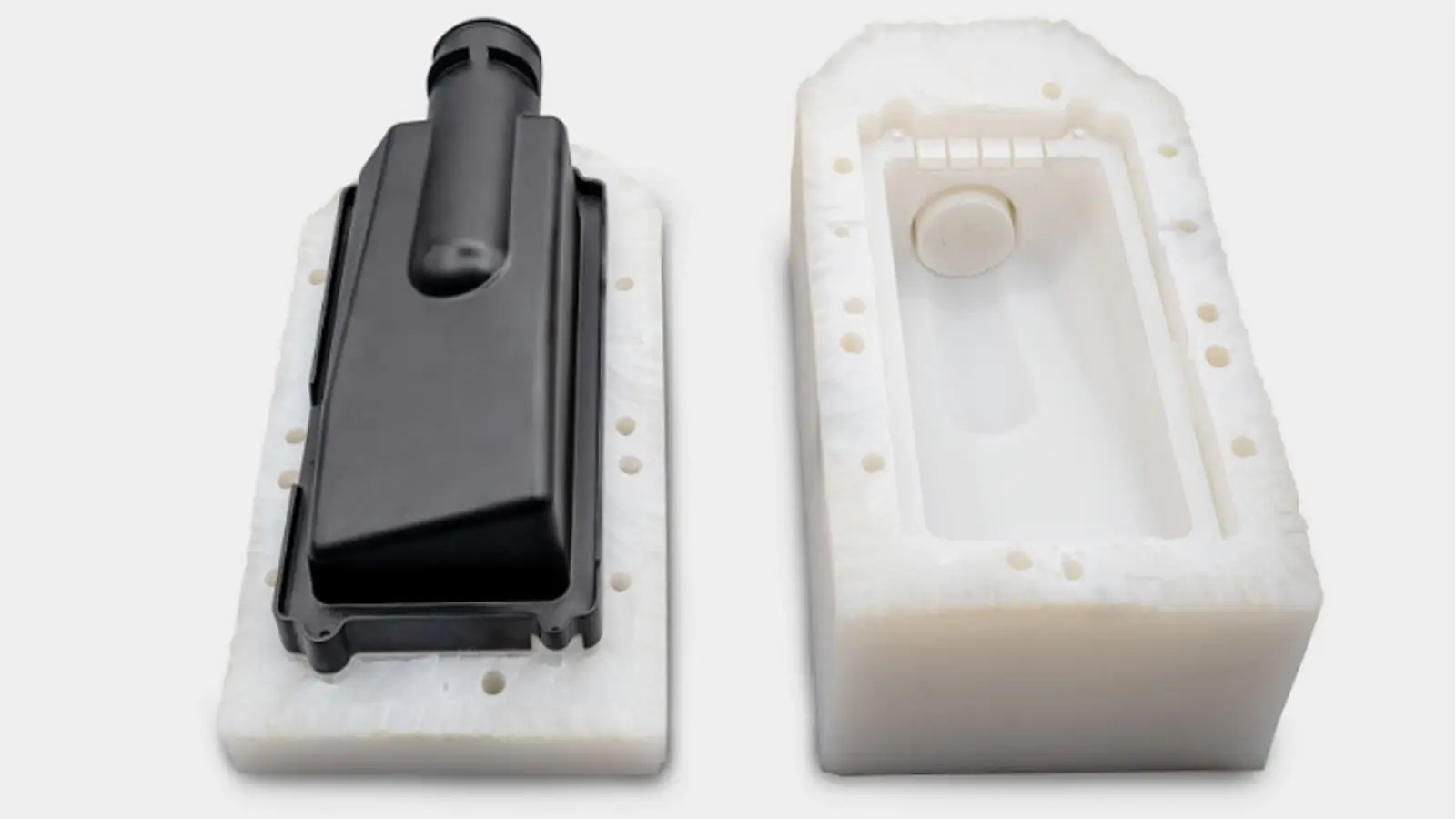
Colocación de aspiradoras
Qué es?
El plástico líquido se vierte en un molde de silicona dentro de una cámara de vacío, Creación de copias detalladas.
Cuando usar:
Ideal para hacer pequeños lotes de prototipos, diseños especialmente transparentes o intrincados como cajas de exhibiciones o electrónica pequeña.
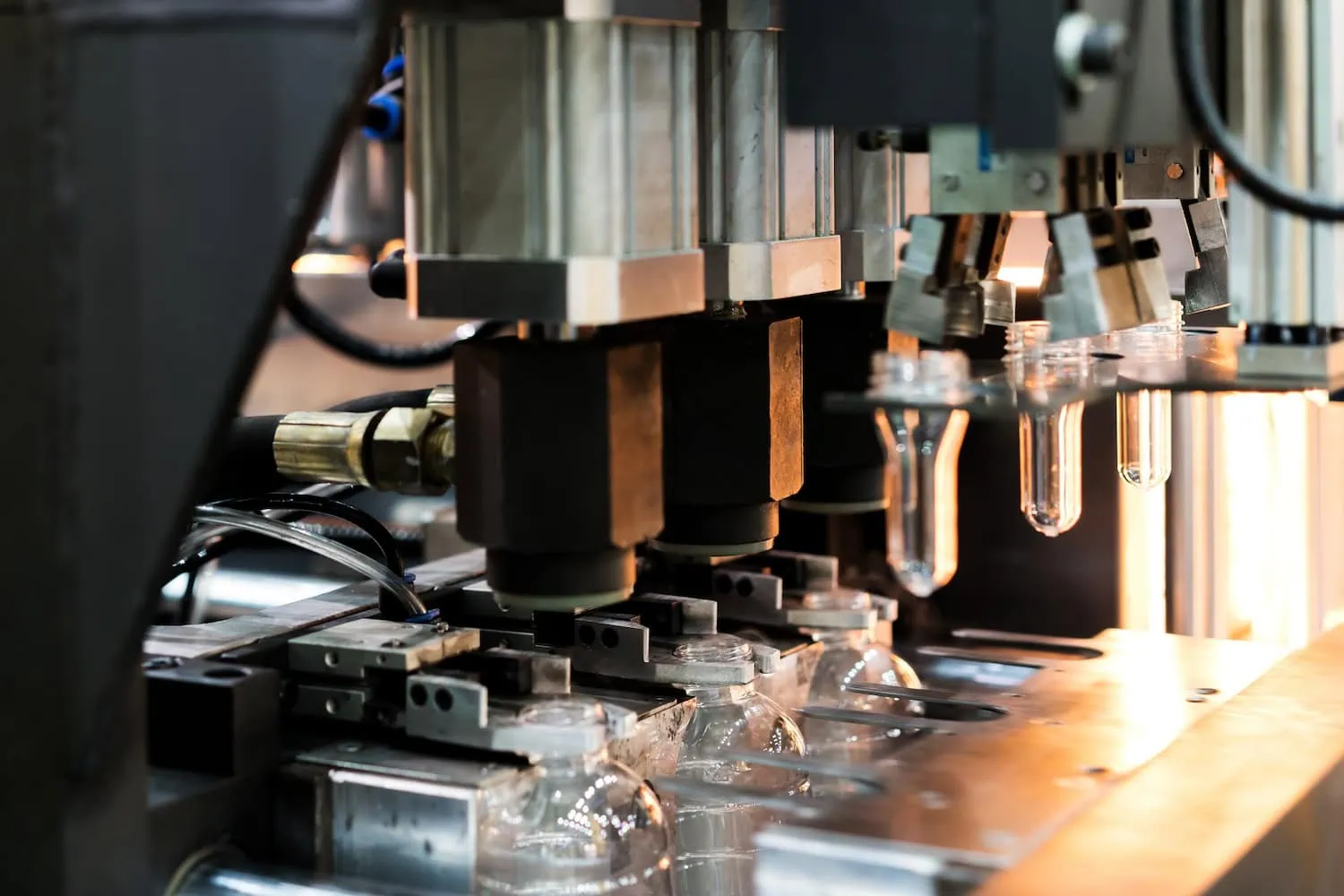
Moldeo por soplado
Qué es?
Un tubo de plástico caliente (parison) está inflado dentro de un molde para crear formas huecas.
Cuando usar:
Perfecto para hacer botellas, contenedores, tanques de combustible, y otros objetos huecos.
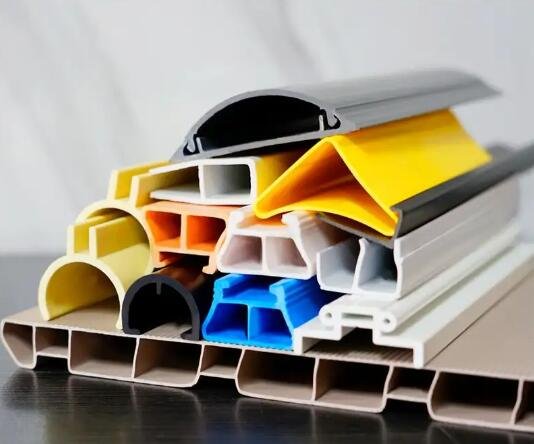
Extrusión de plástico
Qué es?
El plástico caliente se empuja a través de una abertura en forma (morir) Para crear mucho, formas continuas.
Cuando usar:
Utilizado para tubos, tubería, marcos de ventanas, y otras partes con una sección transversal consistente.
Pultrusión de plástico
Qué es?
El plástico reforzado con fibras se tira a través de un baño de resina y un dado calentado, fortaleciendo, Perfiles livianos.
Cuando usar:
Ideal para soportes estructurales, varillas de refuerzo, y piezas livianas duraderas como postes de esquí.
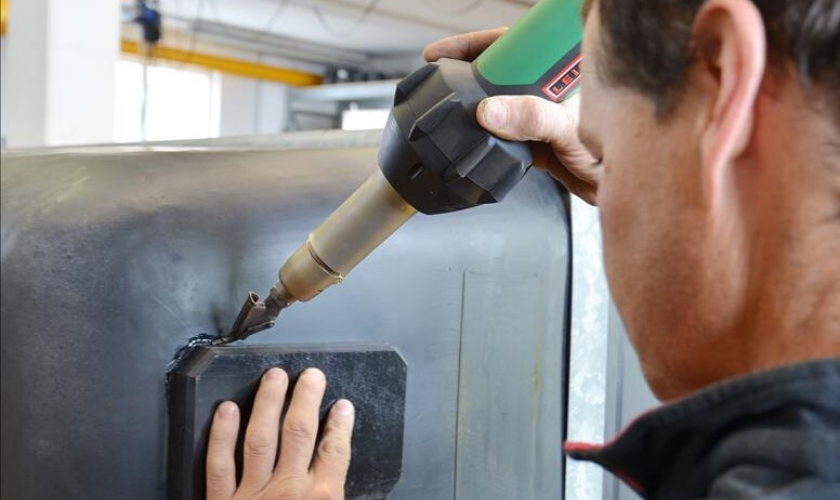
Soldadura de plástico
Qué es?
Unir piezas de plástico con calor y presión, Similar a la soldadura de metal pero con plásticos.
Cuando usar:
Útil para ensamblar formas complejas o reparar artículos de plástico como parachoques de automóviles y recintos electrónicos.
Moldeo rotacional (Moldeo)
Qué es?
El polvo de plástico dentro de un molde se gira y se calienta, recubrir el molde para crear hueco, Partes de espesor uniforme.
Cuando usar:
Genial para grande, productos duraderos como tanques, equipo de juegos, contenedor de almacenamiento, y juguetes.
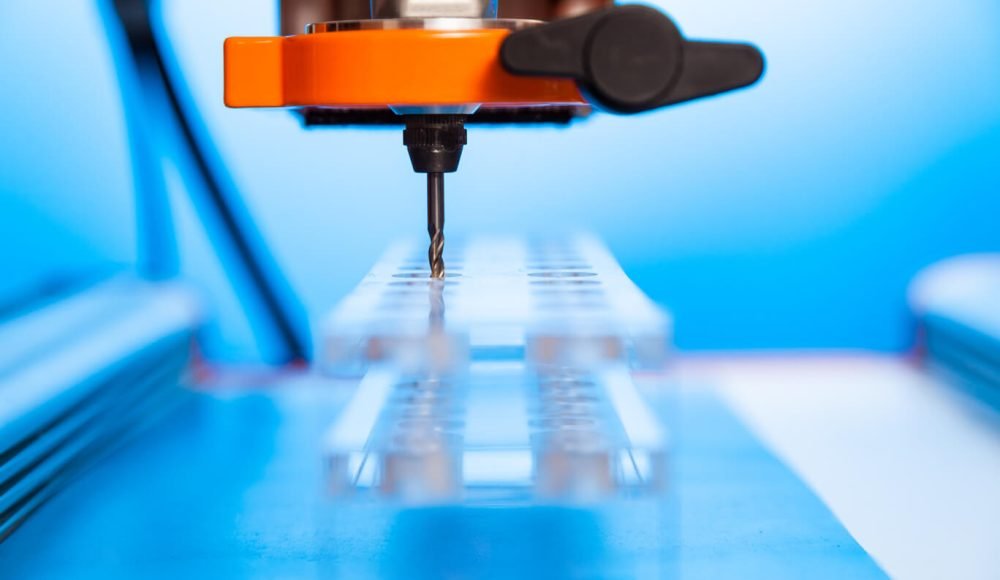
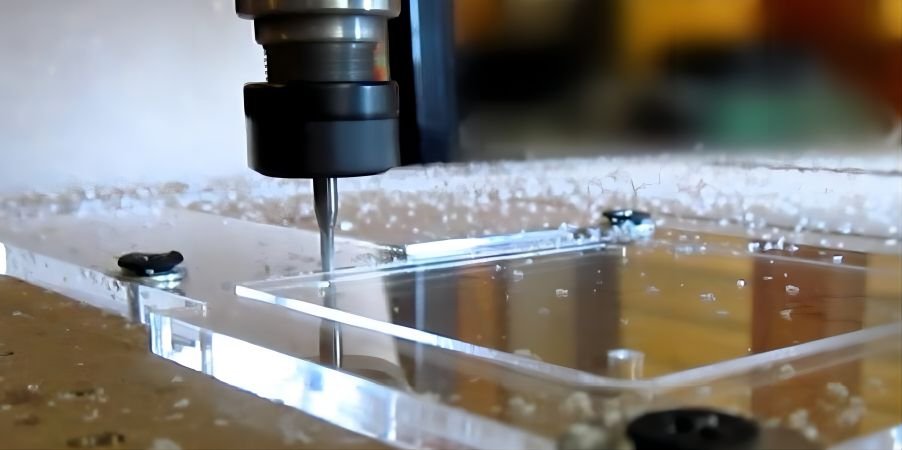
Mecanizado de CNC de plástico
Qué es?
Cortar y configurar bloques de plástico sólidos con herramientas de corte controladas por computadora.
Cuando usar:
Excelente para piezas o prototipos altamente precisos con detalles complejos, como equipos médicos personalizados o piezas automotrices especializadas..
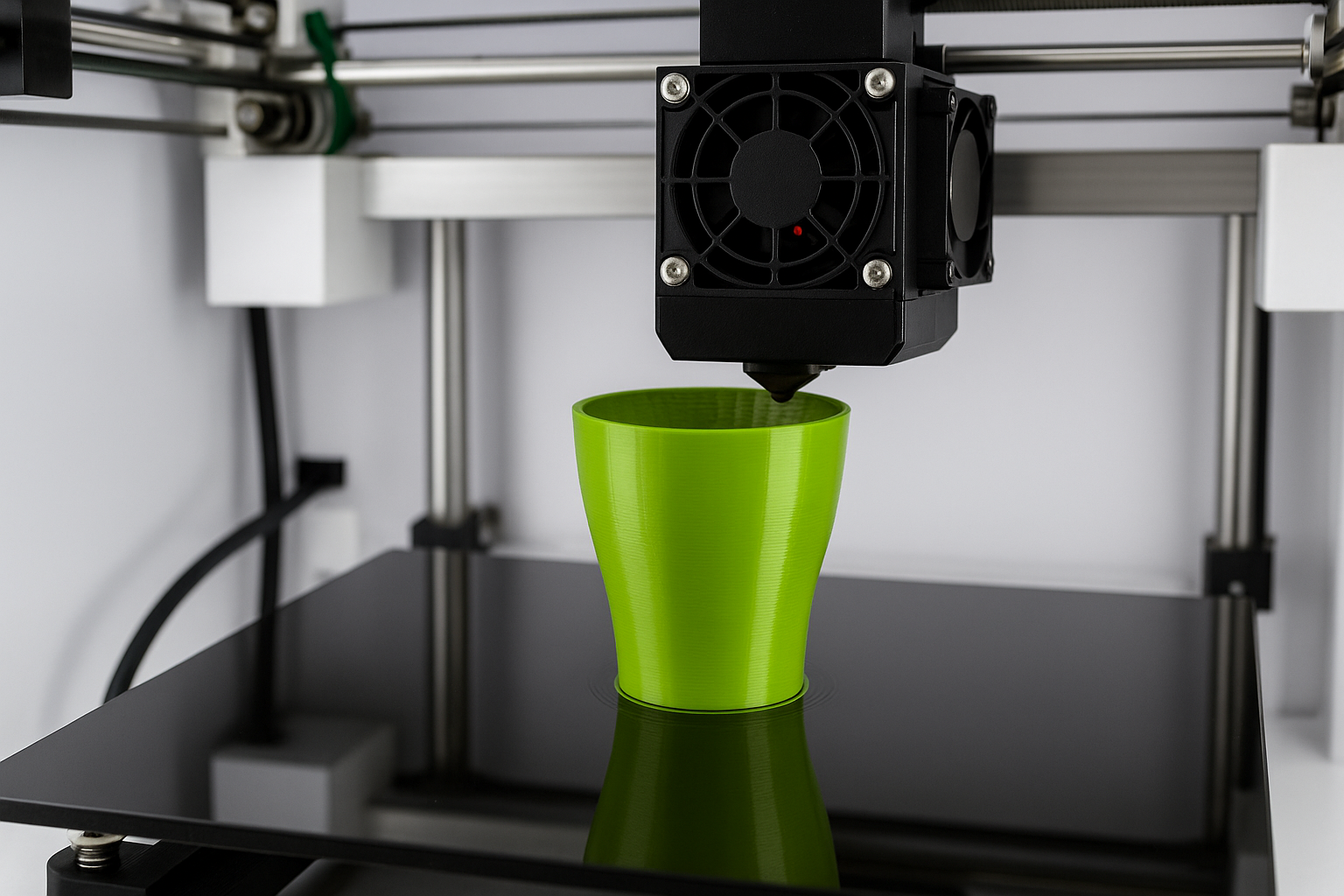
3Impresión D (Fabricación Aditiva)
Qué es?
Impresión de capa de material de plástico capa por capa para construir una parte directamente a partir de un modelo digital.
Tipos comunes:
MDF (Modelado de deposición fusionada): Derrite el filamento de plástico y lo coloca por capa por capa.
SLA (Estereolitmicromografía): Utiliza un láser para endurecer capas de resina en formas precisas.
SLSS (Sinterización láser selectiva): Un láser derrite el plástico en polvo en formas sólidas.
Cuando usar:
Perfecto para prototipos, piezas personalizadas, y formas complejas que no son fácilmente hechas por métodos tradicionales.
Materiales plásticos comunes y sus aplicaciones
| Plástico | Propiedades | Aplicaciones |
| Polietileno | Resistencia química, ligero | embalaje, botellas, bolsas de plástico |
| polipropileno | Resistencia química, aislamiento | Herramientas médicas, piezas automotrices |
| CLORURO DE POLIVINILO | Rigidez o flexibilidad, inercia | Tubería, aislamiento de cable |
| Poliestireno | Rigidez, aislante | Casos de CD, embalaje, aislamiento |
| policarbonato | Fuerza de alto impacto, transparencia | Gafas, lentes automotrices |
| Acrílico (PMMA) | Claridad óptica, ligero | Letreros, lentes, acuarios |
| abdominales | Resistencia al impacto, resistencia al calor | Casos de electrónica, automotor |
| Nylon | Alta resistencia, resistencia al desgaste | Engranajes, aspectos, textiles |
| MASCOTA | Fortaleza, resistencia química | Botellas de bebidas, embalaje |
| PTFE (teflón) | Resistencia química, baja fricción | Utensilios de cocina antiadherentes, focas |
Aplicaciones de la fabricación de plástico
Aeroespacial: Paneles interiores livianos, Windows, aislamiento de cable.
Automotor: Paneles, parachoques, tanques de combustible, adorno interno y externo.
Electrónica: Casquillo de dispositivos, aislamiento de cable, componentes del teclado.
Médico: Herramientas quirúrgicas, implantes, carcasas de dispositivos de diagnóstico.
Construcción: Tubería, aislamiento, techumbre, Windows, revestimiento.
Productos de consumo: Juguetes, Utensilios del hogar, embalaje, muebles.
Ventajas y desventajas de la fabricación de plástico
Ventajas (Ventajas):
Fácil de dar forma y moldear:
Los plásticos se pueden derretir y moldear fácilmente, haciendo que sea sencillo producir piezas con diseños complicados o formas únicas.
Producción asequible:
Hacer piezas de plástico generalmente cuesta menos que el metal u otros materiales, especialmente cuando se produce grandes cantidades. Esto hace de los plásticos una elección popular para la producción en masa..
Ligero pero fuerte:
Las piezas de plástico pesan menos que las de metal, que es beneficioso para muchos usos como automóviles y aviones, donde la reducción de peso mejora la eficiencia y el rendimiento.
Duradero y resistente:
Los componentes de plástico generalmente resisten el óxido, corrosión, y daño de productos químicos. Esto significa que las piezas de plástico pueden durar más en ambientes difíciles.
Altamente personalizable:
Los plásticos se pueden hacer fácilmente en diferentes colores, texturas, e incluso mezclado con otros materiales, Dar a los diseñadores muchas opciones creativas.
Fabricación rápida y flexible:
Los métodos de fabricación de plástico, como la impresión 3D y el mecanizado CNC, permiten cambios rápidos en diseños y tiempos de producción rápidos. Es ideal para probar nuevas ideas y crear prototipos..
Desventajas (Contras):
Problemas ambientales:
Muchos plásticos no se descomponen naturalmente, conduciendo a problemas de contaminación y eliminación de residuos. Reciclar los plásticos también puede ser desafiante.
Sensible al calor:
Los plásticos generalmente no pueden manejar temperaturas muy altas. Ellos pueden derretir, urdimbre, o perder fuerza si se expone al calor excesivo, que limita su uso en configuraciones de alta temperatura.
Menor resistencia en comparación con los metales:
Las piezas de plástico generalmente no son tan fuertes o resistentes como los componentes de metal, haciéndolos inadecuados para aplicaciones que necesitan una carga de carga pesada o una durabilidad extrema.
Desgaste:
Los plásticos pueden rayar, desgastar, o degradarse más rápido que los metales, especialmente cuando se expone a la luz solar (Rayos UV), químicos duros, o estrés repetido.
Los costos iniciales pueden ser altos:
Algunos procesos de fabricación de plástico (como moldeo por inyección) requieren moldes costosos o herramientas por adelantado, que puede hacer que la producción de lotes pequeños sea costoso.
Elegir el método de fabricación de plástico adecuado
Conozca su tipo de plástico
Lo primero es lo primero, averiguar qué tipo de plástico está usando. ¿Es flexible o rígido?? ¿Puede manejar el calor?? Los diferentes métodos de fabricación funcionan mejor con tipos específicos de plásticos, así que elija métodos que coincidan con su material.
Piense en la forma y el tamaño
Considere la forma y el tamaño de su parte. ¿Necesita detalles complejos o diseños simples?? El moldeo por inyección es ideal para detallados, formas complejas. La moldura de soplado es perfecta para artículos huecos, y la extrusión funciona mejor por mucho tiempo, formas continuas como tubos y tuberías.
¿Qué tan preciso debería ser??
Pregúntese qué tan exacto debe ser el producto final. El mecanizado CNC y el moldeo por inyección pueden dar dimensiones muy precisas, mientras que el moldeo rotacional podría ser menos preciso. Elija el método que coincida con el nivel de precisión que necesita.
Verifique los requisitos de calidad
¿Cuál es la fuerza y el acabado requeridos de su parte final?? Por ejemplo, El mecanizado CNC ofrece acabados superficiales de alta calidad, Mientras que la impresión 3D puede dejar capas visibles que necesitan acabado adicional.
Flexibilidad para los cambios
¿Es probable que haga cambios de diseño más adelante?? Si anticipa los ajustes, Elija métodos como mecanizado CNC o impresión 3D, que permiten cambios rápidos y económicos. Moldeo por inyección, por otro lado, implica moldes caros que no son fáciles de modificar una vez hecho.
Presupuesto y costos
Piense cuidadosamente en su presupuesto. Métodos como el moldeo por inyección tienen altos costos iniciales, pero se vuelven más baratos con grandes volúmenes. El mecanizado CNC y la impresión 3D son asequibles para pequeñas cantidades, Pero los costos se suman rápidamente para lotes grandes.
¿Qué tan rápido necesita sus piezas??
Considere su línea de tiempo. Si necesita un cambio rápido, El mecanizado CNC y la impresión 3D a menudo se entregan más rápido. El moldeo por inyección puede requerir tiempos de configuración más largos debido a las herramientas, pero puede producir piezas rápidamente una vez que se complete la configuración.
Ejemplo de proveedor de servicios de fabricación de plástico: Tapas de precisión
Tops Precision se especializa en soluciones integrales de fabricación de plástico, incluyendo mecanizado CNC, moldeo por inyección. Nuestro equipo experimentado proporciona soporte detallado de ingeniería, seguro de calidad, respuesta rápida, y soluciones rentables para garantizar que los proyectos cumplan con las especificaciones y estándares exactas.
Conclusión
La fabricación de plástico sigue siendo indispensable en múltiples industrias debido a su adaptabilidad, rentabilidad, y versatilidad funcional. Seleccionar el método de fabricación correcto implica equilibrar las propiedades del material, Parte de geometría, precisión, volumen de producción, y restricciones presupuestarias. Con una cuidadosa consideración y colaboración con proveedores expertos, Los fabricantes pueden optimizar la producción de componentes plásticos para cumplir con los requisitos exactos de su proyecto.
Preguntas frecuentes
Q1: ¿Cómo selecciono materiales para piezas de plástico??
Considere los requisitos de la aplicación, entorno operativo, color, cumplimiento regulatorio, y propiedades mecánicas/eléctricas.
Q2: Diferencia entre el moldeo por soplado y el moldeo por inyección?
El moldeo por inyección crea piezas sólidas a través de la inyección de resina fundida, Mientras que el moldeo de soplado produce componentes huecos inflando los tubos de plástico calentados.
Q3: ¿Por qué un moho es crucial en la fabricación de plástico??
El molde proporciona la forma y la estructura para la replicación repetida y precisa de los componentes de plástico..
Q4: Son productos de plástico fabricados duraderos?
Generalmente, Los productos de plástico exhiben buena durabilidad, Aunque la vida útil depende de la elección del material, método de fabricación, y condiciones de aplicación.
Q5: ¿En qué se diferencia la fabricación de plástico de la extrusión de plástico??
La extrusión de plástico es una técnica de fabricación específica que produce formas transversales continuas, Mientras que la fabricación de plástico cubre ampliamente las técnicas de moldeo y moldeo.
Q6: Fabricación de plástico vs. flexión de chapa?
La fabricación de plástico cubre técnicas diversas para dar forma a los plásticos, Mientras que la flexión de chapa implica específicamente la deformación de las láminas de metal en ángulos y formas.
Leer más:
Servicios de moldeo por inyección de plástico