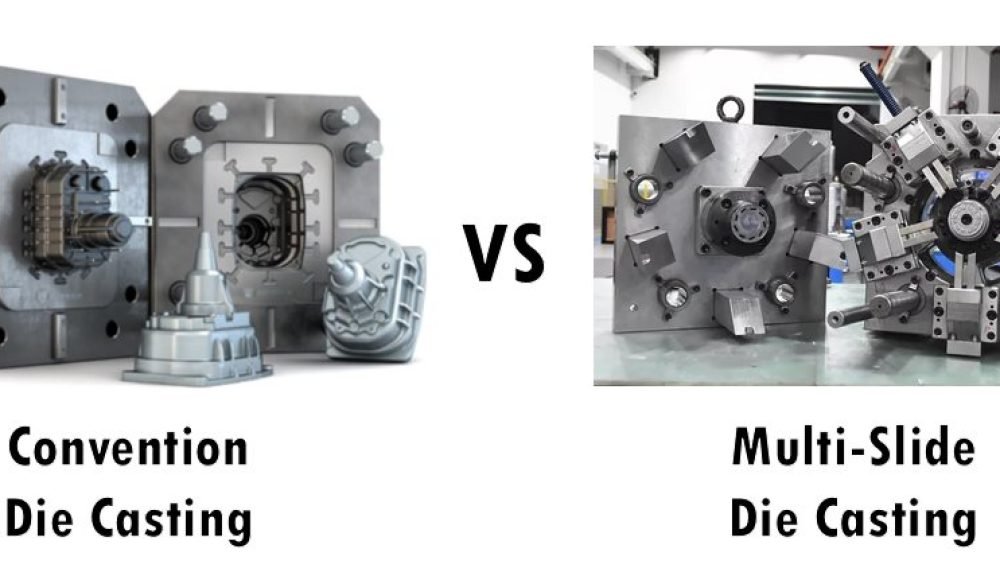
In modern metalworking and precision manufacturing, die casting is one of the most widely used processes for producing complex, high-volume metal parts with excellent dimensional accuracy. Among the various die casting methods, multi-slide die casting and conventional die casting stand out as two distinct techniques, each with its own advantages and ideal applications. This article explores these two processes in detail—explaining how they work, comparing their strengths and limitations, and offering guidance on choosing the right method for your project.
Multi-Slide Die Casting: Precision for Complex Parts
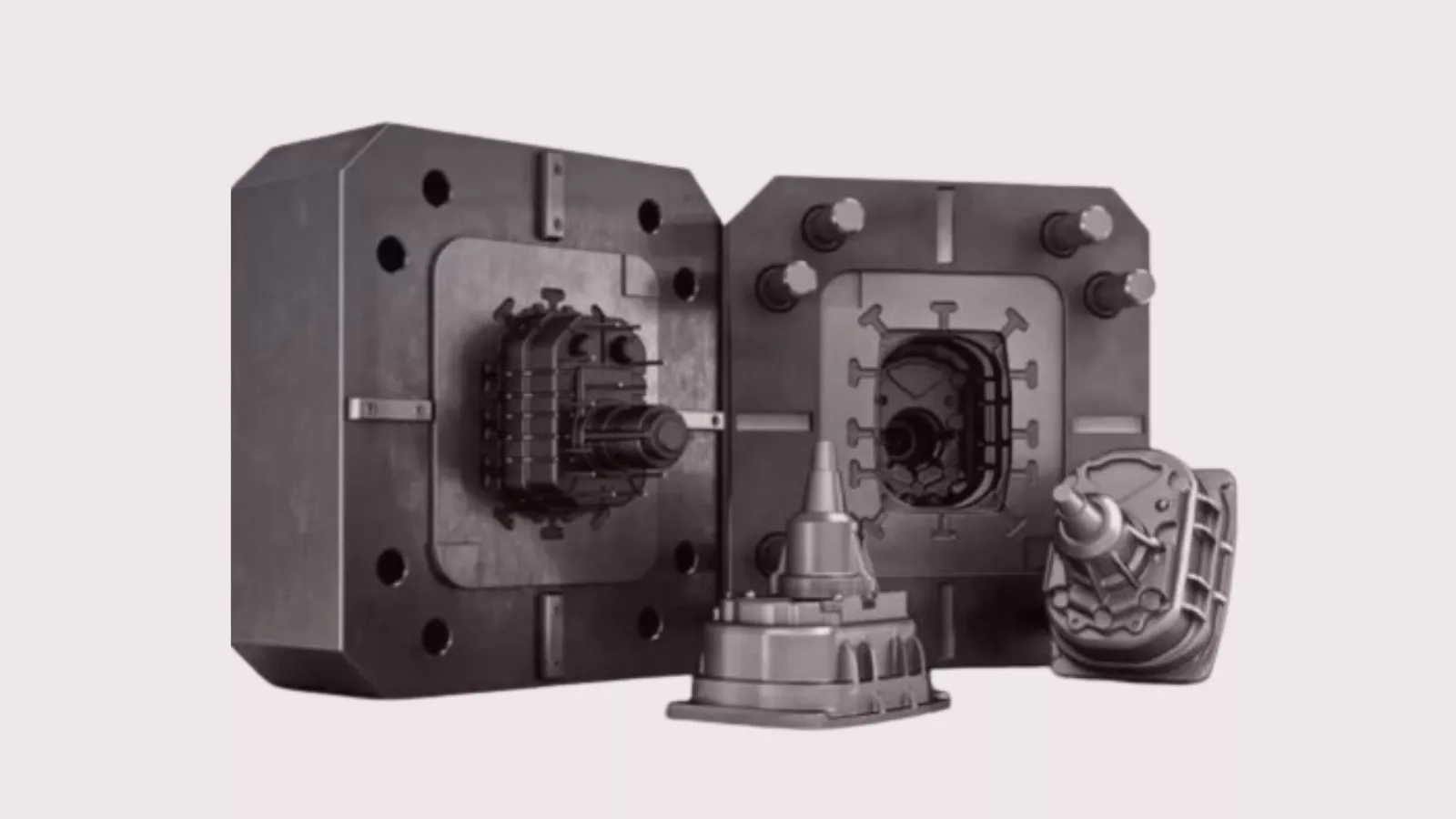
Multi-slide die casting is an advanced form of high-pressure die casting that uses four or more slides—moving sections of the mold that come together perpendicularly to form the cavity. This allows for the creation of extremely detailed and intricate parts with tight tolerances and fine surface finishes.
Key Characteristics:
Uses four or more perpendicular slides.
Enables tooling complexity and access from multiple angles.
Designed for high-volume production of small, complex parts.
Applications:
- Electrical connectors
- Automotive sensors
- Medical device components
- Watch parts
- Lock mechanisms
Advantages:
High precision and repeatability: Capable of holding tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm.
Faster cycle times: Simultaneous slide movement reduces production time.
Superior surface finish: Reduces or eliminates the need for secondary machining.
Thin-walled parts: Ideal for lightweight, compact designs.
Conventional Die Casting: The Standard for Large Components
Conventional die casting, often referred to as high-pressure die casting (HPDC), is a well-established manufacturing process that uses a two-part mold system. These molds—comprising a stationary half and a moving half—form a cavity into which molten metal is injected under high pressure.
Key Characteristics:
Uses two-part tooling (stationary and movable dies).
Suitable for producing larger parts with moderate complexity.
Compatible with a wide range of alloys (aluminum, magnesium, zinc, etc.).
Applications:
- Engine blocks and cylinder heads
- Gearbox housings
- Pump bodies
- Appliance frames
- Lighting enclosures
Advantages:
Efficient for large castings: Can handle bulkier geometries and thicker walls.
Lower tooling costs than multi-slide for simpler shapes.
High-speed production for medium to large parts.
Multi-Slide vs Conventional Die Casting: A Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Multi-Slide Die Casting | Conventional Die Casting |
| Mold Configuration | Four or more slides | Two-part mold system |
| Part Size | Small to medium parts | Medium to large parts |
| Detail Level | Extremely intricate features | Moderate detail |
| Tolerance | ±0.01 mm or better | ±0.05 mm typical |
| Cycle Time | Shorter due to multi-slide ejection | Longer due to two-slide operation |
| Cost | Higher due to tooling complexity | Lower for simpler parts |
| Production Volume | Ideal for high-volume small parts | Suited for high-volume large parts |
| Tool Life | Long, depending on part complexity | Long, but varies with alloy and thermal load |
| Surface Finish | Excellent, minimal post-processing needed | Good, may require machining or polishing |
Choosing the Right Die Casting Method
When selecting between multi-slide and conventional die casting, consider the size, complexity, and precision requirements of your parts:
Choose multi-slide die casting if:
Your parts are small and complex.
You need tight tolerances and fine details.
Surface finish is critical, and secondary operations should be minimized.
Speed and automation are priorities in mass production.
Choose conventional die casting if:
Your components are larger and less intricate.
You’re working with aluminum or magnesium alloys.
Budget constraints favor simpler tooling.
Your project requires robust parts over detailed features.
Partner with TOPS Precision for Expert Die Casting Solutions
At TOPS Precision, we specialize in both multi-slide and conventional die casting technologies to meet the diverse needs of our customers across automotive, electronics, medical, and consumer goods sectors. Our engineers are ready to help you evaluate your part design and recommend the most cost-effective and performance-optimized solution.
Whether you’re manufacturing miniature sensors or heavy-duty housings, TOPS delivers precision, quality, and efficiency every step of the way.
📞 Contact us today to learn more about our die casting capabilities or request a customized quote for your next project.
FAQ
1: What is the main difference between multi-slide and conventional die casting?
The primary difference lies in the mold design and tooling. Multi-slide die casting uses four or more sliding tools that move perpendicularly to form complex cavities, allowing for more detailed parts. Conventional die casting uses a two-part mold, making it more suitable for larger, less intricate components.
2: Which die casting method is better for high-precision small parts?
Multi-slide die casting is the preferred method for high-precision small parts. It provides tight tolerances, superior surface finishes, and shorter cycle times, making it ideal for components like electrical connectors, sensors, and small mechanical assemblies.
3: Is multi-slide die casting more expensive than conventional die casting?
Yes, the initial tooling cost for multi-slide die casting is typically higher due to the complexity of the mold and slide mechanisms. However, it often provides cost savings in high-volume production because of faster cycle times and reduced need for secondary operations.
4: Can conventional die casting be used for small parts?
While conventional die casting can be used for small parts, it is less efficient and may not achieve the same level of detail or tolerance as multi-slide casting. For best results in small-part production, multi-slide die casting is generally more suitable.
5: How do I choose between the two methods for my project?
Your choice should be based on factors like part size, geometrical complexity, tolerance requirements, and budget.
For small, intricate, and high-precision parts, choose multi-slide die casting.
For larger, simpler parts, especially when cost is a concern, conventional die casting is often the better option.