When we hear the word “polishing” most of us think about getting something shiny, such as polishing a car, a piece of jewelry, or even a floor. However, polishing is much more than purely aesthetics; it’s a critical part of the manufacturing and finishing process. In this guide, we cover what polishing is, how it works, and why it’s used in several different industries.
What Is Polishing?
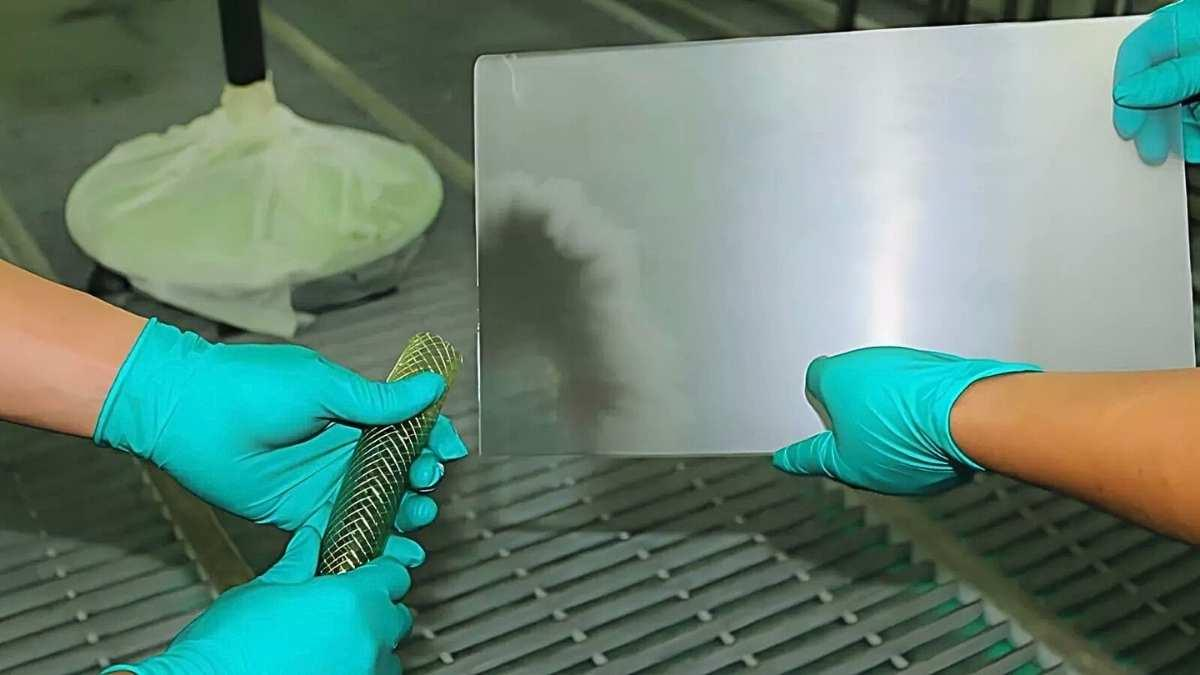
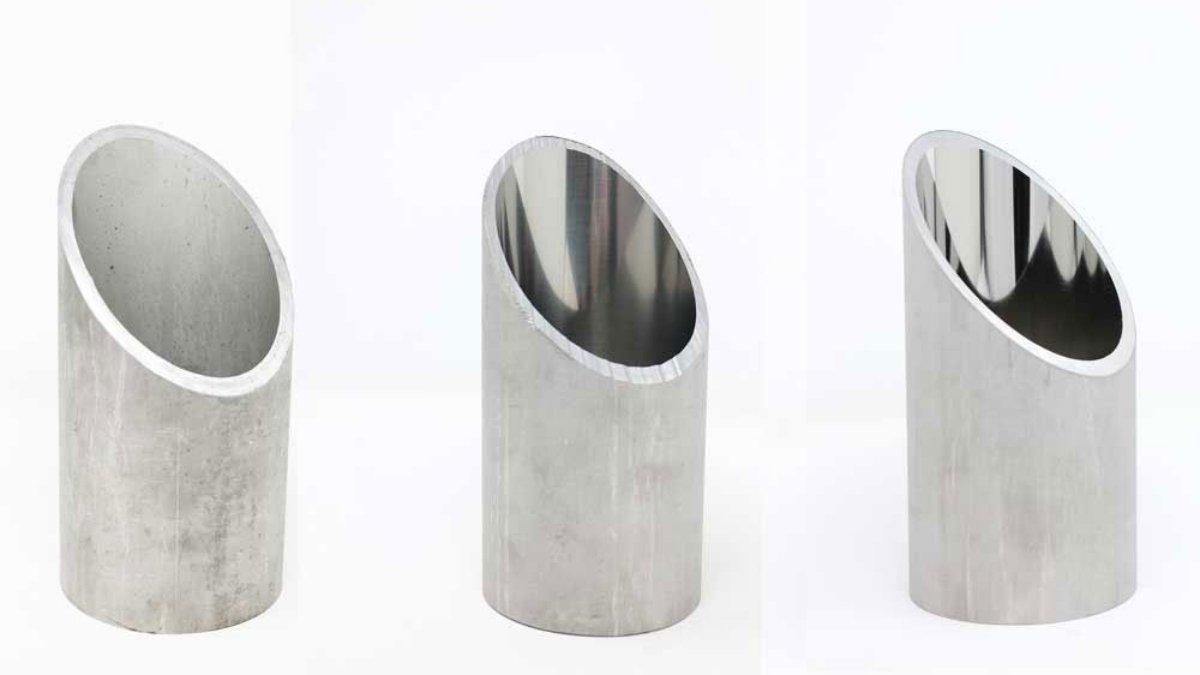
Polishing is a process of finishing that uses abrasive materials to provide a surface with a smooth and shiny appearance. To polish means to buff, a surface is made smooth and shiny by rubbing it.
It is typically performed on a part or material that has been subjected to other machining or shaping processes. It’s used to ensure the surface quality is better, the reflectivity is higher, and sometimes the durability is better.
Polishing is widely utilized in sectors such as metalworking, automotive, jewelry, and electronics.
How Does Polishing Work?
Polishing usually consists of rubbing or buffing a material with an abrasive compound or a polishing wheel. This might be done with machines or done by hand depending on the material. Here’s a simplified way of understanding how polishing works in general:
Surface Preparation: The material is cleaned and prepared. This ensures that any dirt, oil, or other grime is removed so the polishing compound can do its job.
Abrasive action: An abrasive agent (a polishing paste, abrasive cloth, or wheel) is applied to the surface. This abrasive will strip away the finer layers on the material’s surface to even out the imperfections.
Buffing: Once the surface has been smoothed over with the abrasive material, the component is buffed with a soft cloth or wheel to enhance its shine and give the part a reflective finish.
Cleaning — After you reach the desired shine, the part is cleaned to remove any residue from the polishing compound.
Types of Polishing Processes
Some of the common ones include:
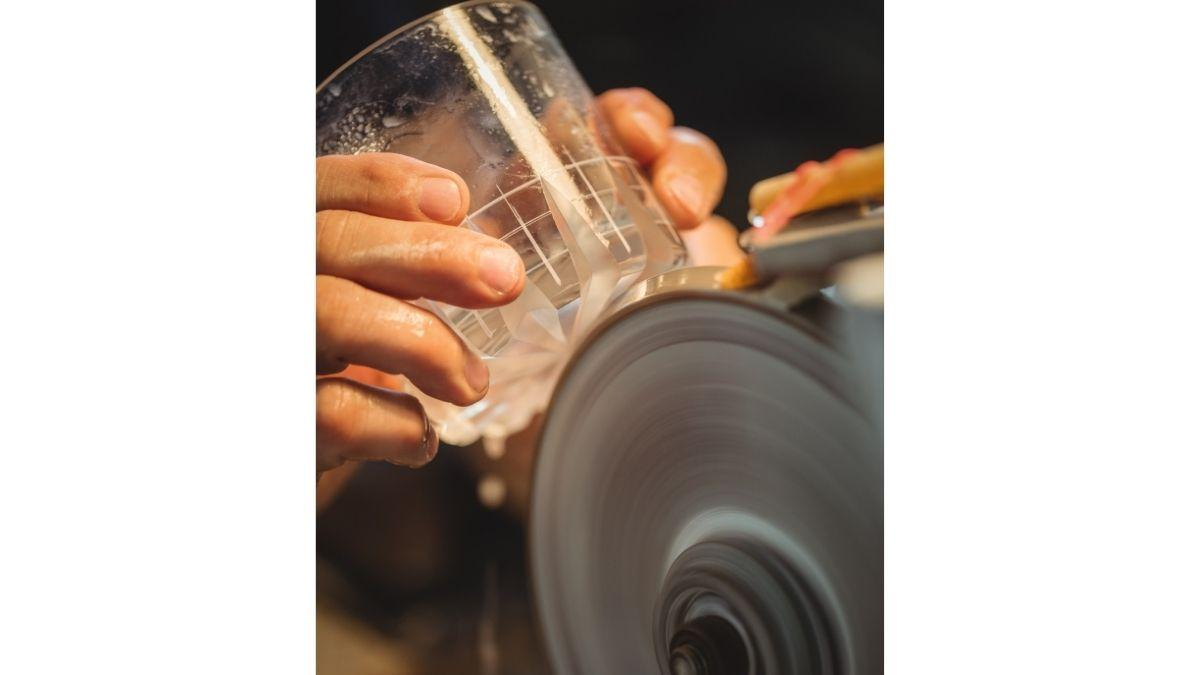
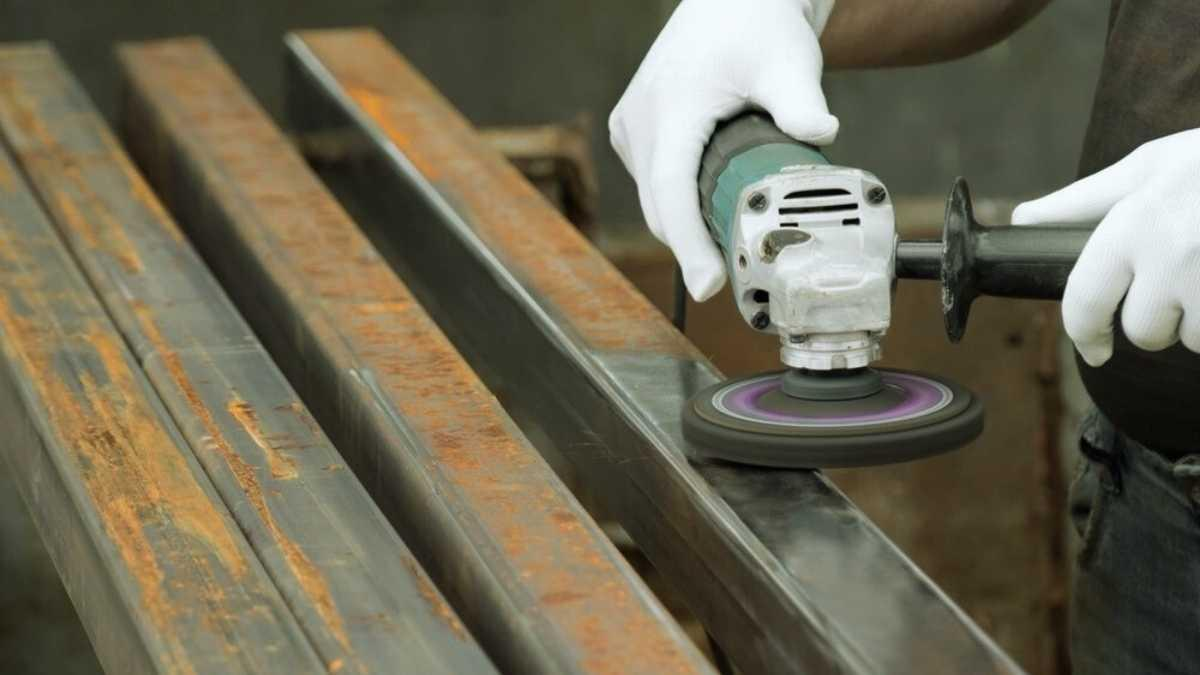
Mechanical Polishing
Mechanical polishing employs abrasive materials (e.g., polishing wheels or pads) that spin at high velocities against a surface to smooth it. This technique is typically used for metal polishing as well and is suitable for more significant or hard-wearing components.
Chemical Polishing
Chemical polishing uses a chemical solution to etch away material on the surface. This solution is capable of dissolving the surface of the material to smoothen it. Commonly used for metals and plastics, this method is best suited for very complex geometries.
Electropolishing
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that combines electricity and a chemical bath to polish metals, including stainless steel, at the atomic level. The part, which is submerged in an electrolyte solution, undergoes an electrochemical reaction that removes the outer layer of the metal and leaves behind a smooth, shiny surface.
Hand Polishing
Polishing compounds and a soft cloth or buffer are usually used to hand polish. This approach is best for the small parts or sensitive surfaces that need a bit more TLC. It’s also a good choice for polishing machined or shaped parts to remove the final marks left behind.
Buffing
Buffing is like polishing, but the intent is to achieve a high-gloss finish rather than to smooth out the surface. It is a gentler, noncharging material than polishing. Buffing is more often performed on plastics or wood and is widely utilized in the automobile and furniture-making industries.
Why Is Polishing Important?
Some industries and services polish for different reasons. Here are some of the most important reasons why it’s a crucial part of the production process:
Hygiene and Aesthetics of Surface Quality
The print quality comes before everything else in some industries, like jewelry and automotive. Polishing enhances the surface finish by getting rid of flaws and increasing the shine of the material. A good polished surface means a better appearance as well as enhancing the impression of quality.
Improved Durability
Most polishing makes a material less porous, making it more durable. With smooth surfaces, there’s less space for contaminants to adhere to and less chance for the material to degrade over time. For instance, utilizing metal polishing can aid in preventing corrosion by eliminating rough corners and ensuring that there are no locations for rust to be developed.
Functional Benefits
Sometimes, you need to polish the functional properties because a product can not stand on its own. Say in the case of machined parts, polishing aids in reducing friction, thereby improving the performance and longevity of a product.
Precision
Polishing plays a vital role in sectors demanding high precision. For example, optical polishing is an important process in the manufacturing of lenses, mirrors, and other optical elements, which must have smooth surfaces to function correctly.
Applications of Polishing
There are various applications of a polishing process in many companies. Let’s explore a few sectors that lean on polishing:
Automotive Industry
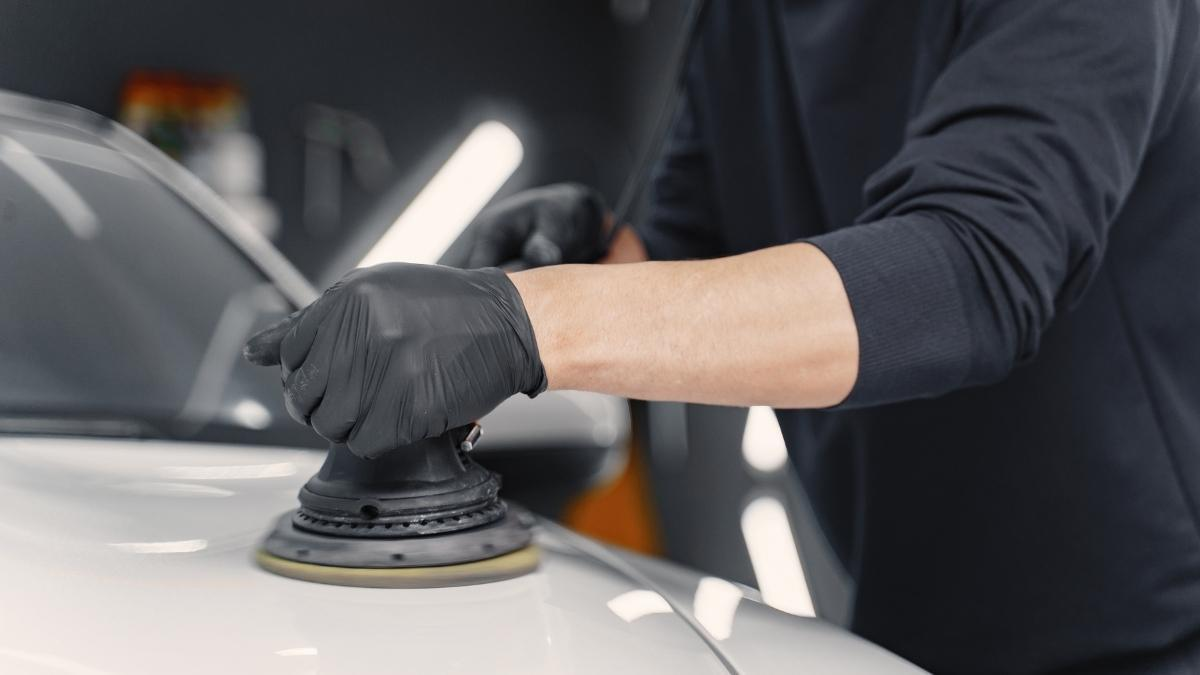
Polishing in automotive is done to improve the finish of car bodies, vehicle wheels, and car parts. Not only a visually appealing, but it helps to protect the vehicle’s surface from the elements. Paint polishing is a common step to eliminate imperfections and give cars a brand-new look.
Jewelry Making
Jewelers can use polishing in the making of rings, necklaces, bracelets, and other accessories. A good polish can make elements like gold, silver, and platinum (very precious metals) shine and reveal their unique beauty also increasing the overall value of the piece.
Metalworking
Metal polishing is utilized in the metalworking industry to finish machined metal parts with a smooth surface: this may be important for visual effect but is crucial if the elements need to function properly. Some of the widely metals that can be polished are Stainless steel, brass, and aluminum.
Medical Devices
Polishing is essential in the medical device industry for biocompatibility,Pharmaceutical equipment and safety. Many components such as implants, surgical tools, and medical instruments require polishing to create a smooth surface to avoid patient irritation or injury when used.
Electronics
Polishing is also used in the electronics industry for smooth surfaces on circuit boards or displays. Polishing not only improves appearance but also some parts to improve performance and electrical conductivity.
Key Considerations for Polishing
While polishing might seem simple, there are some important things to note:
Material Type
These can require very different processes (rubber vs. ceramic vs. metal) For instance, a more abrasive wheel or chemical solution may be needed for metals than for plastics, which usually require less aggressive treatment with a buffing pad. Choose the polishing method always as per the type of material that you’re working on.
Desired Finish
Also important is the final look of the material. If you want a mirror-like shine, then you will need to use finer abrasives and spend more time polishing. However, if a matte/satin finish would work, the process could likely be sped up.
Time and Cost
Depending on the complexity and material to be polished, polishing can be time-consuming. Hand polishing is time-consuming yet highly controlled, while machine polishing is less time-consuming but could potentially cost more because of the equipment.
Conclusion
Although polishing is associated with shiny surfaces, this is a generic process widely used throughout industries to enhance aesthetic quality, durability, precision, and functionality. Whether it’s for a car, a piece of jewelry, or a medical device, a smooth, shiny surface can be everything. Knowing about the different types of polishing methods, and how they have worked will help you to make the choices that are right for your project, and to get a quality finish every time. Contact us for more information.










2 thoughts on “What Is Polishing? A Complete Guide”