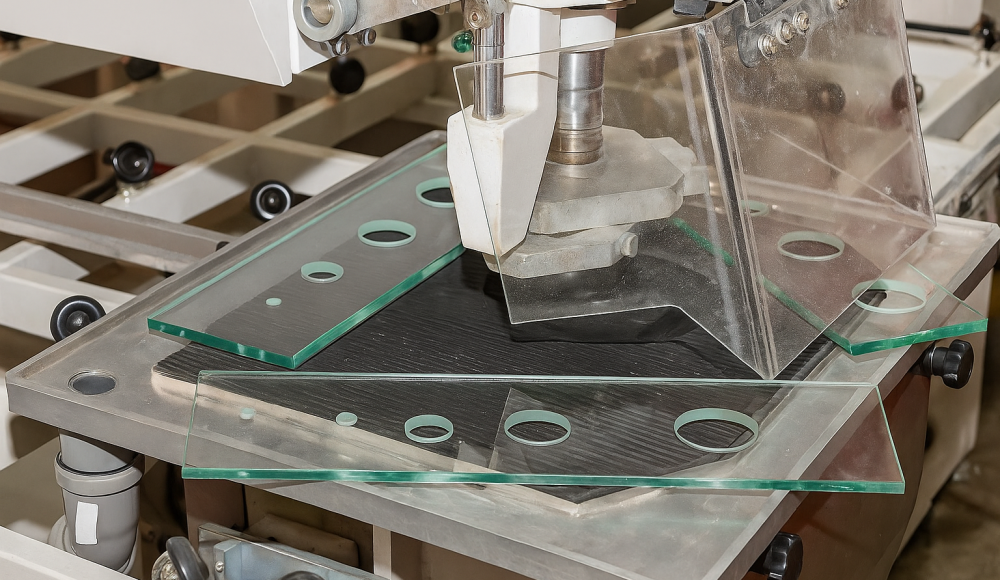
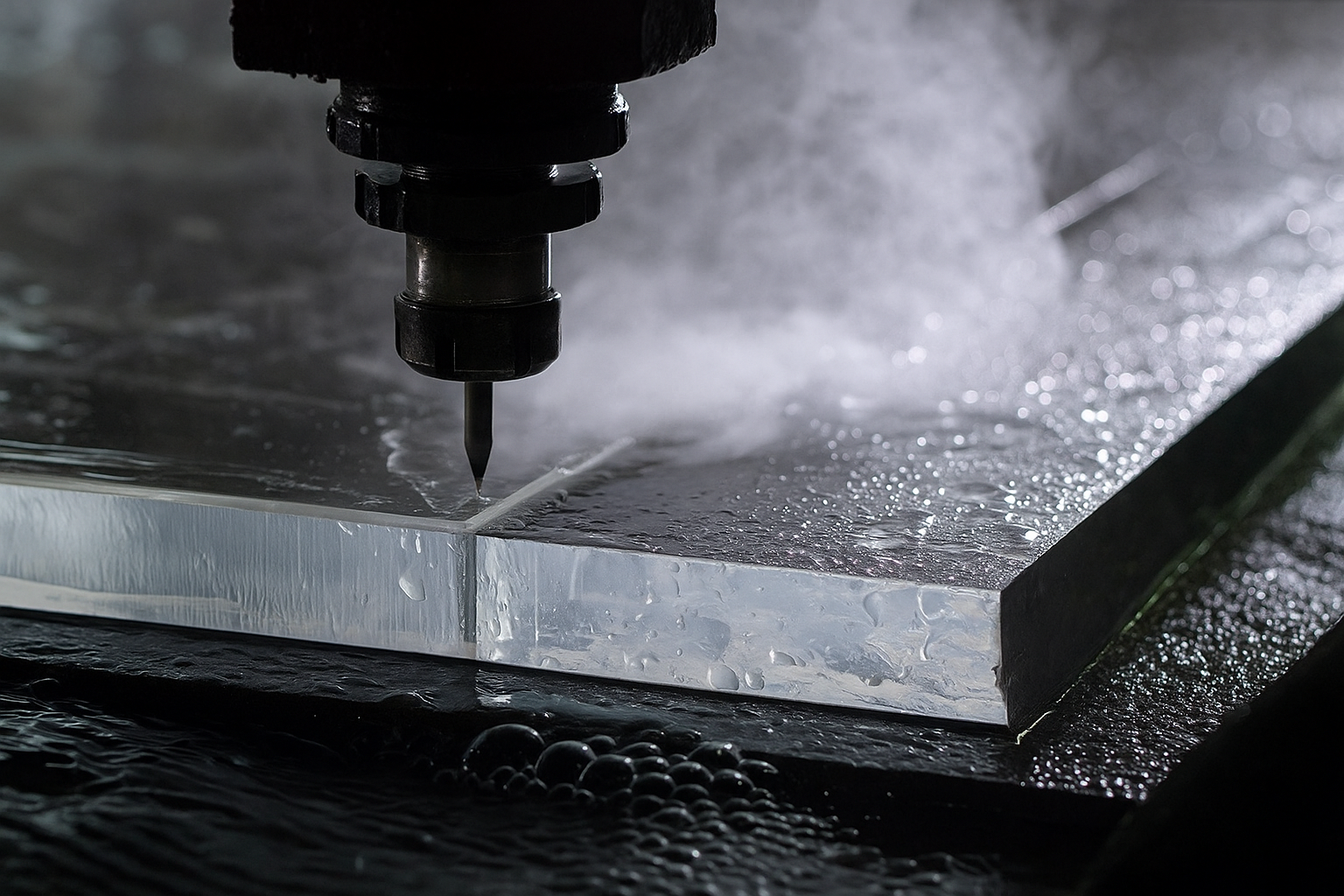
El mecanizado CNC de vidrio ha revolucionado la forma en que se fabrican los componentes de precisión, permitiendo a los diseñadores e ingenieros realizar geometrías complejas y tolerancias estrechas que antes no eran prácticas o imposibles. Desde dispositivos microfluídicos hasta grandes paneles arquitectónicos, Glass Machined CNC ofrece una precisión excepcional, repetibilidad, y acabado superficial. Esta guía profundiza en los métodos, materiales, beneficios, y consideraciones del mecanizado CNC de vidrio, Empoderarlo para tomar decisiones informadas para su próximo proyecto.
¿Puede el vidrio estar mecanizado por cnc??
Sí, avances en la rigidez de la máquina herramienta, diseño de husillo, estampación, y el control de procesos ahora hace que sea factible para el vidrio CNC-Machine de manera confiable. Sin embargo, La fragilidad y la dureza inherentes de Glass requieren técnicas y herramientas especializadas para minimizar el astillado, agrietamiento, y desgaste de herramientas. Con accesorios adecuados, entrega de refrigerante, y optimización de parámetros, El mecanizado CNC puede producir cortes intrincados, agujeros, y texturas superficiales en paneles y componentes de vidrio.
¿Cómo funciona el mecanizado de vidrio CNC??
El mecanizado CNC de vidrio sigue el flujo de trabajo CAD → Cam → CNC CNC, pero con adaptaciones críticas para el comportamiento material.
Flujo de trabajo de CAD tO CAM
Diseño & Tolerancia
Crear modelos 3D en CAD, Especificar dimensiones y tolerancias geométricas (Dios&t).
Identificar superficies críticas (p.ej., caras ópticas) Requerir una planitud o aspereza submicrona.
Generación de trayectoria
En el software CAM, Seleccione la traza de herramientas apropiadas (contornear, bolsillo, perforación).
Definir paso a, atropellado, tasas de alimentación, y velocidades de huso optimizadas para la eliminación de vidrio.
Configuración de la máquina
Fijación
Use Chucks de vacío, almohadillas adhesivas, o mandíbulas suaves para soportar el vidrio sin inducir estrés.
Asegure un apoyo uniforme para evitar la vibración y el agrietamiento.
Estampación & Huso
Emplear fábricas de finales recubiertas de diamantes, ejercicios, y herramientas de molienda/rebabas.
Husillos de alta velocidad (≥ 30,000 RPM) reducir las fuerzas de corte y mejorar el acabado superficial.
Refrigerante & Control de polvo
El refrigerante de la inundación o la micro-lubricación minimiza la acumulación de calor y los escombros.
Los sistemas de extracción integrados capturan el polvo de vidrio para evitar el rascado de la superficie.
Operaciones de mecanizado
Pases de mal humor
Comience con profundidades conservadoras de corte (p.ej., 0.1–0.2 mm) a velocidades de alimentación moderadas para eliminar suavemente el material a granel.
Pases de acabado
Cambiar a finos bajos (≤ 0.05 milímetros) y alimentación reducida para lograr la rugosidad de la superficie objetivo (< Real academia de bellas artes 0.2 micras).
Monitoreo en proceso
Use sensores de vibración y retroalimentación acústica para detectar el desgaste de la herramienta o el agrietamiento en tiempo real.
Pasos posteriores a la mate
Pulido
El pulido secundario con almohadillas de diamantes finas o una lechada puede mejorar aún más la claridad óptica.
Templado/fortalecimiento
El fortalecimiento térmico o químico mejora la dureza, crítico para componentes de carga o de seguridad.
Inspección final
Máquinas de medición de coordenadas (CMMS), interferómetros, y los perfilómetros de superficie verifican las especificaciones geométricas y de superficie.
Técnicas utilizadas en el mecanizado CNC de vidrio
Las propiedades únicas de Glass exigen un conjunto de herramientas diversos de técnicas de mecanizado:
Molienda & Contorno
Elimina el material para formar bordes, lo más hondo, y formas 3D con fábricas de fin de diamante.
Perforación & Aburrido
Crea agujeros precisos de sub-0.5 mm a varios milímetros utilizando taladros recubiertos de diamantes y escariadores.
Grabado & embolsarse
Diamond Cutters talla patrones decorativos, números de serie, o bolsillos poco profundos para juntas.
Ranurado & Ranurado
Forma canales estrechos para sellos o características de ensamblaje; crítico en aplicaciones de manejo de fluidos.
Molienda & Cojinete
Técnicas de refinamiento de superficie que llevan la planitud y la rugosidad a las tolerancias ópticas.
Corte de chorro de agua (Sistemas híbridos)
Cabeza abrasiva de chorro de agua en una plataforma CNC logra perfiles 2D sin estrés térmico.
Fortalecimiento térmico/químico
Tratamientos posteriores a la mate (baños de intercambio de iones o hornos de temple: aumentar la compresión de la superficie y la durabilidad.
Tipos de vidrio adecuados para mecanizado CNC
| Tipo de vidrio | Propiedades clave | Usos comunes |
| Borosilicato | Baja expansión térmica, alta resistencia química | Trabajo, óptica de precisión |
| Lima | Económico, mecanizable, fuerza moderada | Paneles arquitectónicos, componentes decorativos |
| Sílice fusionada | Expansión ultra baja, alta claridad | Obleas de semiconductores, óptica de alta potencia |
| Aluminosilicato | Alta resistencia, buena estabilidad térmica | Pantallas de teléfonos inteligentes, cubiertas de visualización duradera |
| Vidrio de plomo | Índice de refracción alto, denso | Lentes de precisión, prisma |
| Cuarzo | Pureza excepcional, Transparencia UV, alta resistencia | Lámparas UV, Windows de proceso de semiconductores |
Ventajas del mecanizado CNC de vidrio
Alta precisión & Repetibilidad
Lograr tolerancias de ± 10 µm de manera consistente a través de lotes.
Geometrías personalizadas complejas
Producir recortes, microcanales, y superficies de forma libre en una sola configuración.
Acabado superficial superior
Ra hacia abajo a 0.05 µm sin un pulido manual extenso.
Eficiencia de material
Pérdida de kerf minimizada y chatarra a través de trayectoria optimizada y anidación.
Automatización & Seguridad
El control de CNC reduce la exposición del operador a fragmentos de vidrio; Las opciones de carga automatizadas aumentan el rendimiento.
Limitaciones del mecanizado CNC de vidrio
Riesgo de fragilidad
Secciones transversales delgadas (< 2 milímetros) y las esquinas apretadas pueden agrietarse bajo estrés.
Equipo & Costo de herramientas
Los husos de alta precisión y las herramientas de diamantes exigen una inversión de capital significativa.
Experiencia en el operador
Requiere entrenamiento especializado en comportamiento de vidrio, Selección de herramientas, y ajuste de procesos.
Aplicaciones de mecanizado CNC de vidrio
Óptica & Fotónica
Lentes, prisma, guías de onda, y elementos de forma de haz.
Equipo semiconductor
Sustratos de obleas, Windows alineador de máscaras, y cubiertas protectoras.
Médico & Biotecnología
Chips microfluídicos, catéter lumen, cámaras diagnósticas de diagnóstico.
Aeroespacial & Defensa
Windows de presión, carcasa del sensor, y ventanas gráficas de alta temperatura.
Electrónica de consumo
Cubiertas de pantalla táctil, cubiertas de lentes de cámara, y piezas de vidrio decorativas.
Arquitectónico & Decorativo
Paneles de vidrio grabado, accesorios de iluminación, e instalaciones artísticas.
Consideraciones de costos
Gasto de capital
Máquina CNC con huso de alta velocidad: $150,000- $ 500,000+.
Herramientas recubiertas de diamantes: $100- $ 500 por cortador.
Costos operativos
Salarios de operadores calificados, refrigerante, desgaste de herramientas, y mantenimiento.
Economía de volumen
Costos de configuración de compensación de volúmenes más altos; Pequeñas carreras llevan la prima por parte.
Complejidad del diseño
Las características intrincadas aumentan el tiempo del ciclo; equilibrio entre ambiciones de diseño y presupuesto.
Comparación con otros métodos de fabricación de vidrio
| Aspecto | Mecanizado CNC | Corte por láser | Técnicas manuales |
| Precisión | ±10 micras | ± 50–100 µm | ± 100–300 µm |
| 3D Capacidad | Contornos 3D completos | Principalmente perfiles 2D | Formas limitadas |
| Estrés térmico | Mínimo (con refrigerante) | Micro-cracks potenciales | Bajo pero inconsistente |
| Tiempo de configuración | Moderado (Programación de cámaras) | Bajo | muy bajo |
| Acabado de la superficie | RA 0.05-0.2 µm | RA 1-3 µm | Real academia de bellas artes > 3 micras |
Seleccionar un proveedor de mecanizado CNC de vidrio
Equipo & Certificaciones
Busca ISO 9001:2015, AS9100 para aeroespacial, o ISO/IEC 17025 para metrología.
Experiencia técnica
Revisar estudios de casos en óptica, médico, o industrias de semiconductores.
Control de calidad
Sondeo en proceso, Inspección CMM, interferometría, y perfilometría de superficie.
Tiempo de espera & Capacidad
Confirmar las capacidades de rendimiento y los planes de copia de seguridad para corridas urgentes.
Servicios de postprocesamiento
Pulido, templado, revestimiento, e integraciones de ensamblaje.
Estudio de caso: Tapas de precisiónProceso de mecanizado CNC de vidrio
Inspección entrante
Verificar el tipo de vidrio, espesor, y pre-certificación de planitud con interferometría láser.
Optimización de la trayectoria
Use plantillas de leva interna sintonizadas para el compromiso de herramientas mínimo y el control de vibración.
Mecanizado de múltiples etapas
Corte áspero a 20,000 RPM; finalizar 40,000 RPM con 1 µm reducido.
Mejora de la superficie
Polroización de suspensión de diamantes opcional o fortalecimiento de intercambio de iones.
QA final & embalaje
CMM e inspección óptica; Cruce personalizado con espuma de bateo de vibraciones.
Conclusión
El mecanizado CNC de vidrio une la brecha entre la ambición de diseño y la fabricación, Desbloqueo de hazañas de precisión y complejidad que impulsan la innovación en todas las industrias. Al comprender los matices de la selección de herramientas, Parámetros de proceso, y comportamiento material, Puede aprovechar el mecanizado CNC para producir componentes de vidrio que cumplan con los estándares más estrictos de rendimiento y estética. Al evaluar los socios, priorizar la experiencia técnica, sistemas de calidad, y un historial probado en la fabricación de vidrio, como lo demuestra Tops Precision, para garantizar el éxito de su proyecto desde el prototipo hasta la producción.
Leer más:
Servicios de mecanizado de precisión