Let’s walk through the intriguing process of form milling, a crucial part of precision manufacturing. Whether you’re an experienced machinist or someone new to CNC operations, this guide has everything you need to understand this method.
Introduction: Understanding CNC and Milling
CNC machining has reshaped how industries manufacture components. By automating processes, it ensures accuracy and reliability, especially for complex shapes and parts. Among various machining techniques, milling stands out as highly versatile. Using a rotating tool, it carves materials into a variety of shapes and sizes.
However, when intricate details or unique profiles are needed, basic milling might not be enough. That’s where form milling excels, offering precision crafting for detailed designs.
What is Form Milling?
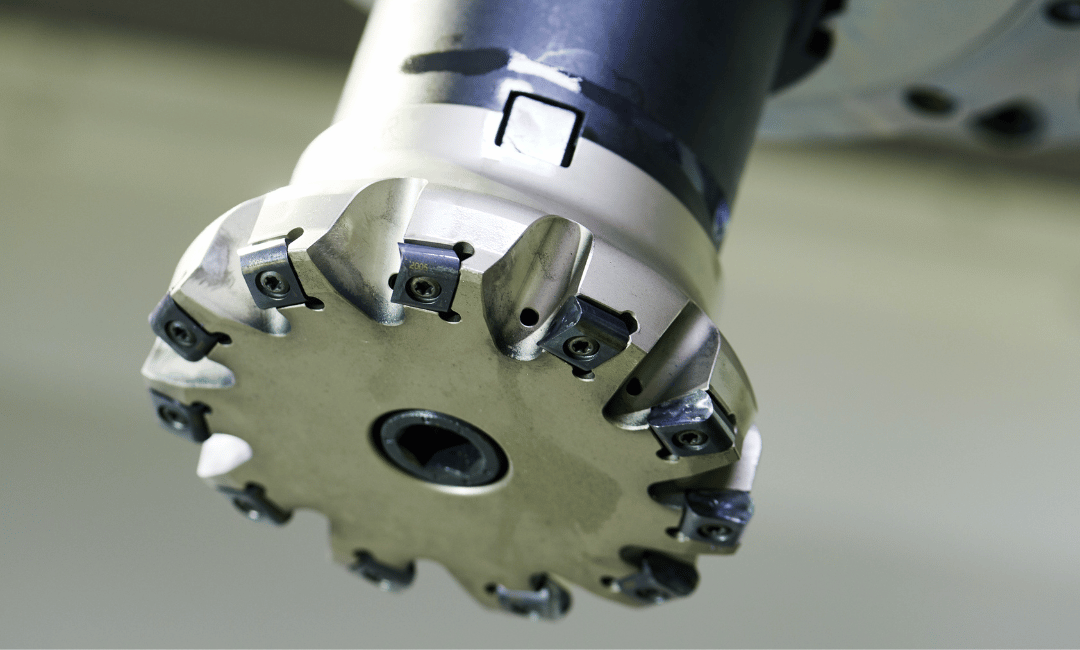
Form milling is a specialized approach to machining. Instead of basic cuts or straightforward curves, it uses custom-made cutters to create exact shapes. Imagine a cutter with a concave design shaping a convex edge—it’s all about matching the tool to the required profile.
Industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare rely heavily on this technique. It’s used for crafting gears, molds, turbine blades, and more. If a project requires accuracy and consistency, especially for high-volume runs, form milling delivers impressive results.
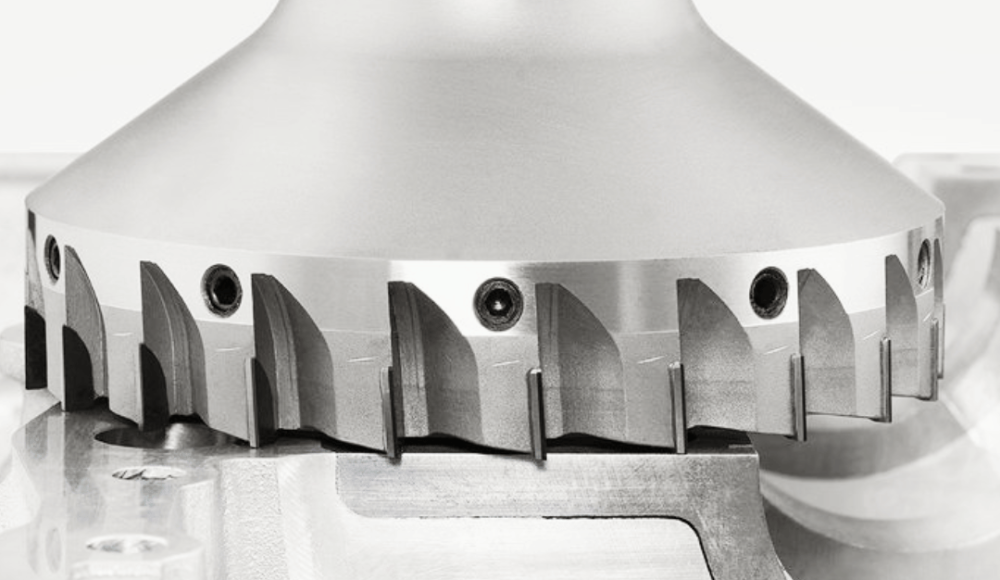
How Form Milling Cutters Are Made
Form milling cutters are precision tools designed to meet specific profiles. They are crafted from durable materials to handle the demands of machining, such as:
- Tool Steel: Known for its toughness and reliability.
- Solid or Brazed Carbide: Offers hardness and excellent resistance to wear.
- Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD): Ideal for ultra-hard and abrasive materials.
- High-Speed Steel (HSS): A flexible option suitable for varied applications.
The manufacturing process typically includes:
- Initial Shaping: The cutter begins as a rough form.
- Profile Grinding: The rough shape is refined into a precise profile.
- Carbide Brazing: Inserts are added for enhanced durability when needed.
- Final Inspection and Refinement: Each tool is carefully checked and polished for accuracy.
- Maintenance and Reconditioning: Worn tools are reconditioned through sharpening or replacing parts, extending their lifespan.
Compatible Materials for Form Milling
Form milling works with a wide range of materials, which makes it incredibly adaptable. Common options include:
- Plastics: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, these are used in diverse applications.
- Composites: Composites are often chosen in sectors like aerospace and automotive.
- Metals: From aluminum to titanium, metals are staples in machining processes.
This versatility makes form milling suitable for countless industries and purposes.
Advantages of Form Milling Compared to Other Techniques
Form milling’s ability to create intricate shapes in a single operation sets it apart from other methods. Unlike conventional milling, which might require several steps and tools, form milling simplifies the process, saving both time and resources. It’s particularly effective for creating multiple features simultaneously while ensuring high-quality surface finishes.
Benefits and Challenges of Form Milling
Let’s take a closer look at what makes form milling effective and where it might pose challenges.
Key Benefits:
- Handles Complex Shapes with Ease: Perfect for detailed profiles and contours.
- High Precision: Delivers uniform results, even in mass production.
- Time-Saving: Reduces the need for multiple setups or tool changes.
- Cost-Effective for Large Runs: While setup costs may be higher, the long-term savings in high-volume production are significant.
Potential Challenges:
- Lengthy Setup Process: Custom tools and programming require careful preparation.
- Higher Initial Costs: Better suited for large-scale projects.
- Requires Expertise: Proper programming and tool setup are essential for success.
How Form Milling Works
The process starts with a clear design phase, where engineers create detailed blueprints or CAD models of the desired shape. Based on these, a cutter is customized to match the design precisely.
Here’s how it unfolds:
- Design and Planning: The desired shape is modeled digitally, ensuring all details are accounted for.
- Cutter Setup: The custom tool is secured in the CNC machine, and the alignment is checked for accuracy.
- Dry Run: A test run ensures all parameters, such as speed and feed rate, are correct.
- Cutting Process: The tool interacts with the material, shaping it to meet the exact specifications.
Precision and attention to detail throughout this process are crucial for achieving the best results.
Types of Form Milling Cutters
Form milling cutters come in various types, each serving a specific function:
- Concave and Convex Cutters: Used to create rounded profiles, such as grooves or ridges.
- Form Tools: Tailored for specific profiles, such as those used in hydraulic systems.
- Corner Rounding Cutters: Add smooth, curved edges, improving aesthetics and functionality.
Choosing the Right Cutter
Selecting the appropriate form milling cutter depends on the project’s needs. Factors to consider include:
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the cutter is suitable for the workpiece material.
- Complexity of the Shape: Intricate designs often require custom cutters.
- Production Volume: For larger runs, custom tools offer better efficiency and cost savings.
Final Thoughts
Form milling is an essential tool in modern machining. Its ability to create detailed and precise components makes it indispensable for various industries. At the same time, the setup may require time and resources, but the consistent results and efficiency it offers in large-scale production more than make up for it. Collaborating with skilled professionals ensures the best outcomes for complex manufacturing needs.
FAQs
- Is form milling suitable for small-scale projects?
It’s typically more cost-effective for high-volume production due to the upfront investment in tools and setup. - How precise is form milling?
Extremely precise—machines often work within tolerances as small as 0.0002 inches. - Can worn cutters be reused?
Yes, many cutters can be resharpened or have their components replaced to extend their lifespan.







1 thought on “Form Milling Essentials-Your Practical Guide”