In the evolving landscape of advanced manufacturing, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines have become indispensable tools that offer automation, accuracy, and efficiency. These programmable machines are used across nearly every industry—from aerospace and automotive to electronics and prototyping. This article explores the 12 major types of CNC machines, how they work, and where they are commonly used.
What Is a CNC Machine?
A CNC machine is an automated machine tool controlled by computer software and integrated hardware. CNC machining is a subtractive process, meaning it removes material from a workpiece (or blank) to create a desired shape. However, some CNC systems, such as 3D printers, use additive manufacturing methods to build parts layer-by-layer.
Whether removing material or adding it, CNC systems rely on CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software to convert digital designs into precise physical components.
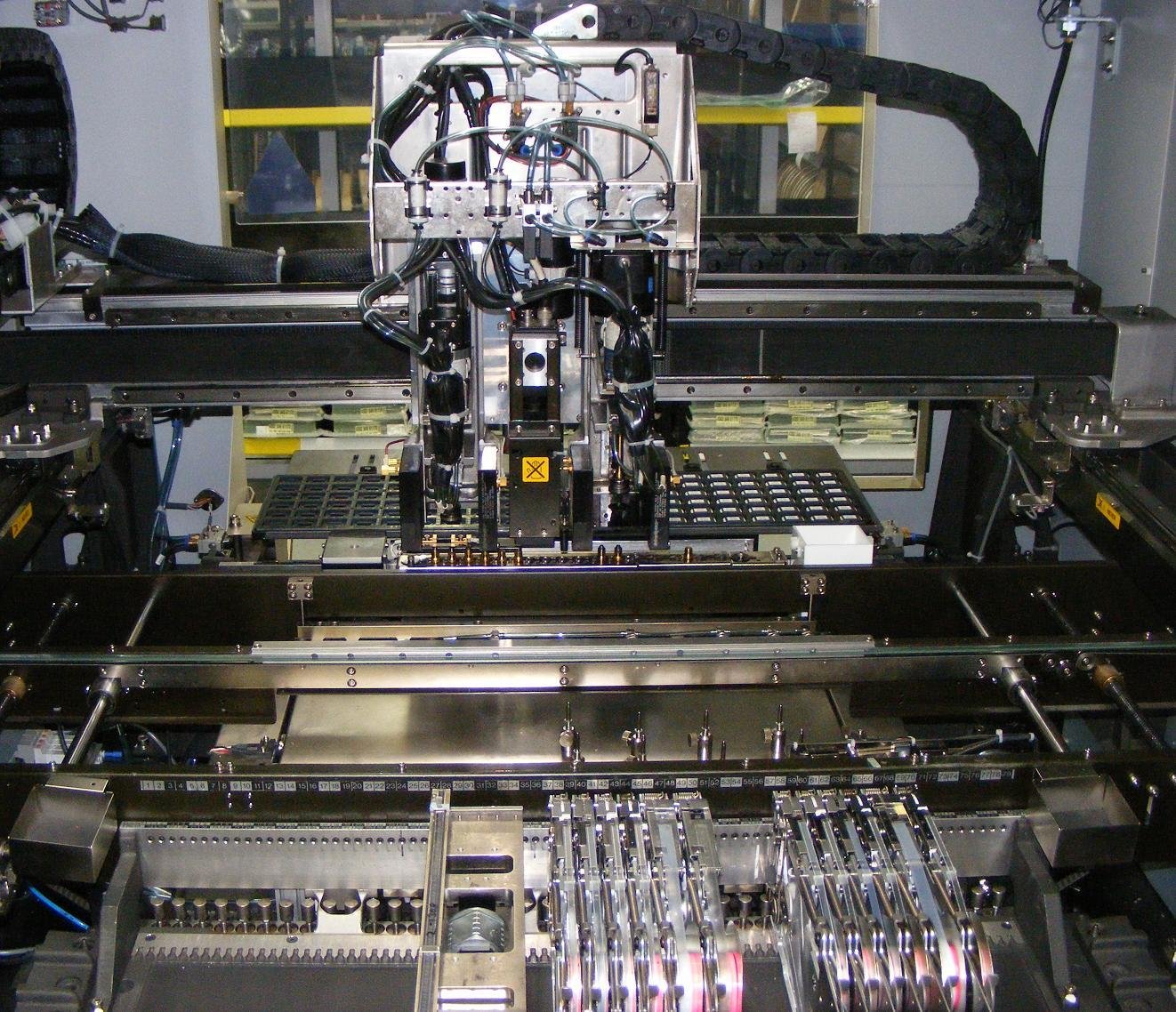
1. Pick and Place Machine
Pick and Place CNC machines are widely used in electronics manufacturing. These machines have multiple robotic nozzles that automatically pick up tiny components such as resistors, ICs, or capacitors and position them accurately onto printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Common Applications:
Mobile phone and tablet assembly
Computer motherboard production
High-speed electronics manufacturing
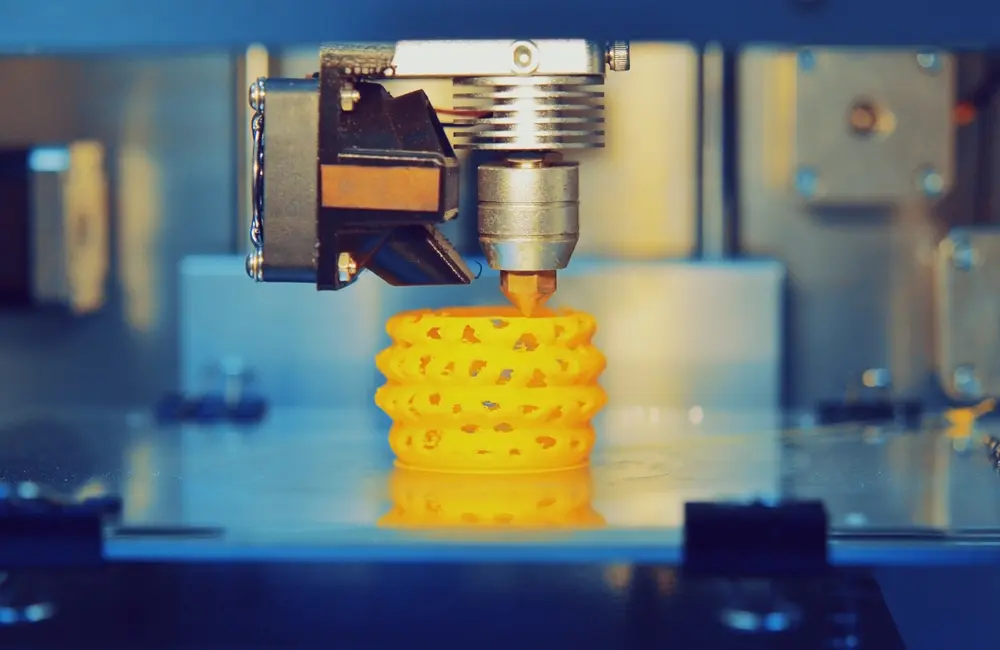
2. CNC 3D Printer
While most CNC machines are subtractive, CNC 3D printers follow an additive manufacturing approach. These machines extrude or cure material—usually plastic, resin, or metal powders—layer by layer to form a complete object from a digital model.
Features:
High design freedom
Excellent for rapid prototyping
Compatible with PLA, ABS, resins, and metal filaments
Industries:
Aerospace and automotive prototyping
Medical implants
Consumer product development
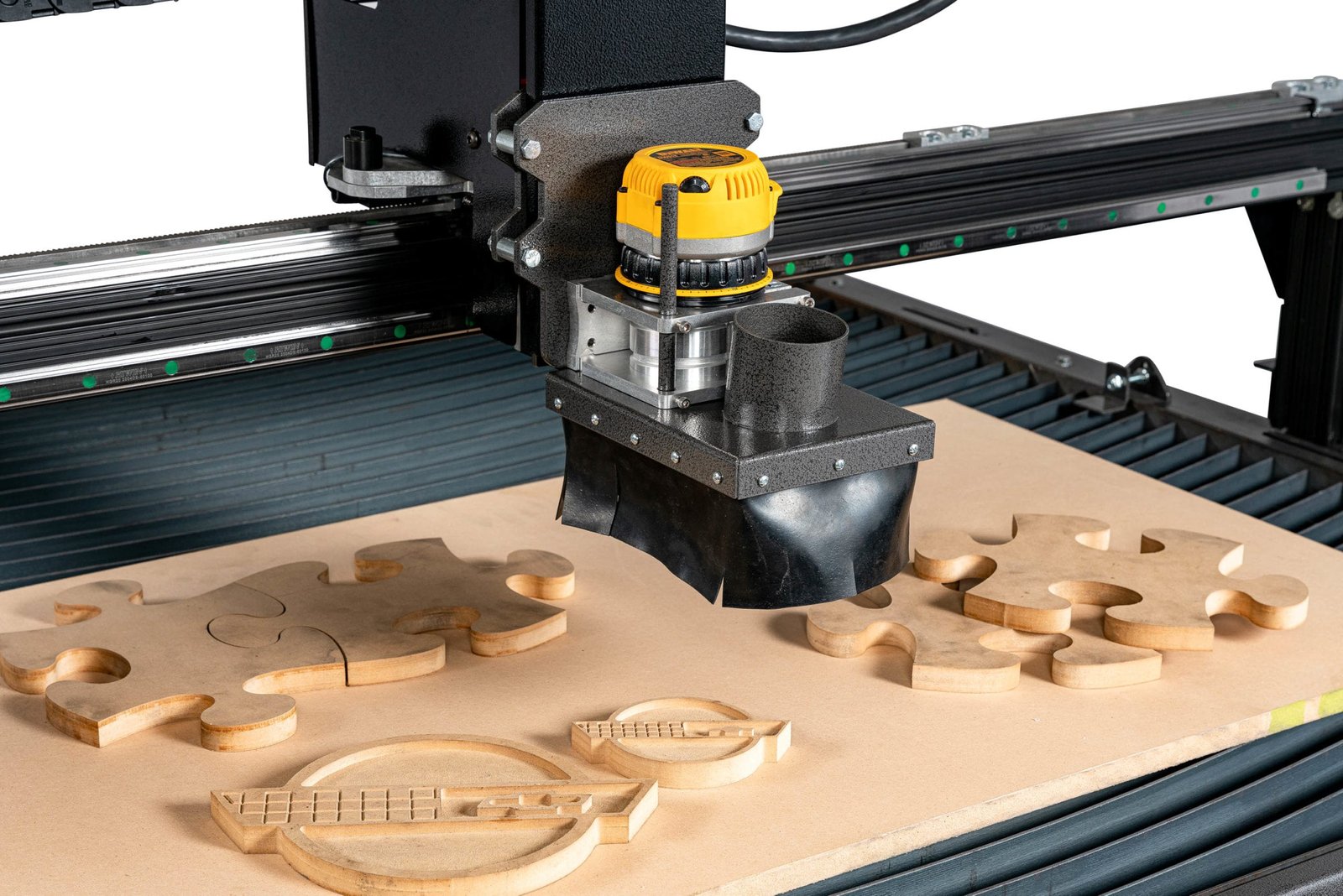
3. CNC Router
CNC routers are ideal for cutting and carving soft materials. Unlike mills, which are typically used for metal, routers are more common for woodworking, plastics, and foams. Routers operate on three axes and can produce detailed engravings, patterns, or cuts.
Materials:
Wood, MDF, plastics
Aluminum and soft composites
Advantages:
High-speed operation
Cost-effective for soft materials
Larger work area compared to typical mills
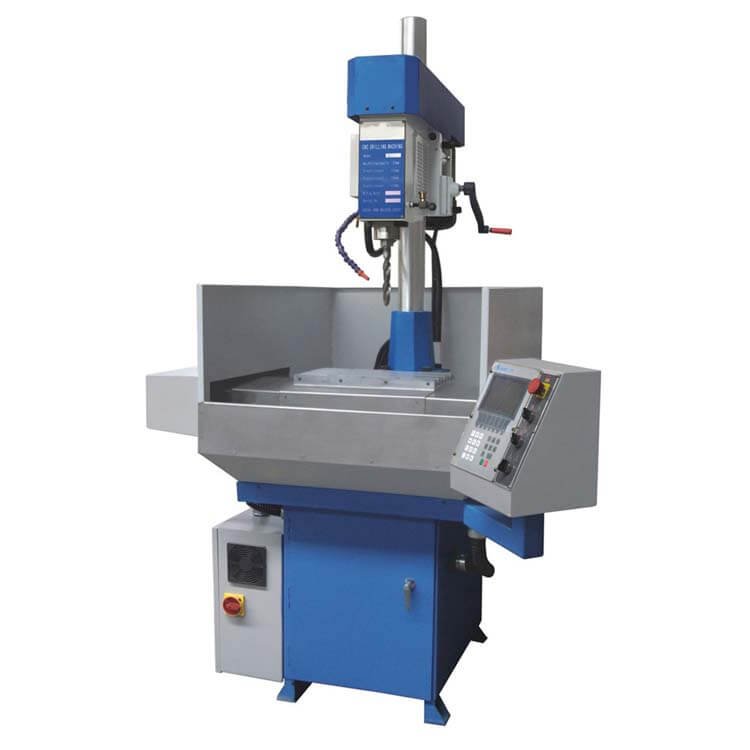
4. CNC Drilling Machine
CNC drilling machines automate the process of creating holes in metal, wood, or composite materials. These machines use various drill bits and can perform operations like peck drilling, reaming, or tapping.
Types of Bits:
Twist drills
Spotting drills
Screw machine drills
Chucking reamers
Typical Uses:
Manufacturing engine blocks
Metal fabrication
Assembly line hole preparation
5. CNC Lathe Machine
CNC lathes perform turning operations, removing material from a rotating workpiece using a single-point cutting tool. These machines can perform complex tasks such as threading, grooving, and facing in a single setup.
Types:
Engine lathe
Turret lathe
Swiss-type lathe
Multi-axis turning centers
Applications:
Shaft and pin manufacturing
Aerospace fasteners
Automotive bushings
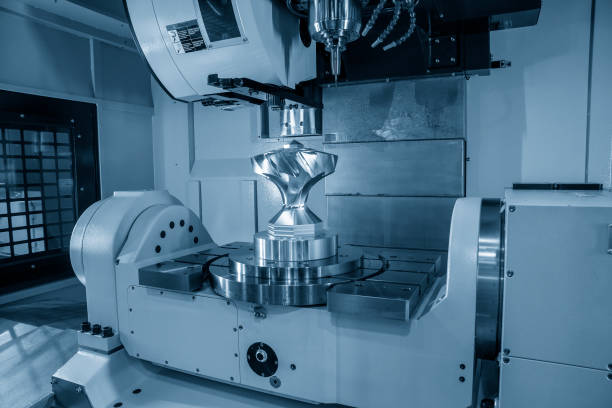
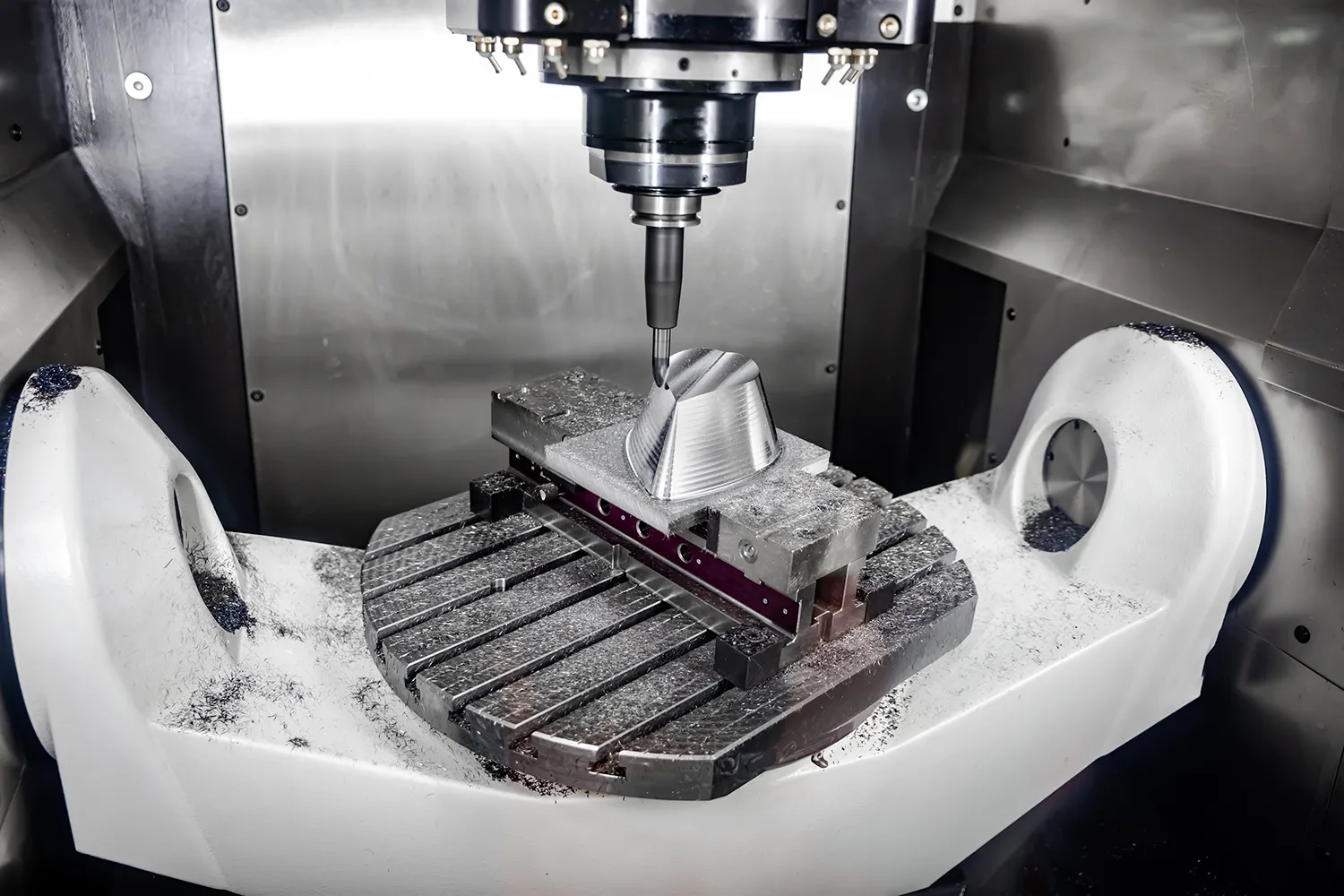
6. 5-Axis CNC Machine
5-axis CNC machines enhance the traditional 3-axis system by adding two additional rotary axes. This allows the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from virtually any direction without manual repositioning.
Key Benefits:
Machine five sides of a part in one setup
Ideal for complex geometries and curved surfaces
Improves accuracy and reduces lead time
Common Uses:
Aerospace structural parts
Medical prosthetics
Intricate mold making
7. CNC Milling Machine
CNC milling machines use rotating multipoint cutters to shape the workpiece. They are highly versatile and capable of producing complex contours and cavities. CNC mills may operate on 3, 4, or even 5 axes.
Cutter Types:
End mills
Face mills
Chamfer mills
Ball nose cutters
Applications:
Precision mold components
Automotive brackets
Custom mechanical parts
8. CNC Plasma Cutting Machine
Plasma cutting CNC machines use an ionized gas torch to slice through electrically conductive materials. The plasma jet reaches temperatures up to 30,000°F, cutting metals with high precision and speed.
Suitable Materials:
Carbon steel
Stainless steel
Aluminum
Brass and copper
Features:
High-speed cutting
Low operational cost
Ideal for sheet metal
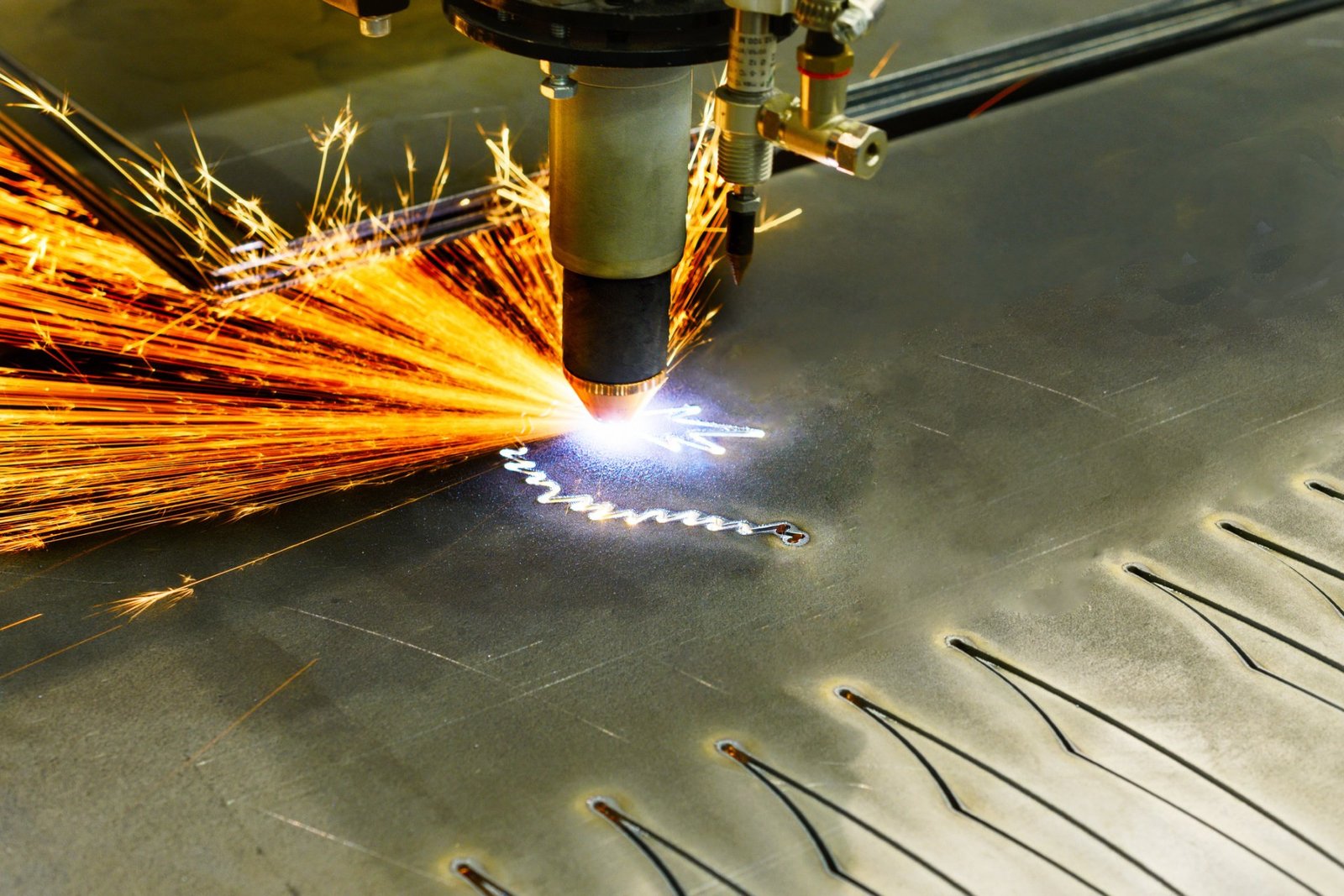
9. CNC Laser Cutting Machine
Laser cutting machines employ focused light energy to vaporize or melt material. These CNC systems can achieve extremely tight tolerances and are used for both cutting and engraving.
Laser Types:
CO₂ Lasers (non-metals, engraving)
Fiber Lasers (metals, high-speed cutting)
Nd:YAG Lasers (precision metal cutting)
Applications:
Signage and displays
Medical device fabrication
Automotive interior trimming
Copper cladding and other architectural products
10. Electric Discharge CNC Machine (EDM)
EDM machines use high-frequency electric discharges (sparks) between an electrode and a workpiece to remove material. It is especially useful for machining hard metals or intricate geometries.
Types:
Wire EDM
Sinker EDM
Advantages:
Precise internal cavities
No mechanical cutting forces
Works on very hard materials
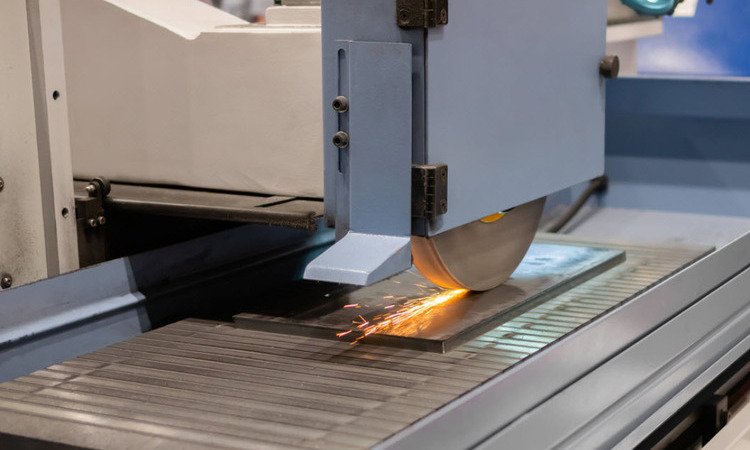
11. CNC Grinding Machine
CNC grinders use abrasive wheels to finish surfaces with very tight tolerances. They are essential for applications where high surface quality and dimensional precision are crucial.
Applications:
Camshafts and crankshafts
Gear manufacturing
Surface finishing of hardened components
Types:
Surface grinding
Cylindrical grinding
Centerless grinding
12. CNC Machine with Automatic Tool Changer (ATC)
CNC machines with automatic tool changers can swap cutting tools during machining without manual intervention. This greatly improves cycle time and supports multi-operation parts in one setup.
Benefits:
Increased machining efficiency
Reduced operator involvement
Ideal for high-volume production
How to Select the Right CNC Machine
Picking the right CNC machine might feel overwhelming at first, especially with so many types out there. But don’t worry—if you break it down, it’s all about figuring out what you want the machine to do, what kind of materials you’ll be working with, and how often you’ll be using it. Here are some easy tips to help you make the right choice:
What Material Are You Working With?
Start by asking yourself: What kind of stuff will I be cutting or shaping?
If it’s wood, foam, or plastic, a CNC router might be perfect.
If it’s metal, you’ll probably need something tougher like a CNC mill, lathe, or plasma cutter.
For complex shapes or hard materials, an EDM machine or 5-axis mill might be the best fit.
How Big Are Your Parts?
Make sure the machine is big enough for your largest part. Always choose a machine that has a slightly bigger work area than your biggest project. This gives you more flexibility down the line.
What Features Do You Need?
Think about:
Speed: How fast do you need the machine to work?
Tool changes: Will you be using lots of different tools? A machine with an automatic tool changer (ATC) can save a lot of time.
Axes: Do you need 3-axis movement, or more? The more axes, the more complex shapes you can make.
Is It Easy to Maintain and Repair?
Like any machine, CNC machines can wear out or break over time. Go for a model that’s well-known and has good support—it’ll be much easier to find replacement parts or get help when something goes wrong.
Power Requirements
CNC machines use a lot of electricity. Before you buy, check the power needs of the machine and make sure your workshop or factory can handle it. Some larger machines may need special power setups.
What’s Your Budget?
Of course, money matters. Some CNC machines are more affordable but may have fewer features. Others cost more but save time and give better results. Think about how much you can spend now and how much time or money the machine might save you later.
Conclusion
CNC machines revolutionize manufacturing by delivering unmatched precision, consistency, and productivity. From subtractive methods like milling and grinding to additive approaches like 3D printing, each CNC machine type serves a distinct role in production.
Understanding the strengths and capabilities of each machine helps manufacturers and engineers select the most efficient solution for their needs.
Read More:
The CNC Machine Shop: A Complete Guide
Types of EDM Machining & Their Applications















2 thoughts on “12 Types of CNC Machines and Their Applications in Modern Manufacturing”